Test: Isomerism of organic compounds - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Isomerism of organic compounds
Which statement is true regarding the following structure?
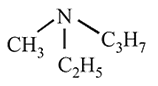
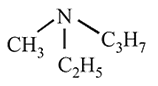
Which of the following amines can be resolved into two enantiomers?


| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The compound which exhibits both geometrical and optical isomerism is
The number of structural isomers for C6H12 is:
Which one of the following pairs of compounds are functional isomers?
Which of the following optically active compounds racemizes in dil. KOH/CH3OH solution?
An optically active compound (A) is treated with NaI in acetone to form compound (B). Determine the optical activity of compound (B).
Which of the following is correct set of physical properties of the geometrical isomers?

A solution of (+)−2 - chloro −2 - phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of small amounts of SbCl5 due to the formation of
The number of optical isomers possible for 2- Bromo-3-Chlorobutane are
How many cyclic structures are possible for C4H6 ?
Which one of the following compounds will not show geometrical isomerism?
Geometrical isomerism can be found in which of the following?
In the following structure, the double bonds are marked as I, II, III and IV. Geometrical isomerism is not present at site (s) :

What is the increasing order of stability of the three main conformations (i.e., Eclipse, Anti, Gauche) of 2-fluoroethanol ?
In open chain structure, how many chiral carbon atoms in D-(-)-Ribose ?


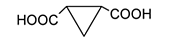








 is present in butyric acid
is present in butyric acid  , aspartic acid
, aspartic acid 
 .
.
















