Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - JEE MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects below.
Solutions of Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects | 10 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 1
When n-type and p-type semiconductors are allowed to come into contact
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 1
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 2
Superconductors are derived from compounds of
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 3
If we mix a pentavalent impurity in a crystal lattice of germanium, what type of semiconductor formation will occur?
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 3
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 4
To get a  - type semiconductor, the impurity to be added to silicon should have which of the following number of valence electrons
- type semiconductor, the impurity to be added to silicon should have which of the following number of valence electrons
 - type semiconductor, the impurity to be added to silicon should have which of the following number of valence electrons
- type semiconductor, the impurity to be added to silicon should have which of the following number of valence electrons
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 4
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 5
 is heated in an atmosphere of sodium vapour. The resultant yellow colour is due to the formation of
is heated in an atmosphere of sodium vapour. The resultant yellow colour is due to the formation of
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 5
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 6
Non stoichiometric defects are formed by
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 6
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 7
What type of crystal defects is indicated in the diagram given below?

Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 7
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 8
Each of the following solids show, the Frenkel defect except
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 8
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 9
Schottky defect in crystals is observed when
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 9
Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 10
Which one of the following has Frenkel defect
Detailed Solution for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects - Question 10
Information about Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric defects, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF


 -type semiconductors are allowed to come into contact then some electrons will flow from
-type semiconductors are allowed to come into contact then some electrons will flow from  to
to  .
. block elements.
block elements. -type, since electron is set free.
-type, since electron is set free.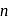 -type, impurity added to silicon should have more than 4 valence electrons.
-type, impurity added to silicon should have more than 4 valence electrons. -centeres that give rise to intresting colour in alkali halides.
-centeres that give rise to intresting colour in alkali halides.
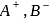 , equal number of cations and anions are missing from their lattice sites so that the electrical neutrality is maintained. The defect is called Schottky defect.
, equal number of cations and anions are missing from their lattice sites so that the electrical neutrality is maintained. The defect is called Schottky defect.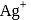 and
and 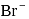 ions.
ions.














