Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - JEE MCQ
Test Description
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure below.
Solutions of Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure | 15 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 1
The molal elevation constant is the elevation in boiling point of
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 1
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 2
Which of the following modes of expressing concentration is independent of temperature?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 3
How many grams of concentrated nitric acid solution should be used to prepare  of
of  ? The concentrated acid is
? The concentrated acid is 
 of
of  ? The concentrated acid is
? The concentrated acid is 
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 3
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 4
Which of the following statements, regarding the mole fraction  of a component in solution, is correct?
of a component in solution, is correct?
 of a component in solution, is correct?
of a component in solution, is correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 4
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 5
The vapour pressure of water at  is 17.54 mm Hg. When 20 g of a non-ionic, substance is dissolved in 100 g of water, the vapour pressure is lowered by 0.30 mm Hg. What is the molecular mass of the substance?
is 17.54 mm Hg. When 20 g of a non-ionic, substance is dissolved in 100 g of water, the vapour pressure is lowered by 0.30 mm Hg. What is the molecular mass of the substance?
 is 17.54 mm Hg. When 20 g of a non-ionic, substance is dissolved in 100 g of water, the vapour pressure is lowered by 0.30 mm Hg. What is the molecular mass of the substance?
is 17.54 mm Hg. When 20 g of a non-ionic, substance is dissolved in 100 g of water, the vapour pressure is lowered by 0.30 mm Hg. What is the molecular mass of the substance?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 5
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 6
Two liquids X and Y form an ideal solution at  , vapour pressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol of Y is
, vapour pressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol of Y is  . At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y is further added to this solution, vapour pressure of the solution increases by
. At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y is further added to this solution, vapour pressure of the solution increases by  . Vapour pressure (in mmHg) of X and Y in their pure states will be, respectively–
. Vapour pressure (in mmHg) of X and Y in their pure states will be, respectively–
 , vapour pressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol of Y is
, vapour pressure of the solution containing 1 mol of X and 3 mol of Y is  . At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y is further added to this solution, vapour pressure of the solution increases by
. At the same temperature, if 1 mol of Y is further added to this solution, vapour pressure of the solution increases by  . Vapour pressure (in mmHg) of X and Y in their pure states will be, respectively–
. Vapour pressure (in mmHg) of X and Y in their pure states will be, respectively–
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 6
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 7
Which of the following is not an ideal solution?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 7
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 8
An azeotropic solution of two liquids has boiling point lower than either of them when it
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 8
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 9
Which among the following will show maximum osmotic pressure?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 9
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 10
Which of the following is not correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 10
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 11
A solution of acetone in ethanol
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 11
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 12
An aqueous solution is  molal in KI. Which change will cause the vapour pressure of the solution to increase?
molal in KI. Which change will cause the vapour pressure of the solution to increase?
 molal in KI. Which change will cause the vapour pressure of the solution to increase?
molal in KI. Which change will cause the vapour pressure of the solution to increase?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 12
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 13
 and
and  are the vapour pressure of pure liquid components,
are the vapour pressure of pure liquid components,  and
and  , respectively of an ideal binary solution. If
, respectively of an ideal binary solution. If 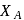 represents the mole fraction of component
represents the mole fraction of component  , the total pressure of the solution will be.
, the total pressure of the solution will be.
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 13
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 14
Which condition is not satisfied by an ideal solution?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 14
Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 15
Which of the following is true regarding azeotropes?
Detailed Solution for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure - Question 15
Information about Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Concentration of Solutions, Vapour pressure, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF





 acid
acid 








 Ideal solution
Ideal solution -dichlorobenzene
-dichlorobenzene  Ideal solution
Ideal solution Non-ideal solution
Non-ideal solution Ideal solution
Ideal solution in case of
in case of 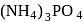 ,
,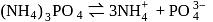
 is diluted with water, concentration decreases, therefore the vapour pressure of the resulting solution increases.
is diluted with water, concentration decreases, therefore the vapour pressure of the resulting solution increases.
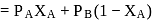
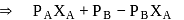

 of mixing should be zero.
of mixing should be zero. on mixing should be zero.
on mixing should be zero.














