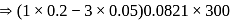Test: Colligative Properties and Abnormal Molecular Masses - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Colligative Properties and Abnormal Molecular Masses
What is the van't Hoff factor of Ferric Sulphate (Assume 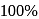 ionization)
ionization)
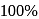 ionization)
ionization) Relative lowering of vapour pressure is directly proportional to
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
When common salt is dissolved in water:
Camphor is used as solvent to determine the molecular mass of non-volatile solute by Rast method because for camphor
 of an aqueous solution of a protein contains its
of an aqueous solution of a protein contains its 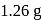 . The osmotic pressure of this solution at
. The osmotic pressure of this solution at  is found to be
is found to be  bar. The molar mass of protein will be
bar. The molar mass of protein will be 
The difference between the boiling point and freezing point of an aqueous solution containing sucrose (molecular 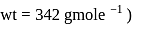 in
in  of water is
of water is  . If
. If  and
and  of water are
of water are  and
and  respectively, the weight of sucrose in the solution is about
respectively, the weight of sucrose in the solution is about
A solution containing 1.8 g of a compound (empirical formula CH2O) in 40 g of water is observed to freeze at −0.465∘C. The molecular formula of the compound is (Kf of water = 1.86 kg K mol−1)
 . If the values of
. If the values of  and
and  of water are respectively
of water are respectively  and
and  , then the elevation of boiling point of the solution in
, then the elevation of boiling point of the solution in  is
is
If the elevation in boiling point of a solution of  of solute
of solute  . wt.
. wt.  in
in 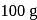 of water is
of water is  , the ebullioscopic constant of water is
, the ebullioscopic constant of water is
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
 and
and  atm are the osmotic pressures of
atm are the osmotic pressures of  (mass/volume) solutions of urea, fructose, sucrose and
(mass/volume) solutions of urea, fructose, sucrose and  respectively at certain temperature. The correct order of their magnitudes is :
respectively at certain temperature. The correct order of their magnitudes is :
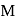 aqueous solution of
aqueous solution of 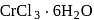 freezes at
freezes at  . Assuming complete ionization of the hydrated complex, which of the following isomers conforms to the observation
. Assuming complete ionization of the hydrated complex, which of the following isomers conforms to the observation  for water
for water 
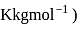 ?
?
 glucose solution. What osmotic pressure develops when the cell is placed in
glucose solution. What osmotic pressure develops when the cell is placed in 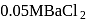 solution at
solution at 
A solution of 0.5 g of a solute (molar mass = 150 g mol−1) in 50 g of a solvent yields a boiling point elevation of 0.40 K. Another solution of 0.60 g of an unknown solute in the same mass of solvent exhibits a boiling point elevation of 0.8 K. The molar mass of unknown solute is :


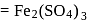
 (complete ionization)
(complete ionization)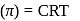
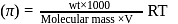

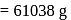



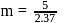 i.e.,
i.e.,  moles in
moles in  water
water moles in
moles in 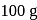 water
water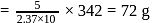
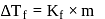


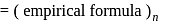

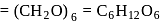





 ;
;
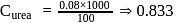
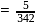

 (effective)
(effective)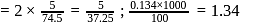


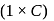 , higher the
, higher the  value and lower the freezing point.
value and lower the freezing point.



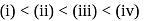
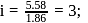

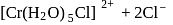


 ionized
ionized 
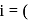 number of ions afterionization
number of ions afterionization