Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - JEE MCQ
Test Description
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential below.
Solutions of Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential | 15 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 1
. In the construction of a salt bridge, saturated solution of KNO3 is used because:
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 1
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 2
During electrolysis, the reaction that takes place at anode is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 3
In an electrochemical cell, the electrode having a lower reduction potential will act as:
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 3
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 4
For an electrolyte solution of  , the conductivity has been found to be
, the conductivity has been found to be 
 . The molar conductivity is
. The molar conductivity is
 , the conductivity has been found to be
, the conductivity has been found to be 
 . The molar conductivity is
. The molar conductivity is
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 4
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 5
Which of the following ion is expected to have highest value of molar conductivity at infinite dilution in the aqueous solution?
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 5
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 6
The specific conductivity of  solution at
solution at  is
is  and the resistance of the cell containing this solution at
and the resistance of the cell containing this solution at  is
is  . The cell constant is
. The cell constant is
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 6
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 7
The standard reduction potential for  is
is  Calculate the reduction potential at
Calculate the reduction potential at 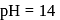 for the above couple.
for the above couple. 
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 7
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 8
When electric current is passed through a cell having an electrolytic solution, the cations move towards the cathode and anions towards the anode. If anode is pulled out from the solution
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 8
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 9
At a certain temperature and at infinite dilution, the equivalent conductances of sodium benzoate, hydrochloric acid and sodium chloride are 240, 349 and  equiv
equiv  respectively. The equivalent conductance of benzoic acid in
respectively. The equivalent conductance of benzoic acid in  equiv
equiv  at the same conditions is
at the same conditions is
 equiv
equiv  respectively. The equivalent conductance of benzoic acid in
respectively. The equivalent conductance of benzoic acid in  equiv
equiv  at the same conditions is
at the same conditions is
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 9
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 10
 (aq) is titrated with
(aq) is titrated with  conductometrically, graphical representation of the titration is :
conductometrically, graphical representation of the titration is :
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 10
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 11
If the resistance of  solution in a conductance cell is
solution in a conductance cell is  and conductivity is
and conductivity is 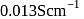 , then the value of cell constant is
, then the value of cell constant is
 solution in a conductance cell is
solution in a conductance cell is  and conductivity is
and conductivity is 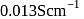 , then the value of cell constant is
, then the value of cell constant is
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 11
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 12
The resistance of 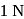 solution of acetic acic is
solution of acetic acic is 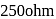 , when measured in a cell of cell constant
, when measured in a cell of cell constant  . The equivalent conductance (in
. The equivalent conductance (in 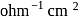 equiv
equiv  ) of
) of  acetic acid will be
acetic acid will be
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 12
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 13
At  , the conductivity of
, the conductivity of  solutions of molarity
solutions of molarity 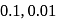 and
and  are recorded as
are recorded as  and
and  respectively. The correct relation between
respectively. The correct relation between  and
and 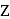 is
is
 , the conductivity of
, the conductivity of  solutions of molarity
solutions of molarity 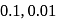 and
and  are recorded as
are recorded as  and
and  respectively. The correct relation between
respectively. The correct relation between  and
and 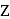 is
is
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 13
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 14
Which of the following statements is correct for the cell Zn ∣∣ Zn+2 ∥ Cu+2 ∣∣ Cu ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 14
Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 15
The corrosion of iron is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon. What are the cell reactions involving in the phenomenon?
Detailed Solution for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential - Question 15
Information about Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Electrochemical cells and Electrode Potential, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF




 has the maximum conductivity due to grotthuss conduction.
has the maximum conductivity due to grotthuss conduction.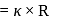



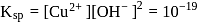


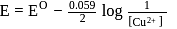

 equiv
equiv 
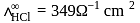 equiv
equiv 
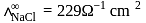 equiv
equiv 


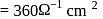 equiv
equiv 
 and
and  are very high as compare to other ions. Initially conductance of solution sharply decreases due to consumption of free
are very high as compare to other ions. Initially conductance of solution sharply decreases due to consumption of free  . After complete neutralization further slightly increases due to presence of
. After complete neutralization further slightly increases due to presence of  .
. cell constant Cell constant
cell constant Cell constant 

 .
.
 .
.

 (anodic reaction)
(anodic reaction)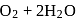

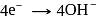 (cathodic reaction)
(cathodic reaction)
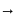

 may be dehydrated to iron oxide
may be dehydrated to iron oxide  or further oxidized to
or further oxidized to  and then dehydrated to iron rust,
and then dehydrated to iron rust,  .
.














