Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - JEE MCQ
Test Description
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids questions and answers have been prepared
according to the JEE exam syllabus.The Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids below.
Solutions of Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids questions in English are available as part of our course for JEE & Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids solutions in
Hindi for JEE course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids | 20 questions in 20 minutes | Mock test for JEE preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for JEE Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 1
Acetic acid can be halogenated in presence of phosphorus and chlorine. Formic acid cannot be halogenated with same way because of
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 1
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 3
A colourless liquid, at room temperature, reacts with soda-lime to form sodium salt of a carboxylic acid and ammonia gas. The liquid is
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 3
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 4
Which of the following on oxidation followed by hydrolysis gives pyruvic acid?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 4
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 5
Identify the correct order of boiling points of the following compounds:

Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 5
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 6
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenol and alcohol because of
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 6
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 7
Which of the following compounds will react with 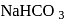 solution to give sodium salt and carbon dioxide?
solution to give sodium salt and carbon dioxide?
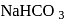 solution to give sodium salt and carbon dioxide?
solution to give sodium salt and carbon dioxide?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 7
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 8
Which of the following acids has the smallest dissociation constant?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 8
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 9
Which of the following orders of relative strengths of acids is correct?
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 9
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 10
An ester is boiled with  . The product is cooled and acidified with concentrated HCl. A white crystalline acid separates. The ester is
. The product is cooled and acidified with concentrated HCl. A white crystalline acid separates. The ester is
 . The product is cooled and acidified with concentrated HCl. A white crystalline acid separates. The ester is
. The product is cooled and acidified with concentrated HCl. A white crystalline acid separates. The ester is
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 10
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 11
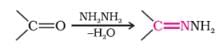
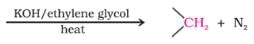
The correct product of the following sequence of reactions


Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 11
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 12
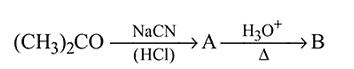
In the above sequence of reactions  and
and 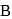 are
are
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 13
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 14
The carboxyl functional group  is present in
is present in
 is present in
is present in
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 14
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 15
Identify the incorrect statement regarding acetic acid.
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 15
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 16
The correct order of increasing acid strength of the compounds
(A) 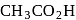
(B) 
(C) 
(D)
is
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 16
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 17
Number of compounds having hydrogen more acidic than cyclo hexan-1,3-dione
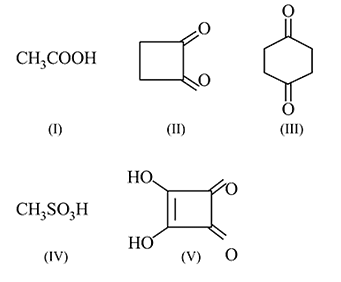

Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 17
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 18
Identify  in the following sequence of reactions-
in the following sequence of reactions-


 in the following sequence of reactions-
in the following sequence of reactions-

Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 18
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 19
Reaction between solid ice and methyl magnesium bromide gives an addition compound which or acidification yields:
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 19
Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 20
 -bonding is the reason for dimerisation of:
-bonding is the reason for dimerisation of:
Detailed Solution for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids - Question 20
Information about Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Preparation and Properties of Carboxylic Acids, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF


 -H-atom.
-H-atom.  has three
has three  -H-atoms but formic acid does not have
-H-atoms but formic acid does not have  -H-atom hence formic acid cannot be halogenated.
-H-atom hence formic acid cannot be halogenated.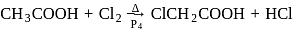
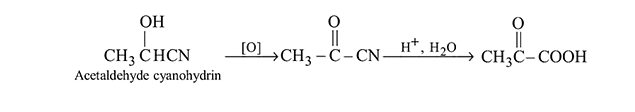
 effect of the - COOH group, H-bonds in acids are much stronger than in alcohols; while aldehydes do not exhibit
effect of the - COOH group, H-bonds in acids are much stronger than in alcohols; while aldehydes do not exhibit  -bonding.
-bonding. ) hence it dissolves in
) hence it dissolves in  ,
,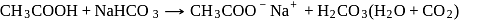









 weaker acid
weaker acid -hexanol are less acidic than carbonic acid and hence do not dissolve in
-hexanol are less acidic than carbonic acid and hence do not dissolve in 
 , further in
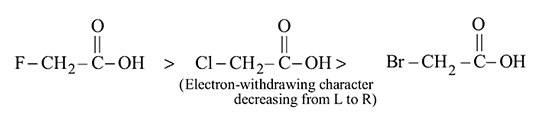
, further in  is more away from the
is more away from the 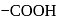 group than in
group than in  .
.
 and HCOOH, both of which are liquids.
and HCOOH, both of which are liquids.

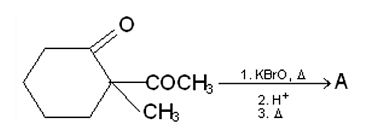
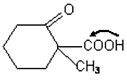

 -keto acid is heated,
-keto acid is heated,  is lost)
is lost)










 (X)
(X) 



 (Y)
(Y) 


 (Z)
(Z)
















