Test: Basic of Mathematics - 1 - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic of Mathematics - 1
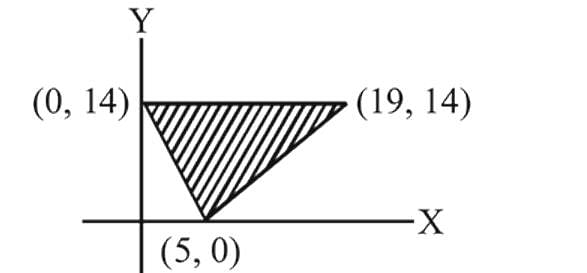
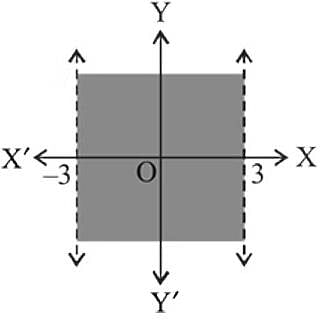
The shaded region shown in the figure is given by the inequations

The number of real values of parameter k for which (log16x)2 − log16x + log16k = 0 will have exactly one solution is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The solution set of the inequality 37 − (3x + 5) ≥ 9x − 8(x − 3) is
Ravi obtained 70 and 75 marks in first two unit tests. Then, the minimum marks he should get in the third test to have an average of at least 60 marks, are
The length of a rectangle is three times the breadth. If the minimum perimeter of the rectangle is 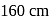 , then what can you say about breadth?
, then what can you say about breadth?
The solution set of (x)2 + (x + 1)2 = 25, where (x) is the least integer greater than or equal to x, is
The solution set of 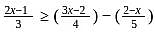 is (−∞, a]. The value of ' a ' is
is (−∞, a]. The value of ' a ' is
For positive real numbers a, b, c such that a + b + c = p, which one does not hold?
If x satisfies the inequalities x + 7 < 2x + 3 and 2x + 4 < 5x + 3, then x lies in the interval


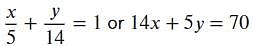

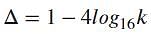
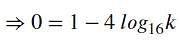




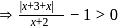

 , i.e.,
, i.e., 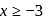 .
.
 and
and 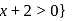
 and
and 
 and
and 
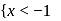 and
and 


 Solution set is (−∞, 2].
Solution set is (−∞, 2].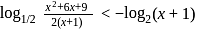 , then
, then  lies in the interval
lies in the interval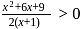 and
and  and
and 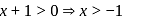




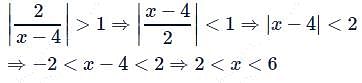
 is x ∈ (4, 6).
is x ∈ (4, 6).




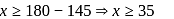
 Minimum marks Ravi should get = 35.
Minimum marks Ravi should get = 35.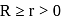 and
and  , then
, then 
 and
and 

 which is true if
which is true if , which is true iff
, which is true iff 
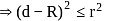
 , which is also
, which is also 
 is equal to
is equal to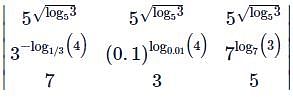

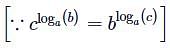




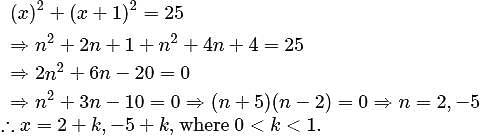



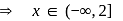
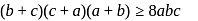
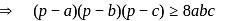

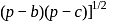



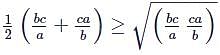
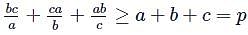
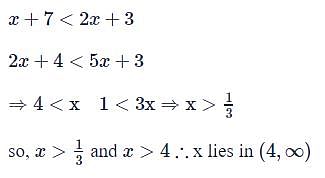
 is
is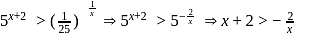
 base
base 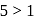 .
.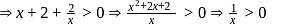
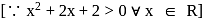
 or
or 
 is
is Dividing the problem into three intervals :
Dividing the problem into three intervals :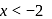 , then
, then 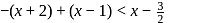

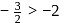 , hence no common values
, hence no common values
 , then
, then 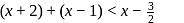
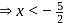
 , hence no common values
, hence no common values 
 , then
, then 


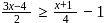 , then x ∈
, then x ∈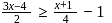

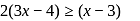 or
or 
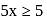 or
or 

 is
is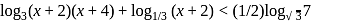
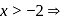 (i)
(i)

















