Jharkhand TGT (JSSC) Mock Test - 2 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Jharkhand TGT (JSSC) Mock Test - 2
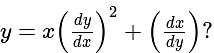
What is the equation of the line which bisects the obtuse angle between the lines x - 2y + 4 = 0 and 4x - 3y + 2 = 0?
In 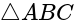 , right angled at
, right angled at 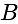 , if
, if 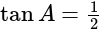 , then the value of
, then the value of 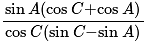 is:
is:
The point of intersection of diagonals of a square 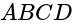 is at the origin and one of its vertices is at
is at the origin and one of its vertices is at 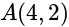 . What is the equation of the diagonal
. What is the equation of the diagonal 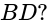
The angle of polarization of glass is 58° and that for water is 53° .The angle of polarization for glass in water is
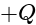 charge is placed. The value of total
charge is placed. The value of totalflux that is coming out of each face is:
Magnetism at the center of a bar magnet is ______.
In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a glass prism for different values of angle of incidence a student would find that the emergent ray:
Which among the following statements is true about Huygen's principle?
One proton enters in a magnetic field of 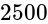 of N / Amp-
of N / Amp- 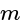 intensity with velocity
intensity with velocity 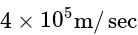 in parallel of field. The force exerted on proton will be:
in parallel of field. The force exerted on proton will be:
The gravitational force between two masses kept at a certain distance is 'P' Newton. The same two masses are now kept in water and the distance between them are same. The gravitational force between these two masses in water is 'Q' Newton then:
At room temperature the substances which retain their ferromagnetic property for a long period of time are called?
A potentiometer wire of length 20 m has a resistance of 50 ohms. It is connected in series with a resistance box and a 5 V storage cell. If the potential gradient along the wire is 0.5 mV/cm, what is the resistance unplugged in the box?
In the p-n junction, the barrier voltage _________________.
A piston-cylinder contains air at 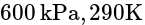 , and a volume of
, and a volume of  . A constant pressure process gives
. A constant pressure process gives 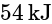 of work out. Find the final volume of the air.
of work out. Find the final volume of the air.
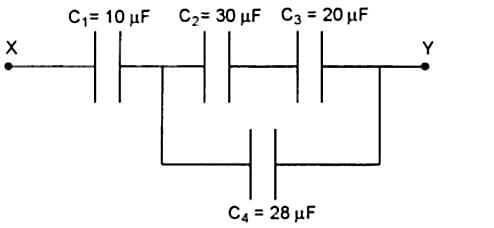
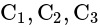 and
and 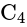 are connected as shown in figure below. Calculate equivalent capacitance of the circuit between points
are connected as shown in figure below. Calculate equivalent capacitance of the circuit between points 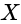 and
and 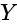 .
.
Which of the following instrument measures arterial blood pressure?
If we observe that the air is moving from place A to place B, then:
In a transistor amplifier, which one of the following capacitors are generally used?


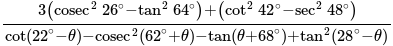 is:
is:
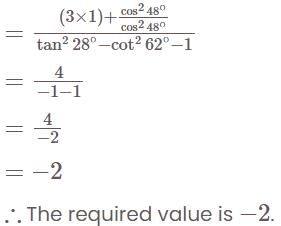
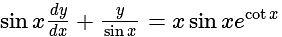
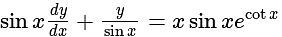
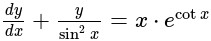
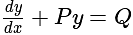
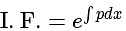
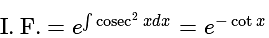
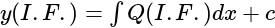
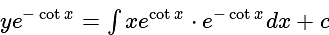
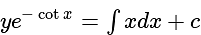
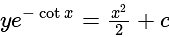

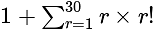 is divisible is:
is divisible is: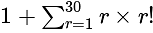
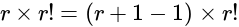
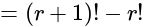
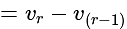
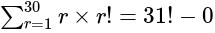
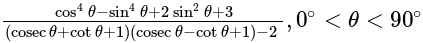 , is equal to:
, is equal to: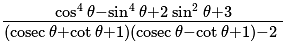
 but we cannot put
but we cannot put 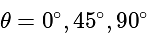
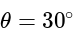
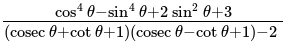
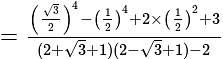
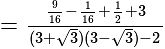
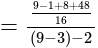
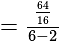
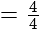
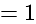
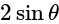 if we put
if we put  it is giving
it is giving 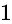 which is satisfying
which is satisfying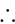 The required answer is
The required answer is 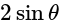 .
.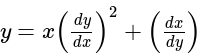
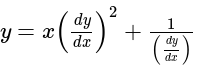
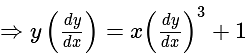
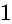 .
.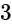 .
.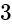 .
.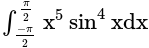 ?
?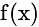 is odd
is odd 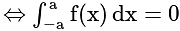
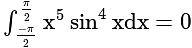
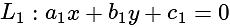 and
and 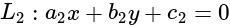 is
is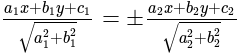
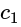 and
and 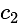 are of the same sign, then evaluate
are of the same sign, then evaluate 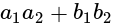 .
.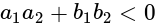 , then taking positive gives acute angle bisector.
, then taking positive gives acute angle bisector.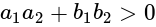 , then positive gives obtuse angle bisector.
, then positive gives obtuse angle bisector.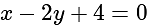 and
and 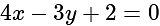
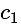 and
and 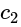 are of the same sign,
are of the same sign,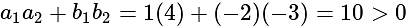
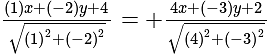
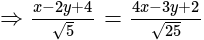
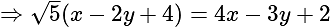
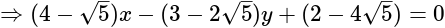
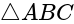 is a right angle at
is a right angle at 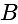 .
.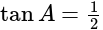
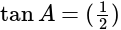
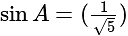
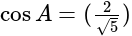
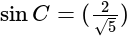
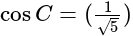
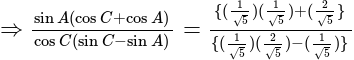
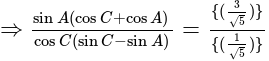
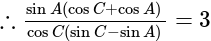
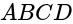 is at the origin and one of its vertices is at
is at the origin and one of its vertices is at 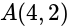 .
.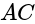 passes through the origin
passes through the origin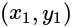 and
and 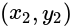 is:
is: 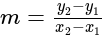 The slope of line
The slope of line 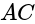 is given by
is given by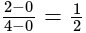
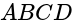 , the diagonals
, the diagonals 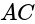 and
and 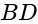 are perpendicular to each other.
are perpendicular to each other.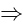 Slope of
Slope of 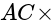 slope of
slope of 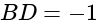 .
.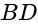 is
is 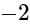 .
.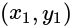 and having the slope '
and having the slope ' 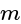 ' is given as:
' is given as: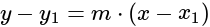
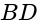 whose slope is
whose slope is 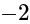 and passes through origin is given by:
and passes through origin is given by: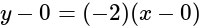
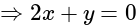
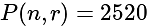 and
and 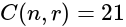 , then what is the value of
, then what is the value of 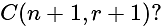
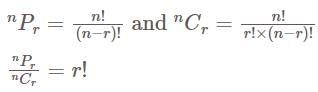
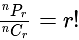
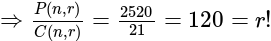
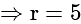
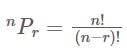
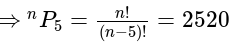
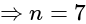
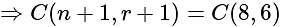
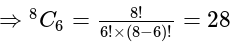
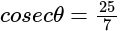 , then
, then 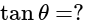
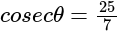
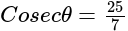
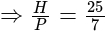
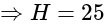 and
and 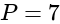
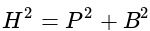
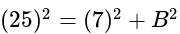
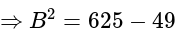
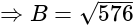
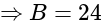
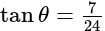
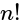 has 17 zeros, then what is the value of
has 17 zeros, then what is the value of 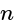 ?
?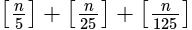
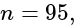 then
then 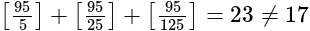
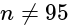
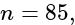 then
then 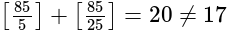
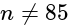
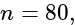 then
then 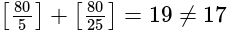
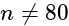
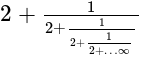 ?
?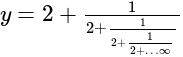
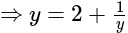
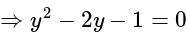
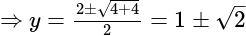
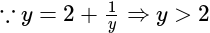
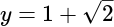
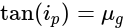 .....(i)
.....(i)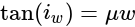 .......(ii)
.......(ii)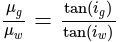
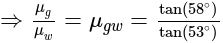
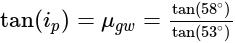
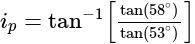
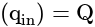
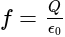
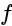 is the total electric flux,
is the total electric flux, 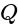 is the charge enclosed by the surface and
is the charge enclosed by the surface and 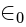 is the permittivity of the free space.
is the permittivity of the free space.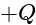 is placed at the centre of the box. The Gauss's law provides the information about the distribution of the electric charges for the closed surface. In the closed surface, the electric flux is directly proportional to the electric charges enclosed in the surface.
is placed at the centre of the box. The Gauss's law provides the information about the distribution of the electric charges for the closed surface. In the closed surface, the electric flux is directly proportional to the electric charges enclosed in the surface.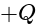 . Since the cube is the closed surface with the six faces, the gauss law can be applied to find the electric flux of it.
. Since the cube is the closed surface with the six faces, the gauss law can be applied to find the electric flux of it.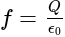
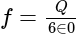
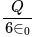
 N / Amp-
N / Amp- 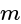
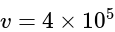 m/s
m/s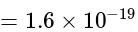 Culomb
Culomb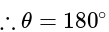
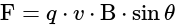
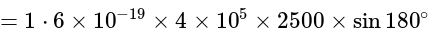
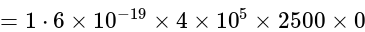
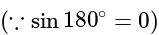
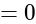
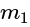 and
and 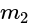 is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance
is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance 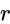 between them.
between them.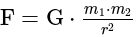
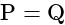
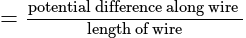 .
. 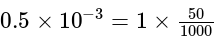
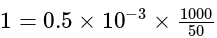
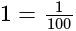
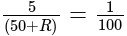
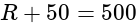
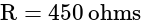
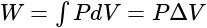
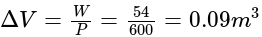
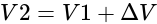
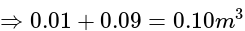
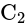 and
and 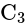 of capacity
of capacity 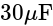 and
and 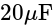 are in series, their combined capacity is given by:
are in series, their combined capacity is given by: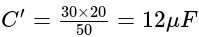
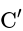 is in parallel with
is in parallel with 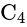 , their combined capacity
, their combined capacity 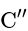 is given by,
is given by,
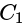 and
and 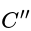 are in series.
are in series. Net capacity of the combination is given by,
Net capacity of the combination is given by,