Jharkhand TGT (JSSC) Mock Test - 5 - Jharkhand (JSSC) PRT/TGT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Jharkhand TGT (JSSC) Mock Test - 5
f : R → and g : [0, ∞) → R is defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = √x. Which one of the following is not true?
Lines are drawn parallel to the line 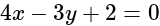 , at a distance
, at a distance 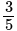 from the origin. Then which one of the following points lies on any of these lines?
from the origin. Then which one of the following points lies on any of these lines?
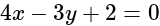 , at a distance
, at a distance 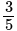 from the origin. Then which one of the following points lies on any of these lines?
from the origin. Then which one of the following points lies on any of these lines?What are the direction ratios of the line of intersection of the planes 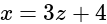 and
and 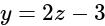 ?
?
If f(x) = |cos x – sin x|, then f'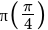 is equal to-
is equal to-
The order and degree of the differential equation 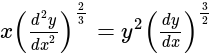 is:
is:
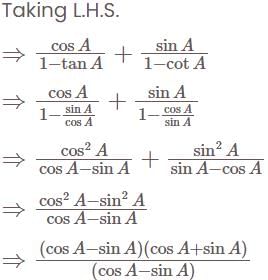
Consider the following:
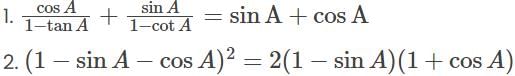
Which of the above is/are identity/identities?
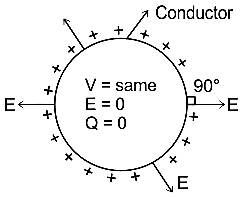
Which among the following statement is correct regarding an ideal conductor in a static electric field?
Four graphs between 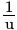 and
and 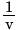 given for spherical mirrors. Which one of them suitable represents a convex mirror, as per the new Cartesian sign convention?
given for spherical mirrors. Which one of them suitable represents a convex mirror, as per the new Cartesian sign convention?
___________ are those which gets strongly magnetised when placed in an external magnetic field.
Which of the following material has the highest relative permittivity?
A ray of light passes from glass 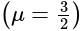 to water
to water 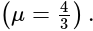 The value of critical angle will be:
The value of critical angle will be:
In class B amplifier, the output current flows for:
A metallic rod when placed in a strong magnetic field, aligns itself at right angles to the magnetic field. The nature of the material is:
The electronegativity of Cesium is 0.7 and that of Fluorine is 4.0. The bond formed between the two is:
Which of the following carbohydrates would be the most abundant in the diet of strict vegetarians?
Fibres of _______ resemble that of silk and hence, it is popularly known as ‘artificial silk’.
Which scientist arranged the Periodic Table of Elements in the order of increasing atomic masses?


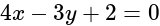 is given as
is given as 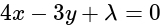
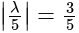
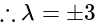
 Required lines are
Required lines are 
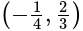
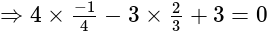
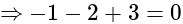
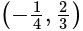 satisfies
satisfies 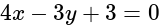 , so there is no need to check other options.
, so there is no need to check other options.
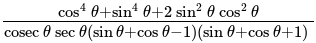 is:
is: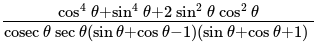
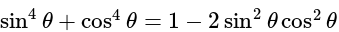
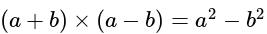
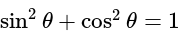
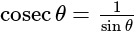
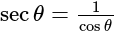
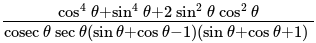
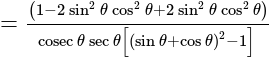
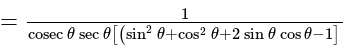
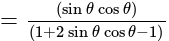
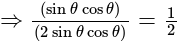
 The value of
The value of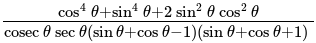 is
is 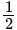 .
.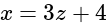 and
and 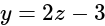
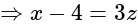 and
and 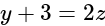
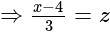 and
and 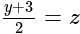
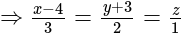
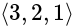 .
.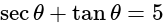 then in which quadrant does
then in which quadrant does 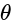 lie?
lie?
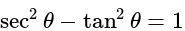
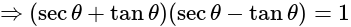
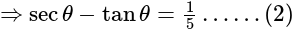
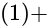 eq. (2)
eq. (2) 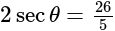
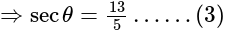
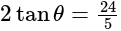
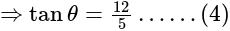
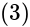 &
& 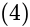 both sec
both sec 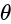 and tan
and tan 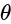 are positive only in the first quadrant.
are positive only in the first quadrant.
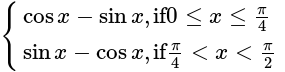
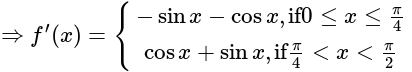
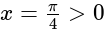
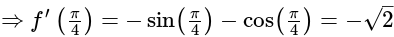
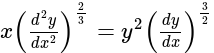
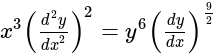
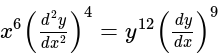
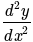
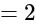
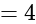
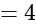
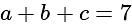 and
and  , then what is the value of
, then what is the value of 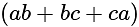 ?
?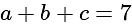

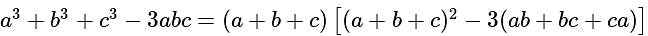
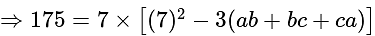
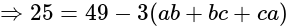
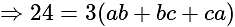
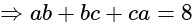
 .
.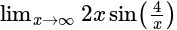
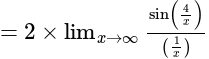
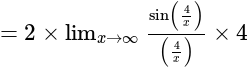
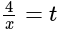

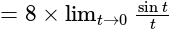
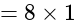
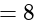
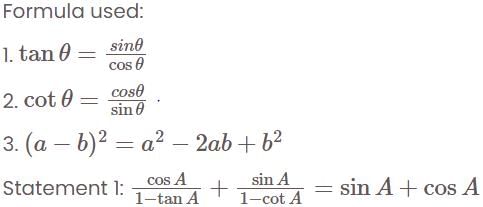

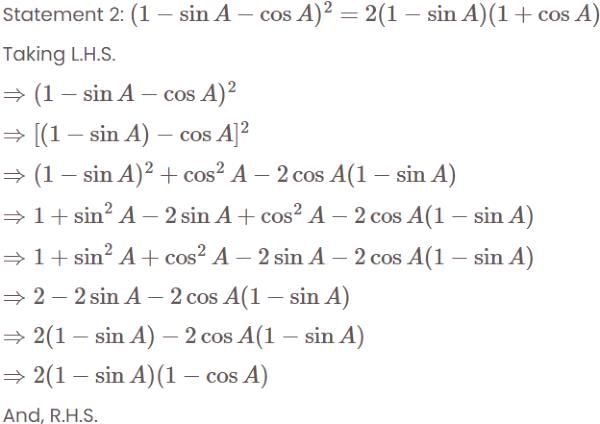
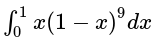 equal to:
equal to: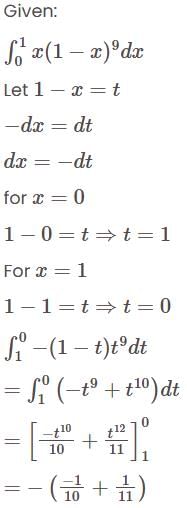

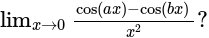
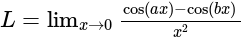
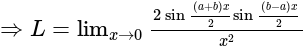
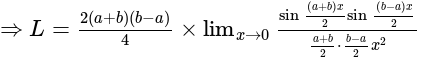
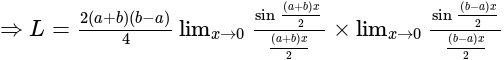
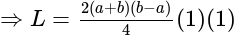
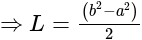
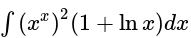 equal to?
equal to?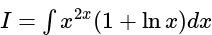
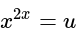
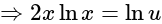
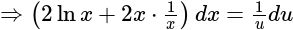
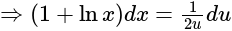
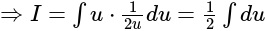
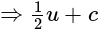
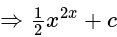
 is always +ve for convex mirror
is always +ve for convex mirror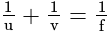
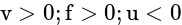
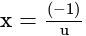 (negative sign shows negative y-axis)
(negative sign shows negative y-axis)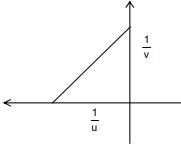
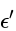 to free space (empty of matter) permittivity '
to free space (empty of matter) permittivity ' 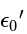 i.e.,
i.e.,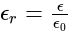
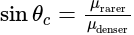
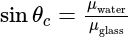
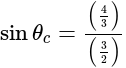
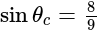
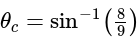
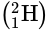 and hydrogen
and hydrogen 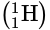 both have same atomic number but different mass number so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties since they have same electronic configuration.
both have same atomic number but different mass number so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties since they have same electronic configuration. are linked by monomers.
are linked by monomers.














