HP Judicial Services (Prelims) Mock - 2 (Criminal Law) - Judiciary Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HP Judicial Services (Prelims) Mock - 2 (Criminal Law)
'A' with the intention of killing 'B', gave him poisoned halwa to eat. 'B' ate a little and threw away the rest, which a child picked up and ate it. The child died of poisoning. 'A' is:
'A' obtains property from 'Z' by saying, ''Your child is in the hands of my gang and will be put to death unless you send us ten lakh rupees." 'A' has committed the offence of:
The Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973, came into force on
The right of private defence of property extends to causing death of the wrongdoer under certain descriptions. Which one of the following descriptions is not included in those?
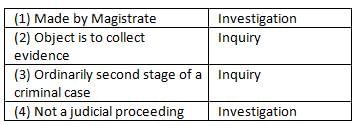
Which of the following combinations are correctly matched?
'A', a public servant, having charge of translation of a document, makes an incorrect translation of that document with intent to cause injury to 'B'. The offence committed by 'A' is
"Section 125 of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 is applicable to all persons irrespective of their religion." It was laid down in
'Protected Area' is defined under which clause of Section 2 of the Wildlife Protection Act?


















