Test: Kinetic theory - Molecular nature of matter & Behaviour of gases (25 Sep) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Kinetic theory - Molecular nature of matter & Behaviour of gases (25 Sep)
In the case of real gases, the equation of state, PV = RT (where P, V and T are respectively the pressure, volume and absolute temperature), is strictly satisfied only if corrections are applied to the measured pressure P and the measured volume V. The corrections for P and V arise respectively due to
Which one of the following quantities can be zero on an average for the molecules of an ideal gas in equilibrium?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Two specific heats of a perfect gas are related by:
One mole of any substance at any temperature, pressure or volume always contains ________ molecules.
Oxygen and nitrogen in two enclosures have the same mass, volume and pressure. The ratio of the temperature of oxygen to that of nitrogen is:
When the temperature goes up, the pressure inside a rigid container will _____.
Four moles of an ideal diatomic gas is heated at constant volume from 20° C to 30° C. The molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure (Cp) is 30.3 Jmol-1K-1 and the universal gas constant (R) is 8.3 Jmol-1K-1. The increase in internal energy of the gas is
A region of the earth’s atmosphere contains n molecules (treated as ideal gas molecules) per unit volume. The temperature of air in the region is T. If k represents Boltzmann’s constant and R represents universal gas constant, the pressure of air in the region is
The average kinetic energy of translation of a molecule of an ideal gas at temperature T is:
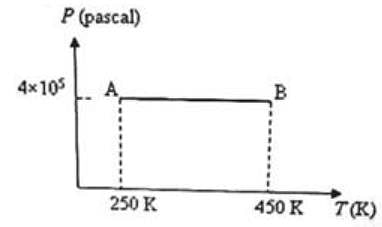
Three moles of an ideal monoatomic gas is initially in the state A shown in the adjoining pressure-temperature graph. It is taken to state B without changing its pressure. If R is the universal gas constant, the work done by the gas in this process is