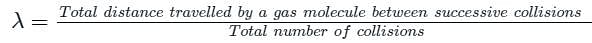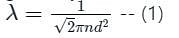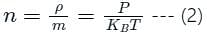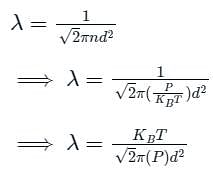Test: Kinetic theory- Mean free path (27 Sep) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Kinetic theory- Mean free path (27 Sep)
The mean free path of moving gas molecules is directly proportional to kth power of diameter of molecule. Here value of k is
Calculate the value of mean free path (λ) for oxygen molecules at temperature 27°C and pressure 1.01 x 105 Pa. Assume the molecular diameter 0.3 nm and the gas is ideal. (k = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1)
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The mean free path of a gas molecule is λ1 at temperature T. The pressure and temperature, of both the gas, are made two times their original value. The new mean free path was found to be λ2. Then λ1:λ2 is -
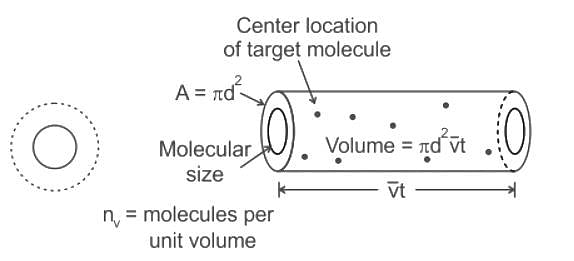
If the gas particles are of diameter 'd', average speed 'v', number of particles per unit volume 'n', then the time between two successive collisions on average is __________.
If the gas particles are of diameter 'd', average speed 'v', number of particles per unit volume 'n', then what is the term "Πd2vt" represents?
The mean free path of a gas molecule depends on
The mean free path of gas molecules is proportional to nth power of diameter of molecules. Here n is
The mean free path λ of a gas molecule as given by Maxwell is related to its diameter a, as
The relation between mean free path λ and the pressure P of any gas is -


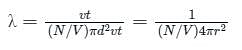
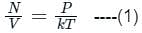

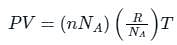
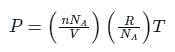
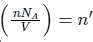 is the number of molecules per unit volume of the gas and
is the number of molecules per unit volume of the gas and 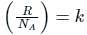 is the Boltzmann constant.
is the Boltzmann constant.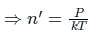
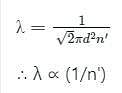
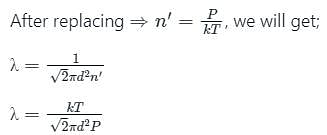
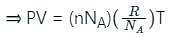
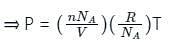
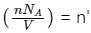 is the number of the molecules per unit volume of the gas and
is the number of the molecules per unit volume of the gas and 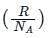 = k, the Boltzmann constant
= k, the Boltzmann constant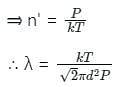
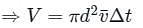
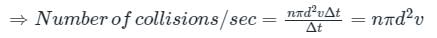
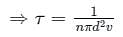
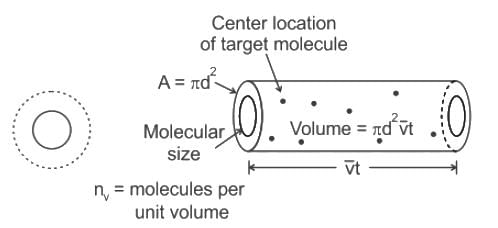
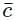 is the average speed of the molecules.
is the average speed of the molecules.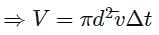
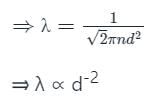
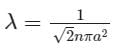 is the mean free path given by Maxwell. So option 2 is correct.
is the mean free path given by Maxwell. So option 2 is correct.