Test: Potential due to a Point Charge & electric Dipole(4 Nov) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Potential due to a Point Charge & electric Dipole(4 Nov)
Electric potential due to a point charge q at a distance r from the point is _______ (in the air).
What is the amount of work done to bring a charge of 4*10-3C charge from infinity to a point whose electric potential is 2*102V?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
What is the electric potential of the system?

Two plates are kept at a distance of 0.1m and their potential difference is 20V. An electron is kept at rest on the surface of the plate with lower potential. What will be the velocity of the electron when it strikes another plate?
Electric field intensity is equal to
A charge of 6 mC is located at the origin. The work done in taking a small charge of -2 x 10-9 C from a point P (0, 3 cm, 0) to a Q (0,4 cm, 0) is
On moving a charge of 20 coulombs by 2 cm, 2 J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is
The amount of work done in moving a charge from one point to another along an equipotential line or surface charge is
Electric field intensity at point ‘B’ due to a point charge ‘Q’ kept at a point ‘A’ is 12 NC-1 and the electric potential at a point ‘B’ due to same charge is 6 JC-1. The distance between AB is
Work done in carrying 2C charge in a circular path of radius 2m around a charge of 10C is


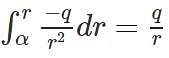 .
.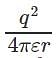 and electric potential between two charges +q and –q is
and electric potential between two charges +q and –q is 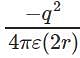 . Therefore the electric potential of the system is
. Therefore the electric potential of the system is 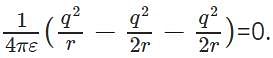 Electric potential is a scalar quantity and thus the system becomes zero-potential-system.
Electric potential is a scalar quantity and thus the system becomes zero-potential-system.














