Test: Integrated Rate Equations(7 Nov) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Integrated Rate Equations(7 Nov)
The half life of a first order reaction is equal to:
For zero order reaction, linear plot was obtained for [A] vs t, the slope of the line is equal to:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The first order rate constant for the decomposition of N2O5 is 6.2 x 10-4 sec-1. The t1/2 of the decomposition reaction is
Find the overall order of a reaction whose rate constant is k = 3x10-4 s-1
Which of the following represents the expression for the 3/4th life of a first order reaction?
The type of reaction that gives constant half life is
The half life period of first order reaction is 15 min. Its rate constant will be equal to
If Ef and Eb are the activation energies of the forward and reverse reactions and the reaction is known to be exothermic, then:
The ratio of the rate constant of a reaction at two temperatures differing by __________0C is called temperature coefficient of reaction.
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by



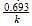 , where k is the rate constant.
, where k is the rate constant.














