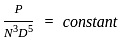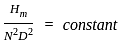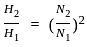BPSC AE Civil Paper 4 (General Engineering) Mock Test - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 4 (General Engineering) Mock Test
What is the SI unit of resistivity?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Free float is mainly used to
The angle of inclination of the plane at which the body begins to move down the plane, is called:
In a simply supported beam of span L subjected to central concentrated load, the central deflection is 24 mm. Then the slope at supports is:
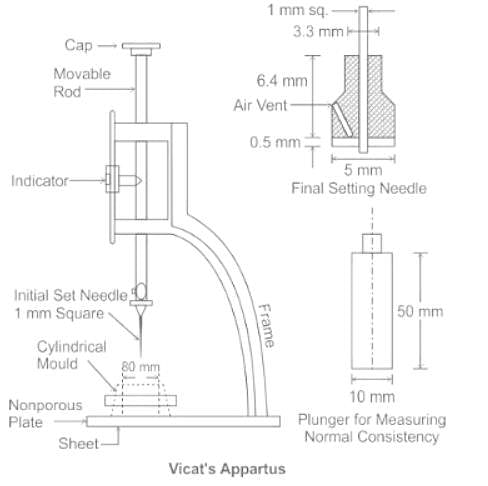
The diameter of plunger used in Vicat apparatus is of
Cast iron contains carbon approximately
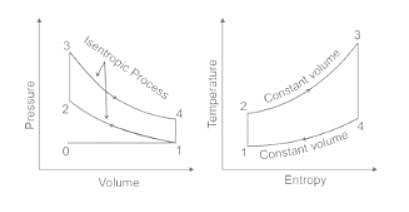
In a thermodynamic system, a process in which volume remains constant is called ______ process.
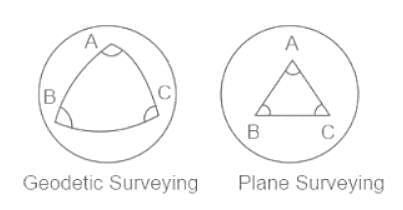
In plane surveying, level lines are considered as ________ and plumb lines are considered as __________.
An air-standard diesel cycle consists of
The Nusselt number, in the case of natural convection, is a function of:
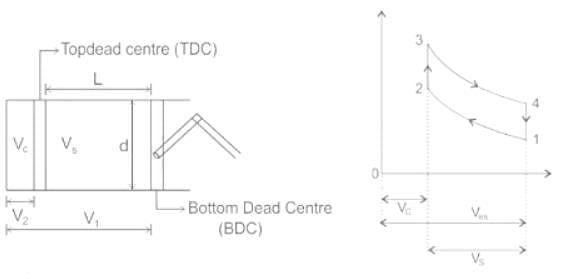
Compression ratio of an internal combustion engine is defined as _______.
[VS = Swept volume, VC = Clearance volume]
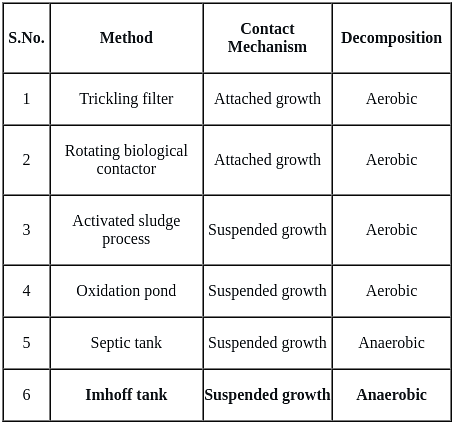
Which of the following unit works in anaerobic conditions?
The example for continuous flow type equipments is
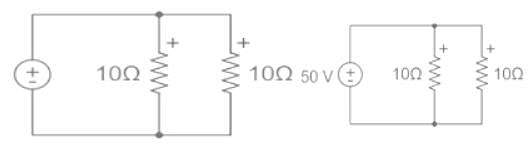
Find the total current flowing in the given circuit.

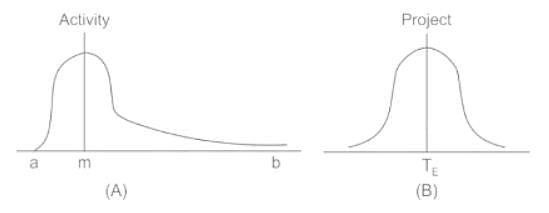
The frequency distribution of duration of an individual activity takes the shape of ______ as per the PERT analysis.
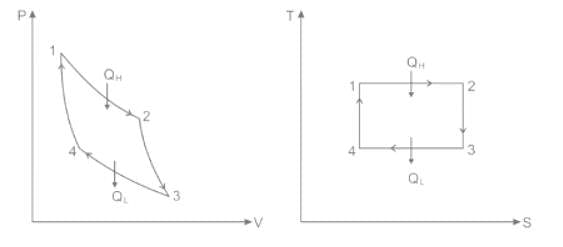
Carnot cycle consists of the following process -
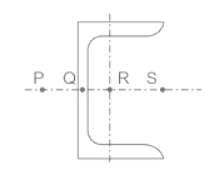
The possible location of shear centre of the channel section, shown below, is
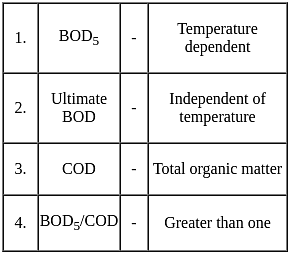
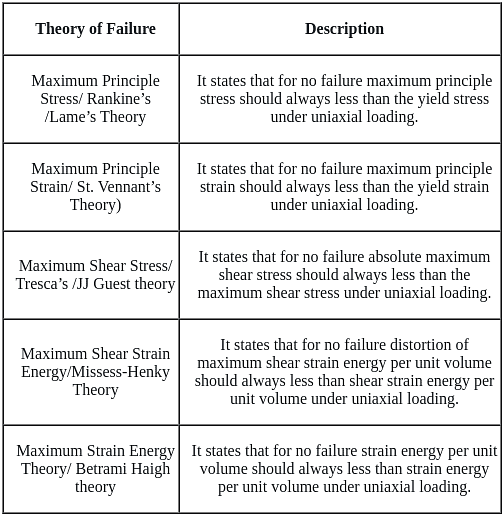
Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
The portions made by cutting standard bricks across their width are known as
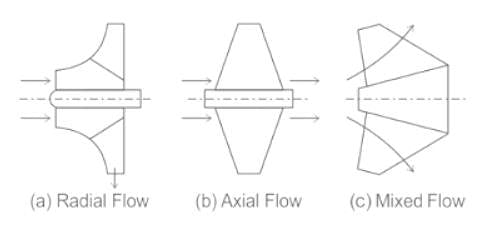
Which of the following is NOT a type of centrifugal pump ?
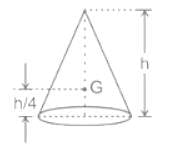
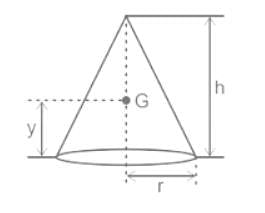
What will be the value of 'y', the distance of center of gravity, for the SOLID CONE given in the figure?
The angle of convergence in venturimeter is


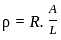
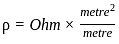
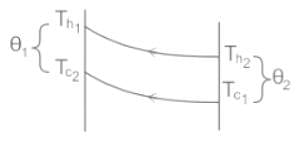
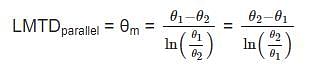

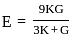
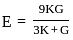
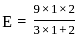
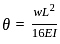
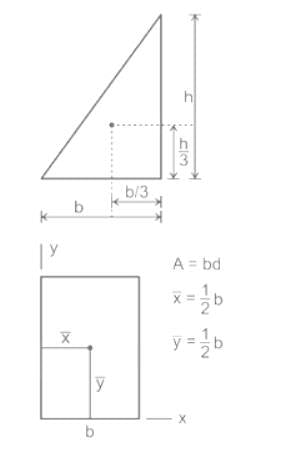
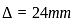 ,
,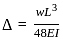
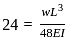
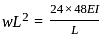
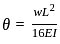
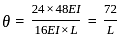




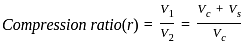
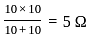




 ,
,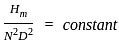 ,
,