BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 1
A wastewater sample of 2 ml is made up to 300 ml in a BOD bottle with distilled water. The initial D.O. of the sample is 8 mg/l and after 5 days it is 2mg/l. Its BOD is:
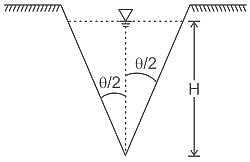
As per Lacey's theory, the wetted perimeter of a regime-channel for a discharge of 100 m3/s, is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If modulus of elasticity of the subgrade is 25 MPa, then deflection at the surface of flexible pavement due to a wheel load of 40 kN and a tyre pressure of 0.6 MPa will be:
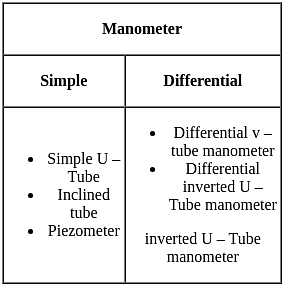
Which of following statements is/are true for manometers?
l) Manometers are easy to operate.
ll) Manometers do not require frequent calibration.
lll) Manometers are made of steel.
In the design of storm sewers 'time of concentration' is relevant to determine the
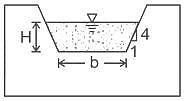
A rectangular suppressed weir is a device used to measure stream flow in an open channel. For a rectangular suppressed weir flowing free, the discharge Q is related to the head H over the weir as _________.
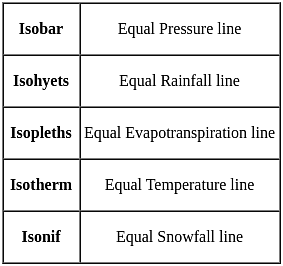
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
1. Isochrones are curves of equal pore water pressure
2. Isochrones depict the variation of the pore water pressure along with the depth of the soil sample
3. Isochrones vary with time
Depth-Area-Duration curves of precipitation are drawn as:
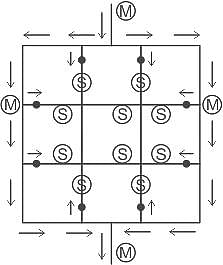
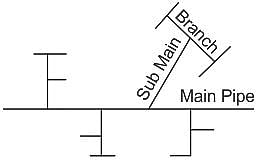
Identify the layout of water distribution system given in image.
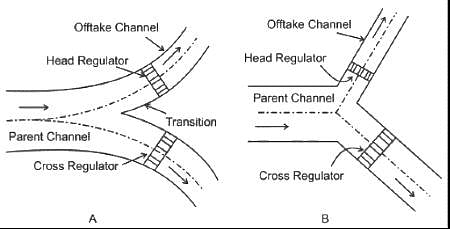
Which of the following is NOT a function of a cross-regulator?
Hydrologic flood routing methods make use of:
Expansion joints are provided if the length of concrete structures exceeds _____
The first watering before sowing the crop is called as
The rain waterholes in the parapet or in edging is called as-
The discharge of water through a rectangular channel of width 6 m is 18 m3/s, when the depth of flow of water is 3 m, then the specific energy of flowing water is
Identify the FALSE statement from the following, pertaining to the design of concrete structures -
Which of the following methods is NOT used for determining total hardness of water?
According to IS: 4111-1986, the spacing of manholes above ______ may be allowed on straight runs for sewers of diameter above 900 to 1500 mm.
The estimated value of elastic modulus (GPa) of concrete of M65 grade as per IS 456 would be approximately:
The pipe joint commonly used in pumping station
In the case of Pelton turbine installed in a hydraulic power plant, the gross head available is the vertical distance between:
In which one of the following grades of a highway is an emergency escape ramp Provided?
Advantages of asphaltic concrete (Bituminous Concrete) are :
(a) Durability
(b) Imperviousness
(c) Load spreading properly
(d) Quickly openable to traffic
(e) Good skid Resistance
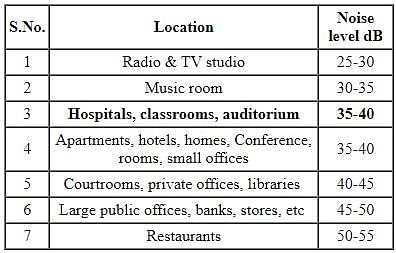
Acceptable noise level in dB for auditorium is:
The percentage compensation ingradient for ruling gradient of 4% and horizontal curve of radius 760 m is
Statement (I): Instantaneous unit hydrograph (IUH) is used in theoretical analysis of rainfall excess-runoff characteristics of a catchment.
Statement (II): For a given catchment, IUH, being independent of rainfall characteristics, is indicative of the catchment storage characteristics.
If the specific energy at the up stream section of a rectangular channel is 3 m and minimum specific energy is 2.5 m, the maximum height of jump without causing afflux will be:



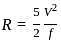

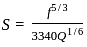

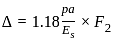
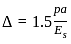
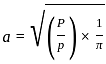
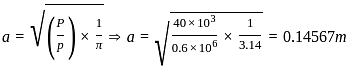
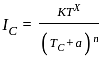

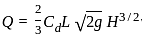
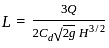

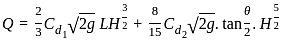
 :
: 



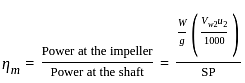




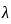 ) of an RC column:
) of an RC column: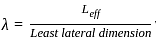
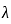 ≤ 3 → Pedestal
≤ 3 → Pedestal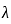 < 12 → short column
< 12 → short column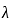 → Long column
→ Long column