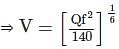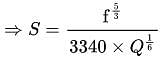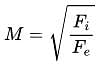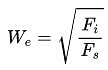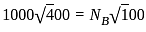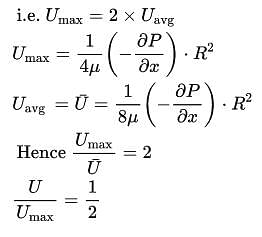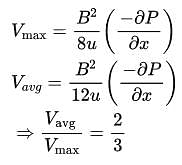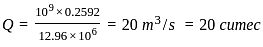BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 2
In small towns, the most appropriate system of sewerage is
When used in road work, the coefficient of hardness of a stone should be greater than
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
According to Lacey's theory of channel design, what will be the velocity of flow in the channel corresponding to a discharge of 140 cumec and silt factor 1.0?
Upon a detailed topographical investigation, an engineer wants to align a canal. Along which of the following should be align the canal?
According to Indian Road Congress, the width of carriageway is
(i) 3.75 m for single lane
(ii) 7.0 m for two lanes without raised kerbs
(iii) 7.5 m for two lanes with raised kerbs
Which of these statement(s) is/are true?
On a road, the speed-density relationship of a traffic stream is given by u = 70 - 0.7 k (where speed u, is in km/h and density k, is in veh/km). At the capacity condition, the average time headway will be:
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
A. Seepage drains reduce the chances of water logging.
B. Water logging makes the land more productive.
C. Fertilisers used in irrigation may contribute in various ways to the problem of water pollution.
D. Water logging is caused due to the presence of permeable strata.
The main function of a divide wall is to
A barrage on a major river in the Gangetic plains has been designed for a flood discharge 7000 m3/s. It has been provided with a waterway of 360 m length. The looseness factor of this barrage is
The temporary hardness of water is due to presence of:
When assessing the strength of a structure or structural member for the limit state of collapse, the values of partial safety factor for reinforcing steel, should be taken as:
Through DAD analysis, the maximum average depth over an area of 103 km2 due to one-day storm was found to be 76.5 cm. For the same area, the maximum average depth for a 3-day storm can be expected to be
Which of the following statements is NOT correct with respect to the slow sand filter in the drinking water treatment plant?
The region between the separation of stream line and the boundary surface of a solid body is known as
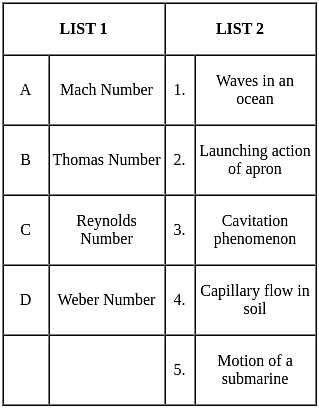
Match LIST 1 (non - dimensional numbers) with LIST - 2 (application) and select the correct answers using the codes given below.
Two Pelton turbines A and B have the same specific speed and are working under the same head. Turbine A produces 400 kW at 1000 rpm. If turbine B produces 100 kW, then its rpm is
If the average centre to centre spacing of vehicles is 30 meters, then the basic capacity of the traffic lane at a speed of 60 kmph is:
Which is the best hydraulic section of the following open channel cross-sections?
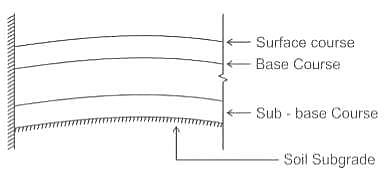
The drainage layer in the highway pavement is known as
The volume of water resulting from a discharge of 1 cumec per day amounts to:
The main constituents of gas generated during anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge are
The ratio of average velocity to maximum velocity for steady laminar flow in circular pipes is
In an ogee shaped spillway, the discharge is proportional to
The total irrigation depth of water, required by a certain crop in its entire growing period of 150 days is 25·92 cm. The cultural command area for a distributaries channel is 1,00,000 hectares. The distributaries channel shall be designed for a discharge of
Corrosion in sewer system occurs due to production of