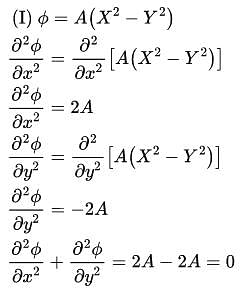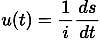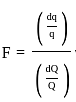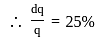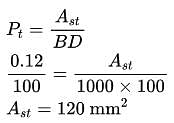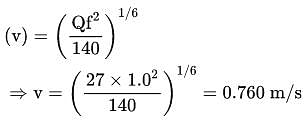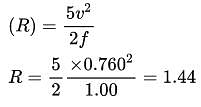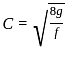BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC AE Civil Paper 6 (Civil) Mock Test - 3
As per public health and environmental engineering organization, for 50,000 - 100,000 population, density of population per hectare will be ________.
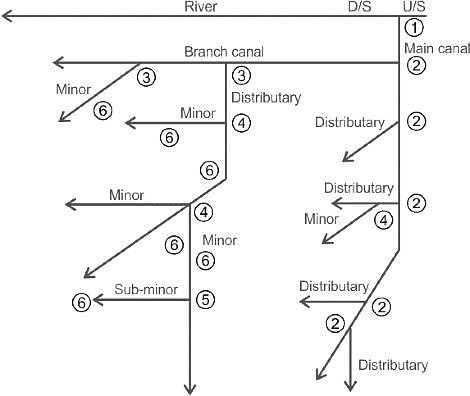
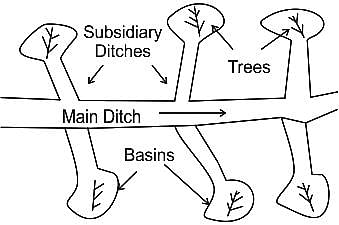
What type of irrigation does this diagram represent?

| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The type of wastewater that originates from the bathroom, kitchen, washing places and wash basins is called:
Verify whether the following functions are valid potential functions.
(i) ϕ = A(X2 - y2)
(ii) ϕ = Acos x
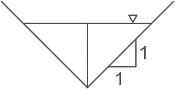
A triangular channel is hydraulically most economical when each of its sloping sides is inclined to the vertical at an angle of
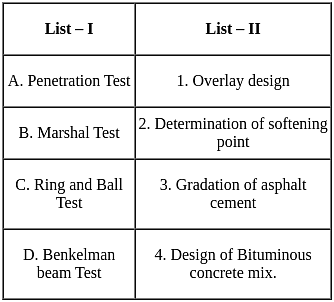
Match list I with list II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the list.
An IUH is a direct runoff hydrograph ?
What will be the density of a fluid having dynamic viscosity of 0.04 poise and kinematic viscosity of 0.04 stokes?
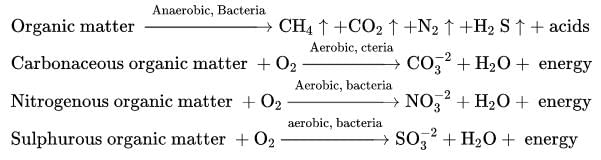
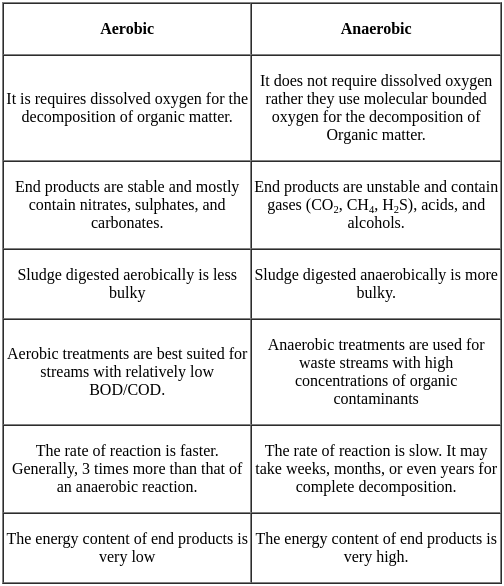
Anaerobic treatment is best suited for:
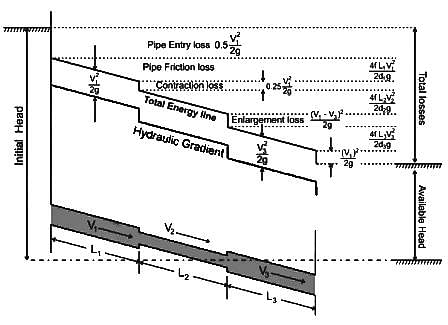
Hydraulic gradient line (HGL) represents the sum of
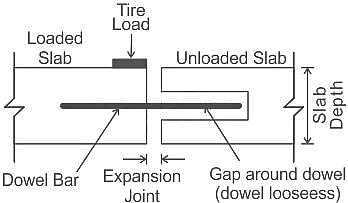
The dowel is used in rigid pavements for
For an irrigation module, the sensitivity was calculated to be 0.5. What would be percent variation in outlet discharge caused, if the percent variation in canal water depth and percentage change in discharge of distributary channel is 50 and 40 respectively.
Total force due to wave action on a gravity dam acts at a height of
If the Froude number of hydraulic jump is 5.5 it can be classified as
The minimum area of steel required per meter width of a slab with overall depth of 100 mm consisting of steel grade Fe500 is
Study the given statements with respect to turbidity of water and select the correct answer.
Statement A : Turbidity of water is not imparted by the dissolved matter present in water.
Statement B : Jackson's turbid meter is a laboratory apparatus which is used to measure the turbidity of water.
Which one of the following is the source of radioactive hazardous waste?
A continuous beam shall be deemed to be deep beam when, the ratio of effective span to overall depth is less than:
According to Khosla’s theory, the undermining of the floor starts from:
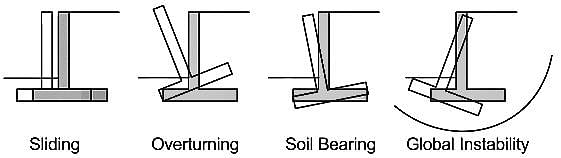
Factor of safety against sliding of the footing when dead load, live load and earth pressure are considered for shallow foundation
The Tie bars in cement concrete pavements are provided across
The following is the one of the main features of the roman roads
The crest of the emergency spillway in placed
Which one of the following problems is required to be studied in the design of earth dams ?
In canal formation, the term ‘balancing depth’ is used to indicate
What is the hydraulic radius of a stable canal carrying a discharge of 27 m3/s using Lacey's method ? (Assume silt factor is 1.0)
Identify the correct statement from the following:
The dimension of the Chezy's coefficient (c) are :
In Gravity dam, the ______ acts in a direction opposite to the acceleration imparted by earthquake forces and is equal to the product of the mass and the acceleration