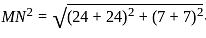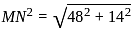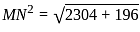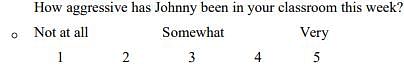UGC NET Paper 1 Mock Test - 8 - UGC NET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UGC NET Paper 1 Mock Test - 8
Which of the following statements about the World Wide Web (WWW) is correct?
Which of the following was a key feature of the educational institutions set up in ancient India under Buddhism?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Which of the following are useful tips in preparing questions for a structured interview?
(A) Introductory questions should be related to pleasantries.
(B) Introductory questions should be related to the research topic.
(C) Questions can be grouped, if the list of questions is long.
(D) General questions should precede specific questions.
(E) Repeat the personal questions again and again to test the truthfulness of the reponses of the interviewee.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
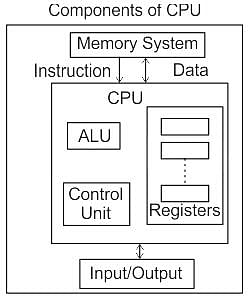
Which of the following are the principal components of the CPU of a computer system?
A. ALU (Arithmetic-Logic Unit)
B. CU (Control Unit)
C. Processor Registers
D. SSD (Solid-State Drive)
E. VRAM (Video RAM)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following best describes the purpose of using ANOVA in research?
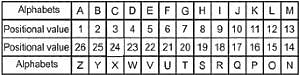
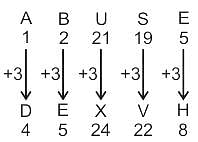
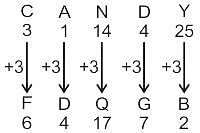
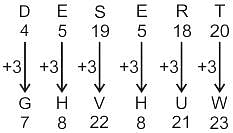
In a certain code language, "ABUSE" is written as "DEXVH" and "CANDY" is written as "FDQGB". How will "DESERT" be written in that language?
The University Grants Commission (UGC) in India serves as the primary regulatory body for higher education. In which of the following ways does the UGC maintain and coordinate university education?
A) It provides recognition to universities in India and disburses funds to such recognized universities and colleges.
B) It drafts the national budget for education and proposes it directly to the Parliament.
C) It directly controls the administrative departments of individual universities and academic staff appointments.
D) It sets the admission criteria and curriculum for all university courses in India.
Choose the right answer from the options given below:
A shopkeeper marks his goods at 80% more than their cost price and allows a discount of 48% on the marked price. His loss percentage is:
Assertion (A) : To communicate well in the classroom is a natural ability.
Reason (R) : Effective teaching in the classroom demands knowledge of the communication process.
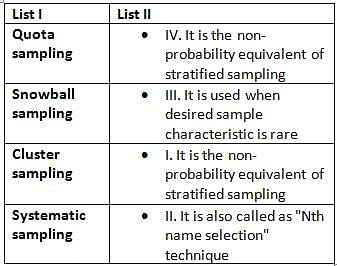
Match List I with List II
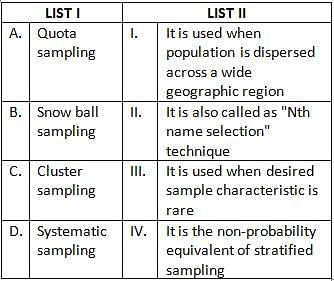
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The length of a train is 200 metres. If the speed of the train is 15 m/s, then how much time (in seconds) will it take to cross a bridge 520 metres long?
Which type of firewall process involves the examination of each packet's information against a set of established rules before deciding to allow it through or discard it?
India has the largest Higher Education System in the World after :
(a) The United States of America
(b) Australia
(c) China
(d) United Kingdom (U.K.)
Select the correct answer from the code given below :
If the average cost prices of articles A, C, D and E is Rs. 350 and article C is sold at 0.8% profit, then find the ratio of the discount per cent on the marked price of article C to that of the discount per cent on marked price of article D
If the selling price of article F is 89% more than the cost price of article E and article F is sold at Rs. 84 discount on its marked price, then find the ratio of the marked-up per cent of article F to the discount per cent given on its marked price.
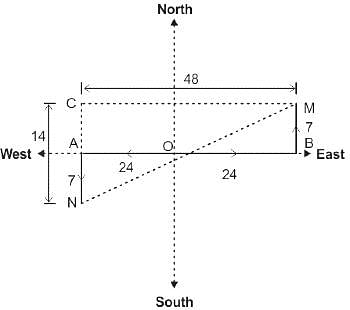
M and N starts from the same point and walks 24 km each in the opposite direction to each other. M turn left and walks 7 km. N turn left and walks 7 km. How far (in km) are they from each other?
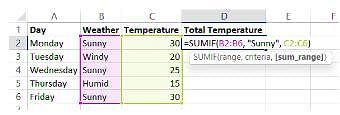
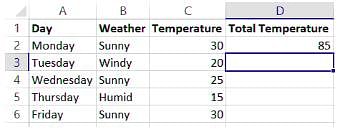
A Consider the following MS-EXCEL spreadsheet:
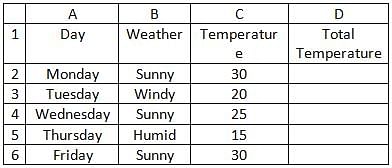
Suppose the formula - SUMIF(B2:B6, "Sunny", C2:C6) is entered into D2, what is the total temperature on sunny days?
With reference to the World Heritage Institute of Training and Research – Asia Pacific (WHITR-AP), consider the following statements.
1. It is a non-profit organization specialized in the area of heritage conservation.
2. It is an institute under the auspices of UNESCO.
3. It aims to strengthen the implementation of the World Heritage Convention 1972 in Asia and the Pacific region.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
What presents a significant obstacle to the detection and treatment of mental health disorders as per the passage?
According to the passage, why has mental health not been a top priority in public health discourse?
What global event spotlighted the importance of mental health as per the passage?
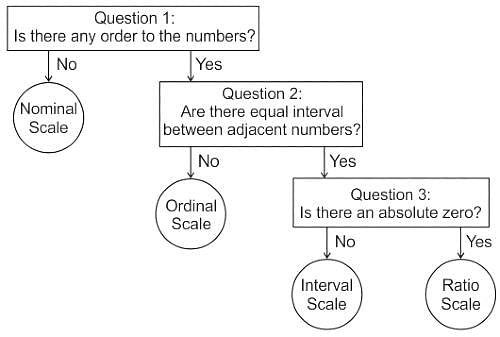
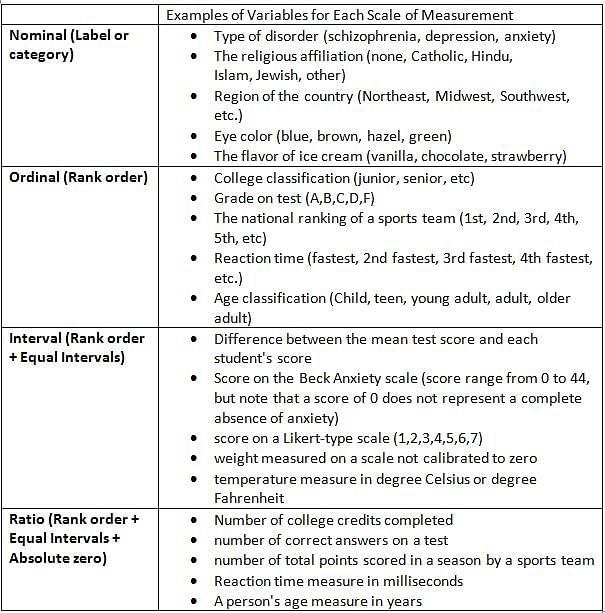
Which of the following is the correct order of measurement scales in increasing order of accuracy, precision and number of operations used?
Which of the following is NOT correct regarding Digilocker, a key initiative under the 'Digital India' program of the Government of India?
NEP-2020 proposes to establish which of the following new bodies?
(A) SSSA
(B) PARAKH
(C) IITI
(D) NTA
(E) NITI
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The time in which a train 1800 m long, travelling at the speed of 30 kmph, will pass a signal pole is:
Statement I: The SWAYAM PRABHA has new content every day for at least 5 hours which would be repeated 4 more times in a day.
Statement II: The SWAYAM PRABHA has content that allows the students to choose the time of their convenience.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below: