Practice Test - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test
The position of an object moving in a straight line can be specified with reference to
If the position- time graph is a straight line parallel to the time axis
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A truck is coming towards you from a distance of 1000m on a straight road at time t=0. At time t=10 seconds it is at a distance of 900 m. The average velocity in m/sec is
A truck has a velocity of 3 m /s at time t=0. It accelerates at 3 m / s2 on seeing police .What is its velocity in m/s at a time of 2 sec
A truck covers 40.0 m in 8.50 s while smoothly slowing down to a final speed of 2.80 m/s. Find its original speed in m/s
A truck is coming towards you from a distance of 1000m on a straight road, at time t=0. It reaches you in 100sec. The average speed in m/s is
A stone thrown from the top of a building is given an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward. Determine the time in seconds at which the stone reaches its maximum height.
g =9.8 m / sec2
100mL of gaseous hydrogen combines with 50 mL of gaseous oxygen to give 100mL of water vapours. This can be explained on the basis of:
The atom with the given atomic number Z=17, and the atomic mass A=35.5 is
In which of the following species the underlined carbon is having sp3 − hybridization
Among the following, the species having the smallest bond length is:
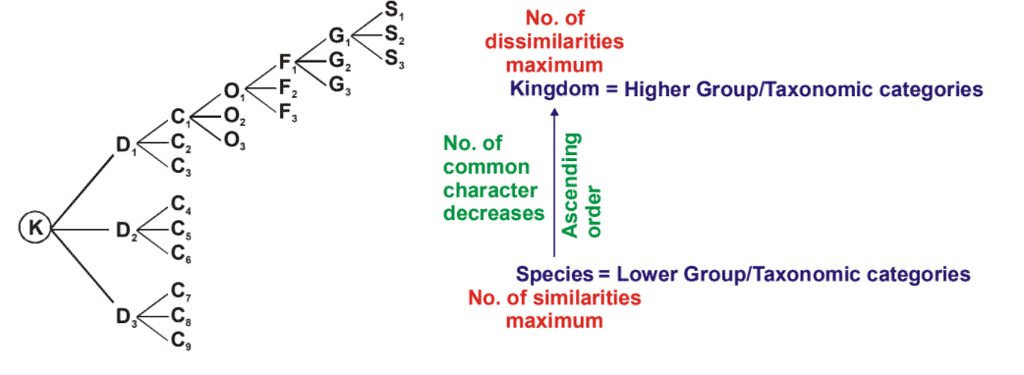
In the taxonomic hierarchy, which category comprises a group of related species with more common characteristics than species of other genera?
As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics
The scientific name of mango is written as Mangifera indica L. Pickup the correct statement about the significance of the letter 'L'.
As we go from species to kingdom in a taxonomic hierarchy, the number of common characteristics:
Which one is important in nutrient recycle and act as decomposer and mineralisers of the biosphere?
In which group of plants does the sporophyte not have a free-living stage?
The phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry is:
Which feature is characteristic of animals belonging to the phylum Cnidaria?
Assertion (A): Nematodes are pseudocoelomates.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.