Test: Transportation Engineering- 2 - GATE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Transportation Engineering- 2
For carrying out bituminous patch work during the rainy season, the most suitable binder is
Bituminous materials are commonly used in highway construction because of their good
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In cement concrete pavements, tie bars are installed in
The following general statement may be made about the penetration value and softening point of bitumen
The minimum length of the overtaking zone should be
In case of the valley curves or sag curves the maximum possible deviation angle is obtained when
The bitumen with viscosity reduced by volatile diluents is known as
On hill roads, the necessity to ease the gradient at horizontal curves by an amount to offset the extra tractive effort involved at curves is known as
According to IRC guidelines, the maximum volume of traffic that a rotary can efficiently handle is
The maximum number of passenger cars that can pass a given point on a lane or roadway during one hour under ideal roadway and traffic conditions is known as
For a highway with the design speed of 50 km/h, coefficient of friction 0.5, perception-brake reaction time of 2.5 s, and average vehicle length 5 m, the spacing between the vehicle length in their movement will be
For a two-lane pavement with radius of curve of 100 m, with design speed of 65 km/h & wheelbase of design vehicle of 6 m, the extra widening necessary will be
Consider the following factors:
1. Reaction time 2. Speed
3. Coefficient of the longitudinal friction
4. Gradients
Which of these factors are taken into account for computing braking distance?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Which one of the following represents the basic capacity of a single lane road? Where, V = speed in km/h, s = average centre to centre spacing of vehicle in m, and h = average time headway between two vehicle in seconds
Which one of the following method of O-D traffic surveys is conducted for comprehensive analysis of traffic and transportation data?
Consider the following parameters related to a rotary intersection:
1. Width of the weaving section
2. Length of the weaving section
3. Proportion of weaving traffic
4. Weaving angle
5. Width of the carriageway at entry
Capacity is generally expressed in terms of
If the normal flows on two approach roads at an intersection are respectively 500 PCU/h and 300 PCU/h, the saturation flows are 1600 PCU/h and 300 CPU/h, the saturation flows are 1600 PCU/h on each road and the total lost time per single cycle is 16 s, then the optimum cycle time by Webster’s method is
When two roads with two-lane, two-way traffic, cross at an uncontrolled intersection, the total number of potential major conflict points would be __________.
On a road the free speed was 65 km/h and the space headway at jam density was 6.25 vpkm. What is the maximum flow which could be expected on this road?


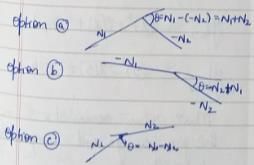



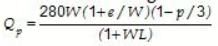 w is width of weaving section e is average of entry e1 and width of nonweaving section e2 for the range e/W = 0.4 to 1.0 L is the length of the weaving section P is proportion of weaving traffic
w is width of weaving section e is average of entry e1 and width of nonweaving section e2 for the range e/W = 0.4 to 1.0 L is the length of the weaving section P is proportion of weaving traffic














