RRB NTPC General Awareness Test - 2 - RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - RRB NTPC General Awareness Test - 2
Which of the following woman became first to win the Grand Swiss in November 2023?
Which of the following rural housing schemes by the Government of India is re-structured into Pradhan Mantri Gramin Awas Yojana?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The deficiency of which of the following vitamins is considered responsible for night-blindness?
Who among the following personalities is associated with the musical instrument Flute?
Who founded the 'Indian Home Rule Society' in London?
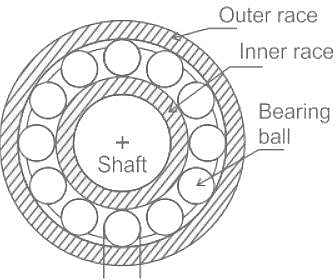
Ball bearings are used to convert static friction into
Which ministry has organized the Divya Kala Mela event in Agartala, Tripura?
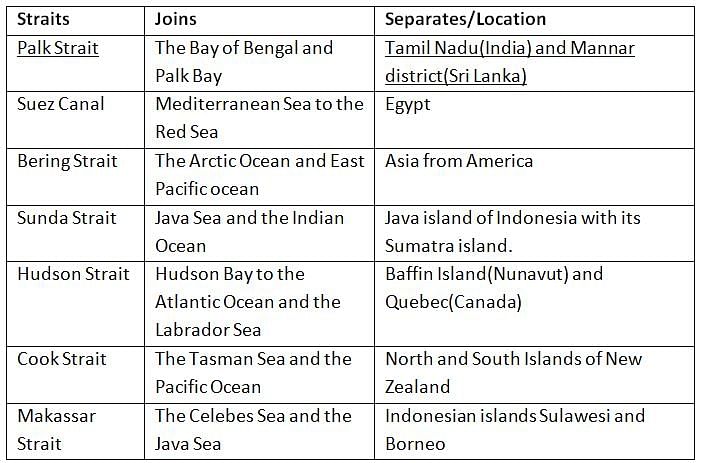
Which among the following straits divide Sri Lanka from India?
What does ‘Chaitya’ in Buddhist architecture refer to?
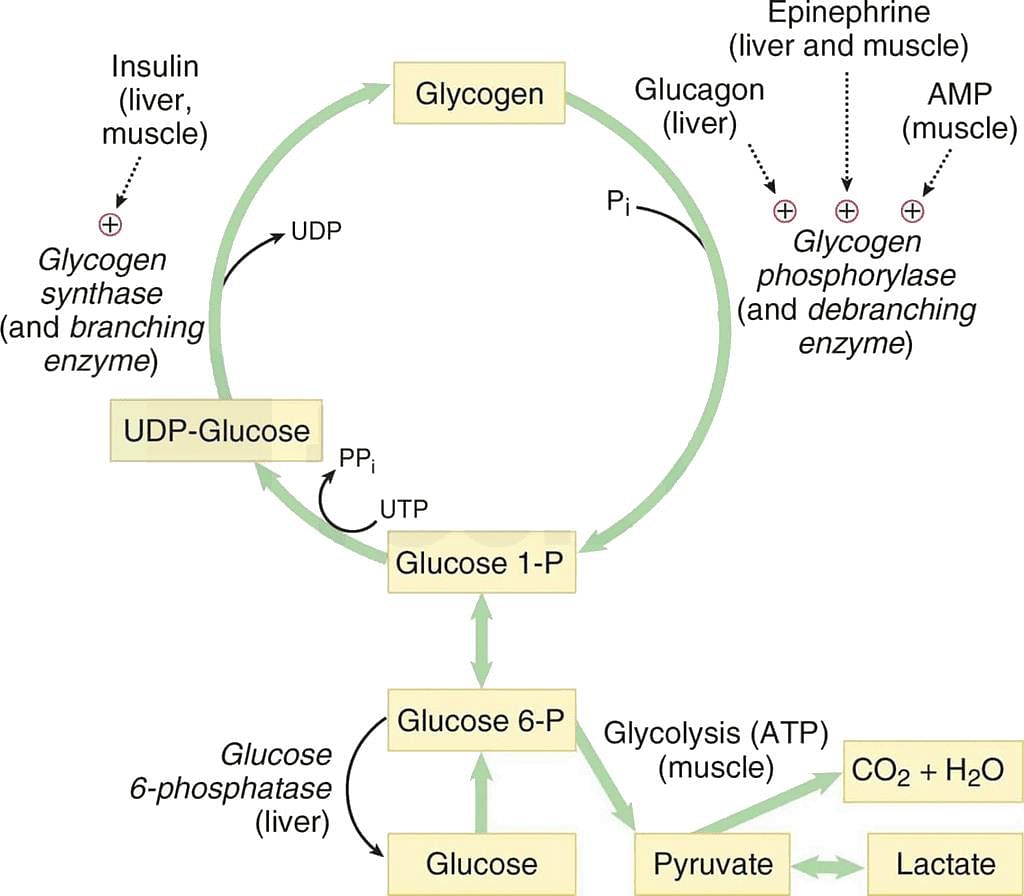
In plants, glucose is stored as reserve energy in form of starch. In which form is glucose stored as reserve energy in humans?
What is the name of the new scheme approved by the Union Cabinet for micro and small enterprises in the fisheries sector?
According to the 2011 Census, which of the following States has the highest (percentage) female literacy rate?
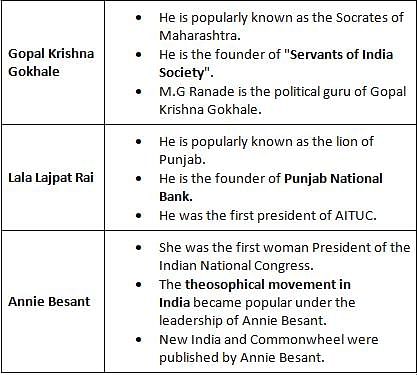
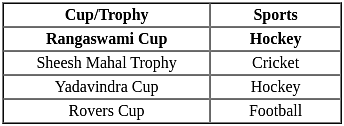
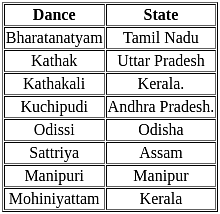
Which of the following combinations are correctly matched?
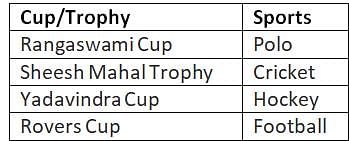
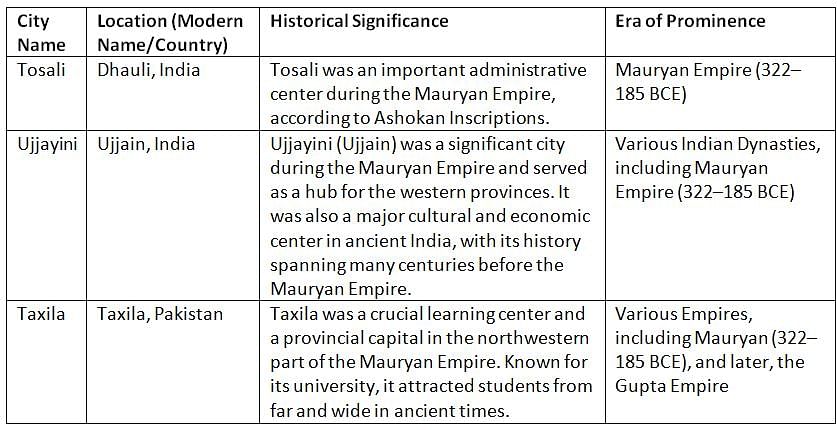
According to the Ashokan Inscription which of the following was NOT a provincial centre in Magadha Empire?
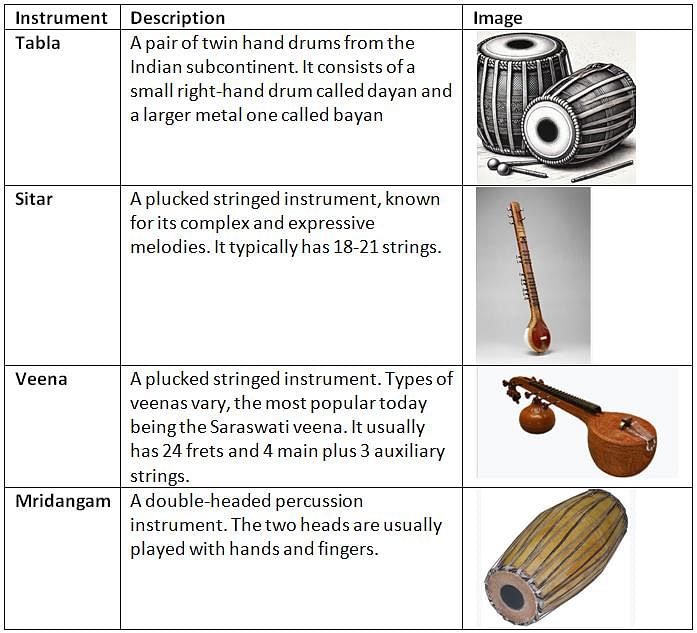
Ilyas Khan was born in Lucknow to a family of musicians. He was famous for playing _______.
Festival of "Ugadi" is celebrated every year on the first day of the Hindu month ________.
From which Article does the President of India derive his/her pardoning power?
Who among the following were prominent leaders of the 'Khilafat Movement'?
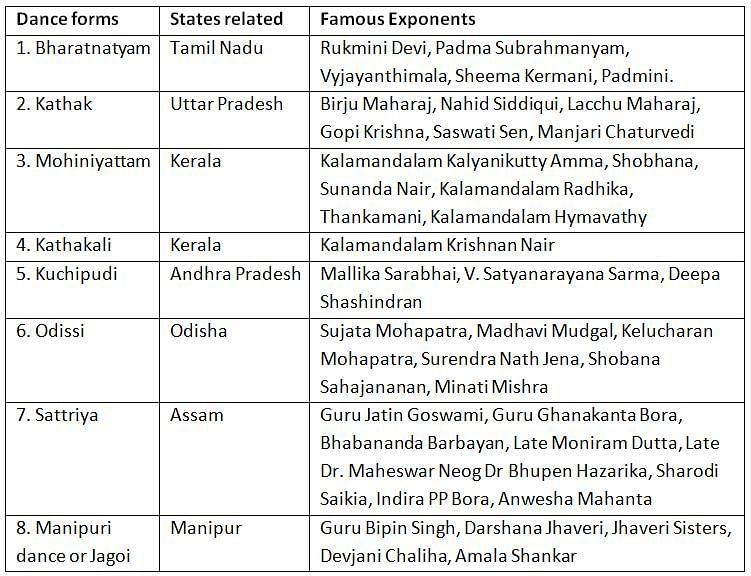
Kalamandalam Kallyanikutty Amma received fame and recognition for her work in ________.
Which ministry has announced the commencement of Phase-V of the Sagar Parikrama initiative?
Provisions related to the seat of the "Supreme Court of India" is mentioned in which article?
Under the provisions of the constitution on which of the following ground the citizenship of India does not lose?
Which organization has released the report "Electricity 2024"?
In 1897, Swami Vivekananda, a disciple of Ramakrishna Paramahansa, established the Ramakrishna Mission in __________