Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Tests > Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Chemistry MCQ
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Chemistry MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Chemical Bonding- 2
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 for Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Chemistry exam syllabus.The Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 MCQs are made for Chemistry 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 below.
Solutions of Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 questions in English are available as part of our course for Chemistry & Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 solutions in
Hindi for Chemistry course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 | 30 questions in 90 minutes | Mock test for Chemistry preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Chemistry Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 2
Among the following pairs in which the two species are not isostructural is:
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 3
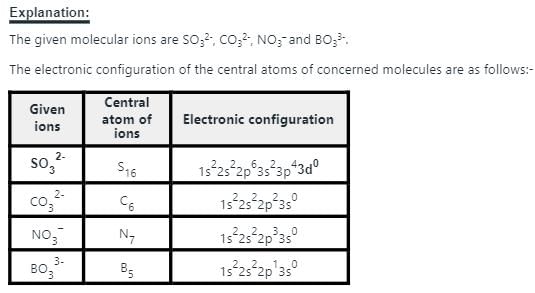
Which of the following set of ions/ molecules is isoelectric and structural?
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 3
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 4
In allene (C3H4), the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 4
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 5
The atom that form discrete polyatomic molecule in its elemental state are:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 5
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 7
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 8
Which of the following species has two non bonded electron pairs on the central atom:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 8
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 9
The shape and expected hybridization of BrO3- and HOCl are:
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 11
The hybridization of atomic orbital of nitrogen in NO2+, NO3- and NH4+ are:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 13
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 15
Covalent-molecules are usually held in a crystal structure by
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 17
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 19
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 23
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 26
In octahedral structure the pair of ‘d’ orbitals invo lved is:
Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 28
Hybridization state of boron and oxygen in boric acid is:
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 28
Detailed Solution for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 - Question 30
Information about Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Chemical Bonding- 2, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF



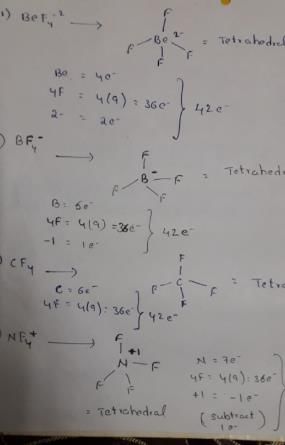 Isoelectronic species are those have same number of electrons.
Isoelectronic species are those have same number of electrons.


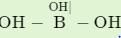 ; has a network structure in which boron is trigonal having sp2 and each oxygen atom is tetrahedral having sp3-hybridization with two lone pair of electrons on oxygen.
; has a network structure in which boron is trigonal having sp2 and each oxygen atom is tetrahedral having sp3-hybridization with two lone pair of electrons on oxygen.










