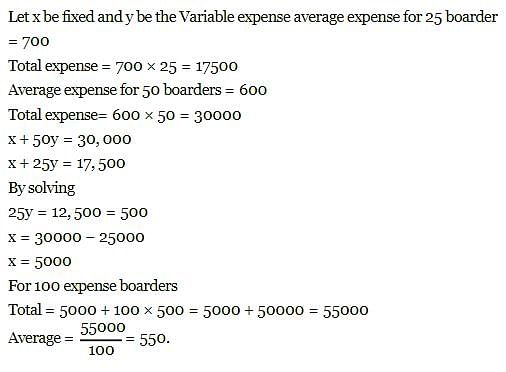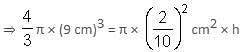Uttarakhand D.El.Ed Mock Test - 2 - UTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Uttarakhand D.El.Ed Mock Test - 2
What led to the introduction of the Cabinet Mission Plan?
What is the approximate population of India as of the latest available data?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Direction: In each of the following questions you are given a figure followed by four alternatives (a), (b), (c) and (d). Choose the alternatives which is closely resembles the mirror image of the given combination.
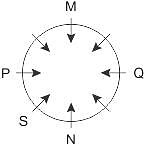
Choose the alternatives which is closely resembles the mirror image of the given combination.
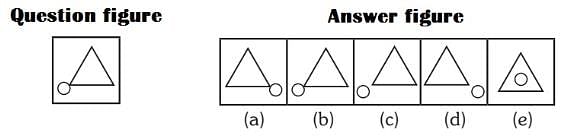

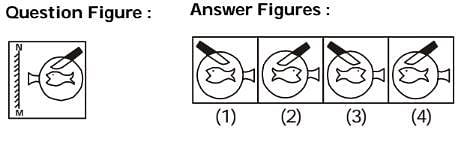
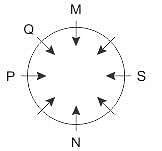
If a mirror is placed on the line MN, then which of the answer figures is the correct image of the given question figure?
A starts from his house and moves towards B’s house which is 4km North. After walking for three-fourth of the distance he finds B coming towards him along with C, who is A’s enemy. Wanting to avoid him, A takes a left turn and runs for a distance of 2kms. Now, if from this point (say ‘P’) he decides to go to B’s house, how much distance would he need to cover?
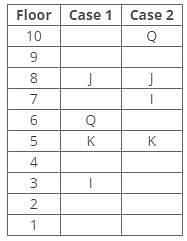
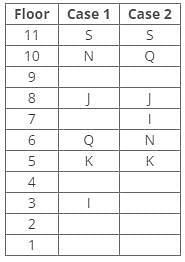
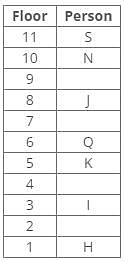
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
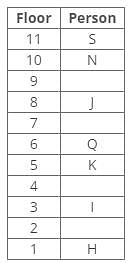
A certain number of people live on different floors of a building, where the bottommost floor is numbered 1 and the floor above it is 2 and so on. There is no vacant floor in the building.
J lives three floors above K. One person lives between J and N. The number of persons living between Q and K is equal to the number of persons living between N and S. The number of persons living below H is equal to the number of persons living above S. Q lives three floors above I. The number of persons living between I and N is one less than the number of persons living below J. K lives on the 5th floor. S doesn’t live on a perfect square-numbered floor. One person lives between I and H. One person lives between Q and J.
Q. How many persons live above N?
Among P, Q, R, S and T each having a different height. Q is shorter than only T and S is shorter than P and R. Who among them is the shortest?
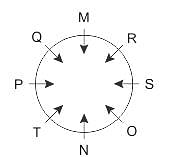
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions besides.
M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T are sitting around a circular table and all are facing the centre of the table. M is sitting fourth to the right of N. P is sitting second to the left of N. Q is sitting third to the right of S. T is sitting second to the left of O. S is not sitting beside P. O is not sitting beside M.
Q. Who among the following is the immediate neighbour of P and M?
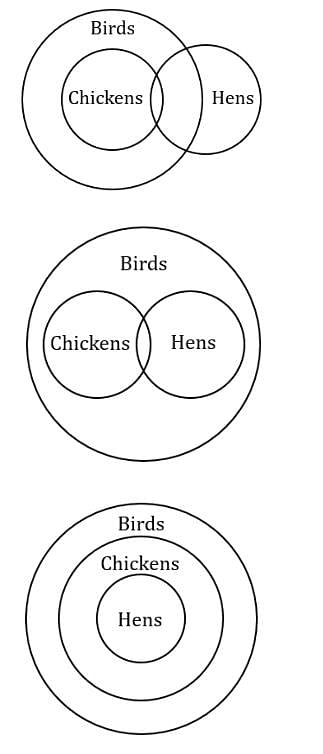
Statement 1: All chickens are birds.
Statement 2: Some chickens are hens.
Statement 3: Female birds lay eggs.
If the above statement are facts, then which of the following must also be a fact?
I. All birds lay eggs.
II. Hens are birds.
III. Some chickens are not hens.
Q: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z.
Which letter in this alphabet is the eighth letter to the right of the letter which is tenth letter to the left of the last but one letter of the alphabet?
If A is 1.5 times B, then B is what percent of A + B?
Last year, the ratio between the salaries of A and B was 3 : 4. But, the ratios of their individual salaries between the last year and this year were 4 : 5 and 2 : 3, respectively. If the sum of their present salaries is Rs. 4160, then how much is the salary of A now?
If three numbers are in the ratio of 1 : 3 : 5 and half the sum is 9, then the ratio of cubes of the numbers is:
The present ratio of ages of P and Q is 3: 5. 10 years ago, this ratio was 1: 2. Find the sum total of their present ages.
The average weight of A, B and C is 45 kg. If the average weight of A and B be 40 kg and that of B and C be 43 kg, what is the weight of B?
Total expenses of a boarding house are partly fixed and partly varying linearly with the number of boarders. The average expense per boarder is Rs. 700 when there are 25 boarders and Rs. 600 when there are 50 boarders. What is the average expense per boarder when there are 100 boarders?
A dog sees a cat. It estimates that the cat is 25 leaps away. The cat sees the dog and starts running with the dog in hot pursuit. If in every minute, the dog makes 5 leaps and the cat makes 6 leaps and one leap of the dog is equal to 2 leaps of the cat. Find the time in which the cat is caught by the dog (assume an open field with no trees).
A and B together can complete a work in 3 days. They start together but after 2 days, B left the work. If the work is completed after two more days, B alone could do the work in
What will be the ratio of simple interest earned by certain amount at the same rate of interest for 5 years and that for 15 years?
A machine costs ₹ 1025. If it is sold at a loss of 25%, what will be its cost price as a percentage of its selling price?
The marked price of a table is ₹1200, which is 20% above the cost price. It is sold at a discount of 10% on the marked price. find the profit per cent.
A sphere of diameter 18 cm made up of copper is melted and converted into a wire of diameter 4 mm. Find the length of the wire (in metres).
Through which Amendment of Constitution education has become fundamental right ?



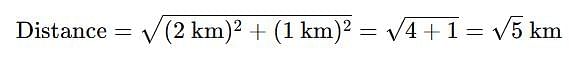


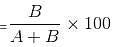
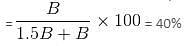
 B's weight = 31 kg.
B's weight = 31 kg.