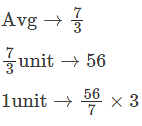BPSC Practice Test- 2 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC Practice Test- 2
Consider the following statements about the Bihar Prohibition and Excise Act, 2016:
1. It prescribes severe penalties for producing illicit liquor.
2. It has completely eradicated the illegal liquor trade in Bihar.
3. It was implemented to address public health issues caused by alcohol.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The accidental touch of Nettle leaves creates a burning sensation, which is due to inject of
Which of the following are widely used in genetic engineering?
Of the three numbers, the first is twice the second and is half of the third. If the average of these numbers is 56, the numbers in order are:
From which district of Bihar was the Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyan launched by the Prime Minister in 2020?
Which of the following is the largest city situated on the banks of river Ganga?
What percentage of Bihar's land has been carved out of Jharkhand state?
With which country has the Union Cabinet approved the signing of MoU for cooperation in the field of disability ?
Which of the following is not included in the Fundamental Duties under the Indian Constitution?
By whom does the judge of the Supreme Court resign from his post ?
Some rulers of the Khalji dynasty as given below:
A: Alauddin Khalji
B: Qutb-ud-din Mubarak
C: Khusrau Khan
D: Jalal-ud-din Khalji
Arrange them according to their reign.
Who among the following Indian revolutionaries conceived an armed insurrection against the British in cooperation with Germany?
Which of the following is the main provision of Rajagopalachari Formula?
Hot desert regions are found mostly in the western part of the continents between which latitudes?
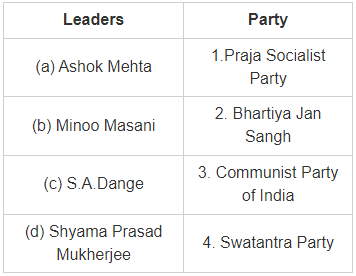
Match the following leaders listed in List A to Parties in List B.
Assertion (A): Green Revolution has resulted in the growth of food grain production in India.
Reason (R): Regional disparities have aggravated due to the green revolution in India.
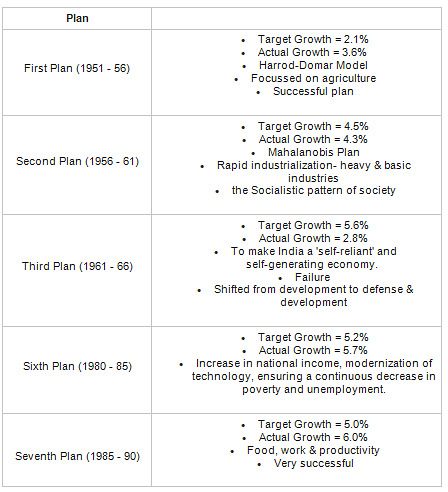
Which five year plan proposed to make India a 'self-reliant' and 'self-generating' economy?
The buildings of Raj Bhavan, Chief Secretariat, and High Court in Patna are influenced by which style?
Who among the following prepares the geographical maps of India?
Which of the following bill can be returned by the President for reconsideration?