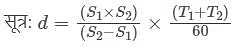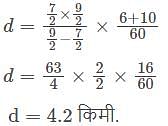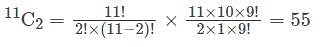BPSC Practice Test- 4 - BPSC (Bihar) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BPSC Practice Test- 4
Who among the following was/was an economic critic of colonialism in India?
Dadabhai Naoroji
G. Subramanya Iyer
R .C .Dutta
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Dadabhai Naoroji
G. Subramanya Iyer
R .C .Dutta
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
1902 AD Lord Curzon constituted a University Commission involving Indian members, who were they?
Which state government has announced to set up the country's first ambulance network for animals?
Who has won the Vijay Hazare cricket trophy 2021-22 held in the month of December 2021?
Which house of Parliament is called 'House of Representatives'?
Which of the following is the most important role played by ribosomes in the cells?
Which of the following are called scavengers of ecosystems?
In a chemical substance, the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass, this is called
Which one of the following movements had contributed to a split in the Indian National Congress resulting in the emergence of 'moderates and 'extremists'?
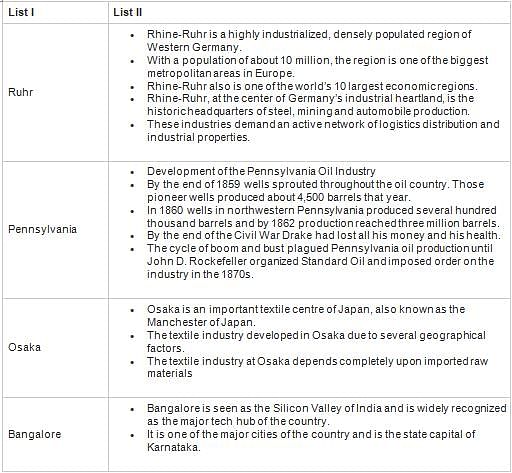
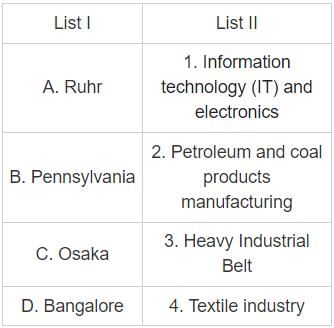
Match List – I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
The winter rains caused by Western Disturbance in North Western Plain of India gradually decreases from?
Which one of the following is not the necessary condition for the issue of a writ of Quo Warranto?
Which of the following is NOT possible by a law of Parliament under Article 3 of the Constitution?
Amita travels from her house at 3(1/2)km/h and reaches her school 6 minutes tale. The next day she travels at 4(1/2)km/h and reaches her school 10 minutes early. What is the distance between her house and the school.
How many different ways two cricketer can be selected for batting in a cricket match?
The first state to provide co-ownership of women in husband's ancestral property - ?
Which one is not correctly matched in relation to the travelers coming to Bihar and their country?
Recently, in which district of Bihar, the remains of 2500 years old ancient structures have been found?
Consider the following statements and choose the correct answer?
The Government of India and the Asian Development Bank have signed a loan agreement of $ 84 million to improve and expand water supply in which cities of Bihar
Which of the following is a feature of the Indian Constitution?