Test: Thermodynamics And Thermochemistry - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermodynamics And Thermochemistry - 2
Enthalpy change for a reaction does not depend upon:
The heat of combust ion of carbon to CO2 is –393 KJ/mol. The heat released upon format ion of 35.2 g of CO2 from carbon and oxygen gas is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the reaction:
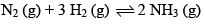
Carried out at constant temperature and pressure. If ΔH and ΔU are enthalpy and internal energy changes for the reaction, which of the following expressions is true?
The work done in ergs for the reversible expansion of one mole of an ideal gas from a volume of 10L to 20L is:
Work done during isothermal expansion of 1 mole of an ideal gas from 10 atm to 1 atm at 300K is:
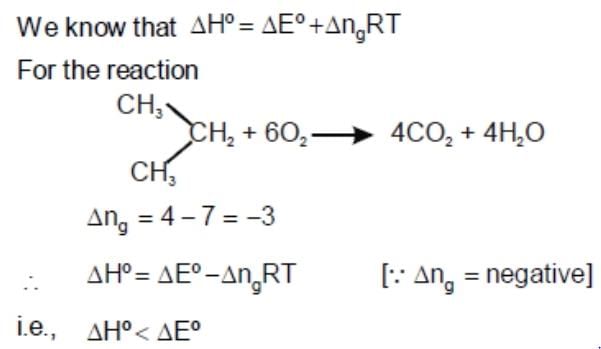
ΔE° of combustion of isobut ylene is x KJ mol-1. The value of ΔH° is:
The free energy change for a reversible reaction at equilibrium is:
The heat of neutralization of a strong acid and a strong alkali is 57.0 KJ mol–1. The heat released when 0.5 mole of HNO3 solution is mixed with 0.2 mole of KOH is:
Heat of formation of H2O is –286 KJ per mole and H2O2 is –188 KJ mol–1. The enthalpy change for the reaction
The species which by definition has ZERO standard molar enthalpy of formation at 298 K is
Given that bond energies of H–H and Cl–Cl are 430 and 240 KJ mol–1 respectively, and ΔHf for HCl is -90 KJ mol-1. Bond enthalpy of HCl is:
One mole of methanol when burnt in O2 gives out 723 KJ mol–1 heat. If one mole of O2 is used, what will be the amount of heat observed:
The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction:
Are 30 KJ mol–1 and 105 JK–1mol–1 respect ively. The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is:
The change in the entropy for the fusion of 1 mole of ice is:
(Melting point of ice = 273 K, molar enthalpy of fusion of ice = 6.0 KJ mol–1):
For a spontaneous process, the correct statement is:
The abso lute enthalpy of neutralization of the reaction:
For the reaction of one mole of zinc dust with one mole of sulphuric acid in a bomb calorimeter, ΔU and W corresponds to:
Standard enthalpy and standard entropy changes for the oxidation of NH3 at 298 K are –382.64 KJ mol–1 and – 145.6 JK–1mol–1, respectively. Standard Gibb’s energy change for the same reaction at 298 K is:
The heat capacity of 10 mol of an ideal gas at a certain temperature is 300 JK–1 at constant pressure. The heat capacity of the same gas at the same temperature and at constant volume would be:
The internal pressureof a real gas is related to the compressibility factor
Entropy is:
(I) It is the degree of disorder of randomness in a system
(II) Entropy is a state function and mixing is always positive
(III) Entropy is a intensive property
(IV) Entropy of solid is minimum and gases is maximum
(V) Entropy increase wit h temperature, complexity and atomicity
The correct statement is:
From the following pairs, choose the substances with the higher entropy per mole at a given temperature:
(I) O2 gas at 5 atm or O2 gas at 0.5 atm
(II) Br2 (L) or Br2 (g)
Among the following, the system require higher amount of thermal energy to giving the temperature 800C:
What is the internal pressure for 4 mole of Vander Waals gas:
Which of the following statement is correct:
for ideal and Vander Waals gases respectively:
A piston-cylinder contains 0.5 kg of air at 500 kPa and 500 K. The air expands in a process so the pressure is linearly decreasing with volume to a final state of 100 kPa and 300 K. Find the work in the process.





 =
= 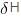 (Enthaply of fusion) /T (Temperature)
(Enthaply of fusion) /T (Temperature)














