Test: Context Free Language- 2 - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Context Free Language- 2
Let 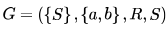 be a context free grammar where the rule set R is
be a context free grammar where the rule set R is 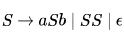 Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the languages:
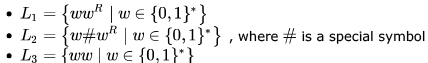
Which one of the following is TRUE?
In the context-free grammar below, S is the start symbol, a and b are terminals, and ϵ denotes the empty string.
The grammar generates the language
In the context-free grammar below, S is the start symbol, a and b are terminals, and ϵ denotes the empty string
Which of the following strings is NOT generated by the grammar?
The two grammars given below generate a language over the alphabet {x, y, z}
Which one of the following choices describes the properties satisfied by the strings in these languages?
Consider the grammar given below
Consider the following strings.
Which of the above strings are generated by the grammar ?
Consider the following grammars. Names representing terminals have been specified in capital letters.
Which one of the following statements is true?
A CFG G is given with the following productions where S is the start symbol, A is a non-terminal and a and b are terminals.
Which of the following strings is generated by the grammar above?
The language generated by the above grammar over the alphabet is the set of
Which of the following languages are context-free?
Consider the following context-free grammar over the alphabet ∑ = {a,b,c } with S as the start symbol:
Which one of the following represents the language generated by the above grammar?
If G is a grammar with productions
where S is the start variable, then which one of the following strings is not generated by G ?
Consider a CFG with the following productions.
S is the start symbol, A and B are non-terminals and 0 and 1 are the terminals. The language generated by this grammar is

















