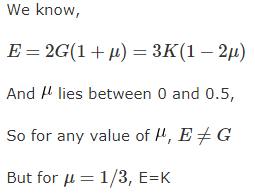Test: Stress & Strain - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Stress & Strain - 2
What is the phenomenon of progressive extension of the material i.s., strain increasing with the time at a constant load, called?
Which one of the following features improves the fatigue strength of a metallic material?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For a linearly elastic, isotropic and homogeneous material, the number of elastic constants required to relate stress and strain is:
What are the materials which show direction dependent properties, called?
In a homogenous, isotropic elastic material, the modulus of elasticity E in terms of G and K is equal to
If E, G and K denote Young's modulus, Modulus of rigidity and Bulk Modulus, respectively, for an elastic material, then which one of the following can be possibly true?
Consider the following statements:
1. Two-dimensional stresses applied to a thin plate in its own plane represent the plane stress condition.
2. Under plane stress condition, the strain in the direction perpendicular to the plane is zero.
3. Normal and shear stresses may occur simultaneously on a plane.
Which of the above statements is /are correct?
When a composite unit consisting of a steel rod surrounded by a cast iron tube is subjected to an axial load.
Assertion (A): The ratio of normal stresses induced in both the materials is equal to the ratio of Young's moduli of respective materials.
Reason (R): The composite unit of these two materials is firmly fastened together at the ends to ensure equal deformation in both the materials.
Which one of the following is correct?
When a nut is tightened by placing a washer below it, the bolt will be subjected to
A cube having each side of length a, is constrained in all directions and is heated uniformly so that the temperature is raised to T°C. If α is the thermal coefficient of expansion of the cube material and E the modulus of elasticity, the stress developed in the cube is:
A steel rod 10 mm in diameter and 1m long is heated from 20 °C to 120°C, E = 200 GPa and α = 12 × 10-6 per °C. If the rod is not free to expand, the thermal stress developed is:
The temperature stress is a function of
1. Coefficient of linear expansion 2. Temperature rise 3. Modulus of elasticity The correct answer is:
Assertion (A): Specimens for impact testing are never notched.
Reason (R): A notch introduces tri-axial tensile stresses which cause brittle fracture.
Which of the following materials generally exhibits a yield point?
What is the safe static tensile load for a M36 × 4C bolt of mild steel having yield stress of 280 MPa and a factor of safety 1.5?
Select the proper sequence
1. Proportional Limit 2. Elastic limit 3. Yielding 4. Failure
A heavy uniform rod of length 'L' and material density 'δ' is hung vertically with its top end rigidly fixed. How is the total elongation of the bar under its own weight expressed?
A rod of length, "i " tapers uniformly from a diameter ''D1' to a diameter ''D2' and carries an axial tensile load of "P". The extension of the rod is (E represents the modulus of elasticity of the material of the rod)
A weight falls on a plunger fitted in a container filled with oil thereby producing a pres sure of 1.5 N/mm2 in the oil. The Bulk Modulus of oil is 2800 N/mm2. Given this situation, the volumetric compressive strain produced in the oil will be:
The outside diameter of a hollow shaft is twice its inside diameter. The ratio of its torque carrying capacity to that of a solid shaft of the same material and the same outside diameter is
For an isotropic, homogeneous and linearly elastic material, which obeys Hooke's law, the number of independent elastic constant is:
The reactions at the rigid supports at A and B for the bar loaded as shown in the figure are respectively.
A. steel rod of diameter 1 cm and 1 m long is heated from 20°C to 120°C. Its α = 12´10-6 / K and E=200 GN/m2. If the rod is free to expand, the thermal stress developed in it is:
In a simple tension test, Hooke's law is valid upto the
Assertion (A): For a ductile material stress-strain curve is a straight line up to the yield point.
Reason (R): The material follows Hooke's law up to the point of proportionality.
Which one of the following materials is highly elastic?
A bar of diameter 30 mm is subjected to a tensile load such that the measured extension on a gauge length of 200 mm is 0.09 mm and the change in diameter is 0.0045 mm. The poisson’s ratio will be
The independent elastic constants for a homogeneous and isotropic material are
A copper rod 400 mm long is pulled in tension to a length of 401.2 mm by applying a tensile stress of 330 MPa. If the deformation is entirely elastic, the Young’s modulus of copper is