Test: One Dimensional Unsteady Conduction & Free & Forced Convection - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: One Dimensional Unsteady Conduction & Free & Forced Convection - 1
The ratio 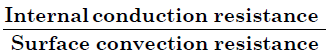 is known as
is known as
Assertion (A): In lumped heat capacity systems the temperaturegradient within the system is negligible
Reason (R): In analysis of lumped capacity systems the thermalconductivity of the system material is considered very highirrespective of the size of the system
Reason (R): In analysis of lumped capacity systems the thermalconductivity of the system material is considered very highirrespective of the size of the system
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A thermocouple in a thermo-well measures the temperature of hot gas flowing through the pipe. For the most accurate measurement of temperature, the thermo-well should be made of:
A thermocouple in a thermo-well measures the temperature of hot gas flowing through the pipe. For the most accurate measurement of temperature, the thermo-well should be made of:
Assertion (A): During the temperature measurement of hot gas in aduct that has relatively cool walls, the temperature indicated by the thermometer will be lower than the true hot gas temperature.
Reason(R): The sensing tip of thermometer receives energy from the hot gas and loses heat to the duct walls.
A coolant fluid at 30°C flows over a heated flat plate maintained at aconstant temperature of 100°C. The boundary layer temperature distribution at a given location on the plate may be approximated asT = 30 + 70exp (–y) where y (in m) is the distance normal to the plate andT is in °C. If thermal conductivity of the fluid is 1.0 W/mK, the local convective heat transfer coefficient (in W/m2K) at that location will be:
The ratio of energy transferred by convection to that by conduction iscalled
The ratio of energy transferred by convection to that by conduction iscalled
The ratio of energy transferred by convection to that by conduction iscalled ]
Consider a hydrodynamically fully developed flow of cold air through a heated pipe of radius ro. The velocity and temperature distributions in the radial direction are given by u(r) and T(r) respectively. If um, is the mean velocity at any section of the pipe, then the bulk-mean temperature at that section is given by:
The velocity and temperature distribution in a pipe flow are given by u(r) and T(r). If um is the mean velocity at any section of the pipe, the bulk mean temperature at that section is:
Assertion (A): When heat is transferred from a cylinder in cross flow to an air stream, the local heat transfer coefficient at the forwar dstagnation point is large.
Reason (R): Due to separation of the boundary layer eddiescontinuously sweep the surface close to the forward stagnation point.
Consider the following statements:
If a surface is pock-marked with a number of cavities, then ascompared to a smooth surface.
1. Radiation will increase
2. Nucleate boiling will increase
3. Conduction will increase
4. Convection will increaseOf these statements:
Assertion (A): All analyses of heat transfer in turbulent flow musteventually rely on experimental data.
Reason (R): The eddy properties vary across the boundary layer and noadequate theory is available to predict their behaviour.
In the case of turbulent flow through a horizontal isothermal cylinderof diameter 'D', free convection heat transfer coefficient from thecylinder will:
For laminar flow over a flat plate, the local heat transfer coefficient 'hx'varies as x-1/2, where x is the distance from the leading edge (x = 0) ofthe plate. The ratio of the average coefficient 'ha' between the leading edge and some location 'A' at x = x on the plate to the local heat transfer coefficient 'hx' at A is
For fully-developed turbulent flow in a pipe with heating, the Nusselt number Nu, varies with Reynolds number Re and Prandtl number Pr as
Natural convection heat transfer coefficients over surface of a verticalpipe and vertical flat plate for same height and fluid are equal. Whatis/are the possible reasons for this?
1. Same height
2. Both vertical
3. Same fluid
4. Same fluid flow pattern
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Which one of the following statements is correct?
The non-dimensional parameter known as Stanton number (St) isused in
Which one of the following statements is correct?
The non-dimensional parameter known as Stanton number (St) isused in

















