Test: Hydraulic Turbine, Buoyancy & Flotation - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Hydraulic Turbine, Buoyancy & Flotation - 2
The specific speed of an impulse hydraulic turbine will be greater than the specific speed of a reaction type hydraulic turbine.
Specific speed of a Kaplan turbine ranges between
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Match List-I (Phenomena) with List-II (Causes) and select the correct answer:

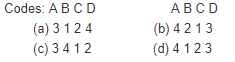
Assertion (A): In turbo machines, stalling is a local phenomenon while surging affects the whole machine.
Reason (R): Stalling occurs when flow breaks away from the blades while surging causes complete breakdown of the flow.
The gross head on a turbine is 300 m. The length of penstock supplying water from reservoir to the turbine is 400 m. The diameter of the penstock is 1 m and velocity of water through penstock is 5 m/s. If coefficient of friction is 0.0098, the net head on the turbine would benearly
Match List-I (Flow parameter) with List-II (Type of turbine) and select the correct answer:
Consider the following types of water turbines:
1. Bulb
2. Francis
3. Kaplan
4. Pelton
The correct sequence of order in which the operating head decreases while developing the same power is
Consider the following energies associated with a Pelton turbine:
1. Mechanical energy
2. Kinetic energy
3. Potential energy
The correct sequence of energy conversion starting from the entry offluid is:
Which one of the following statements regarding an impulse turbine iscorrect?
The gross head available to a hydraulic power plant is 100 m. The utilized head in the runner of the hydraulic turbine is 72 m. If the'hydraulic efficiency of the turbine is 90%, the pipe friction head is estimated to be:
As water flows through the runner of a reaction turbine, pressure acting on it would vary from:
Bodies in flotation to be in stable equilibrium, the necessary and sufficient condition is that the centre of gravity is located below the………………..
Assertion (A): The buoyant force for a floating body passesthrough the centroid of the displaced volume.
Reason (R): The force of buoyancy is a vertical force & equal tothe weight of fluid displaced.
Resultant pressure of the liquid in case of an immersed body acts through which one of the following?
Which of the following statement is true?
For floating bodies, how is the metacentric radius defined?
Consider the following statements:
The metacentric height of a floating body depends
1. Directly on the shape of its water-line area.
2. On the volume of liquid displaced by the body.
3. On the distance between the metacentre and the centre ofgravity.
4. On the second moment of water-line area.
Of these statements correct are:
Stability of a freely floating object is assured if its centre of
A cylindrical piece of cork weighting 'W' floats with its axis in horizontal position in a liquid of relative density 4. By anchoring the bottom, the cork piece is made to float at neutral equilibrium position with its axis vertical. The vertically downward force exerted by anchoring would be:
A large metacentric height in a vessel
If a piece of metal having a specific gravity of 13.6 is placed inmercury of specific gravity 13.6, then
What are the forces that influence the problem of fluid static?
A bucket of water hangs with a spring balance. if an iron piece issuspended into water from another support without touching the sides of the bucket, the spring balance will show
A metallic piece weighs 80 N air and 60 N in water. The relativedensity of the metallic piece is about
Which of the following advantages is/are possessed by a Kaplan turbine over a Francis turbine?
1. Low frictional losses.
2. Part load efficiency is considerably high
3. More compact and smaller in size.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below
Assertion (A): A Kaplan turbine is an axial flow reaction turbine withits vanes fixed to the hub.
Reason (R): Water flows parallel to the axis of rotation of the turbineand a part of the pressure energy gets converted to kinetic energyduring its flow through the vanes.
The use of a draft tube in a reaction type water turbine helps to:
Which of the following water turbines does not require a draft tube?
Which one of the following forms of draft tube will NOT improve the hydraulic efficiency of the turbine?

















