Test: Line Balancing & Break Even Analysis - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Line Balancing & Break Even Analysis - 2
Match List-l (Parameter) with List-II (Definition) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:


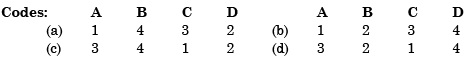
Process I requires 20 units of fixed cost and 3 units of variable cost per piece, while Process II required 50 units of fixed cost and 1 unit of variable cost per piece. For a company producing 10 piece per day
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A production line is said to be balanced when
Match List-I (Methods) with List-II (Applications) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
A production system has a product type of layout in which there are four machines laid in series. Each machine does a separate operation. Every product needs all the four operations to be carried out. The designed capacity of each of the four machines is 200, 175, 160 and 210 products per day. The system capacity would be:
M/s. ABC & Co. is planning to use the most competitive manufacturing process to produce an ultramodern sports shoe. They can use a fully automatic robot-controlled plant with an investment of Rs. 100 million; alternately they can go in for a cellular manufacturing that has a fixed cost of Rs. 80 million. There is yet another choice of traditional manufacture that needs in investment of Rs. 75 million only. The fully automatic plant can turn out a shoe at a unit variable cost of Rs. 25 per unit, whereas the cellular and the job shop layout would lead to a variable cost of Rs. 40 and Rs. 50 respectively. The break even analysis shows that the break even quantities using automatic plant vs traditional plant are in the ratio of 1: 2. The per unit revenue used in the break even calculation is:
A new facility has to be designed to do all the welding for 3 products: A, B and C, Per unit welding time for each product is 20 s, 40 s and 50 s respectively. Daily demand forecast for product A is 450, for B is 360 and for C is 240. A welding line can operate efficiently for 220 minutes a day. Number of welding lines required is:
Process X has fixed cost of Rs. 40,000 and variable cost of Rs. 9 per unit whereas process Y has fixed cost of Rs.16, 000 and variable cost of Rs. 24 per unit. At what production quantity, the total cost of X and Yare equal?
A company has four work centres A, B, C and D, with per day capacities of 450 units, 390 units, 360 units and 400 units respectively. The machines are laid down in order A, B, C, and D and product has to be operated on all these machines for getting converted into finished product. The actual output turns to be 306 units per day. What is the system efficiency?
Which one of the following information combinations has lowest break-even point?
An operations consultant for an automatic car wash wishes to plan for enough capacity of stalls to handle 60 cars per hour. Each car will have a wash time of 3 minutes, but there is to be a 20% allowance for set-up time, delays and payment transactions. How many car wash stalls should be installed?
The indirect cost of a plant is Rs 4,00,000 per year. The direct cost is Rs 20 per product. If the average revenue per product is Rs 60, the break-even point is:
An operations consultant for an automatic car wash wishes to plan for enough capacity to handle 60 cars per hour. Each car will have a wash time of 4 minutes, but there is to be a 25% allowance for setup time, delays and payment transactions. How many car wash stalls should be installed?
If the fixed cost of the assets for a given period doubles, then how much will the break-even quantity become?
Consider the following sets of tasks to complete the assembly of an engineering component:
Task Time (in seconds) Precedence
The expected production rate is 3000 units per shift of 8 hour duration. The minimal number of workstations that are needed to achieve this production level is
Process X has a fixed cost of Rs 40,000 per month and a variable cost of Rs 9 per unit. Process Y has a fixed cost of Rs 16,000 per month and a variable cost of Rs 24 per unit. At which value, total costs of processes X and Y will be equal?
A product is manufactured by processing on the four workstation (WS). The capacity of each machine on these workstations is given in the diagram as shown above. In the diagram M1, M2A, M2B, M3, M4A and M4B are the machines and 500, 275, 275, 560, 200 and 200 are their capacities in number of products made per shift. If the products made in this system are 5%, then what will be the output from this system?
Consider the following statements:
The break-even point increases
1. If the fixed cost per unit increases
2. If the variable cost per unit decreases
3. If the selling price per unit decreases
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Match List-I (PPC functions) with List-II (Activity) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
If the total investment is Rs. 5,00,000 for a target production, the income for the current year is Rs. 3,00,000 and total operating cost is Rs. 1,00,000; what is the economic yield?
A work shift is for 8 hours duration; 30 minutes lunch break and two 15 minutes (each) tea breaks are allowed per shift. If products are to go out after assembly at the rate of 60 per shift, and total assembly time content for a product is 42 minutes, then minimum number of work stations needed is:
Based on the given graph, the economic range of batch sizes to be preferred for general purpose machine (OP), NC machine (NC) and special purpose machine (SP) will be:
Match List-I (Element of cost) with List-II (Nature of cost) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Assertion (A): A larger margin of safety in break-even analysis is helpful for management decision.
Reason (R): If the margin of safety is large, it would indicate that there will be profit even when there is a serious drop in production.
Fixed investments for manufacturing a product in a particular year is Rs. 80,000/- The estimated sales for this period is 2, 00,000/-. The variable cost per unit for this product is Rs. 4/-. If each unit is sold at Rs.20/-, then the break even point would be:
Match List -I (Sym bols) with List-II (Meaning) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists; related to P/V chart on Break-Even Analysis as shown in the above figure:
The fixed costs for a year is Rs. 8 lakhs, variable cost per unit is Rs. 40/- and the selling price of each unit is Rs. 200/-. If the annual estimated sales is Rs. 20,00,000/-, then the break-even volume is :
If Break-even point = Total fixed cost then X is the
Two jigs are under consideration for a drilling operation to make a particular part. Jig A costs Rs. 800 and has operating cost of Rs. 0.10 per part. Jig B costs Rs. 1200 and has operating cost of Rs. 0.08 per part. The quantity of parts to be manufactured at which either jig will prove equally costly is:
A company sells 14,000 units of its product. It has a variable cost of Rs. 15 per unit. Fixed cost is Rs. 47,000 and the required profit is Rs. 23,000 Per unit product price (in Rs.) will be:

















