Test: Thin Cylinders & Thick Cylinders - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thin Cylinders & Thick Cylinders - 2
The maximum principal strain in a thin cylindrical tank, having a radius of 25 cm and wall thickness of 5 mm when subjected to an internal pressure of 1MPa, is (taking Young's modulus as 200 GPa and Poisson's ratio as 0.2)
A thin walled cylindrical vessel of well thickness, t and diameter d is fitted with gas to a gauge pressure of p. The maximum shear stress on the vessel wall will then be:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A cylindrical container of radius R = 1 m, wall thickness 1 mm is filled with water up to a depth of 2 m and suspended along its upper rim. The density of water is 1000 kg/m3 and acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2. The self-weight of the cylinder is negligible. The formula for hoop stress in a thin-walled cylinder can be used at all points along the height of the cylindrical container.
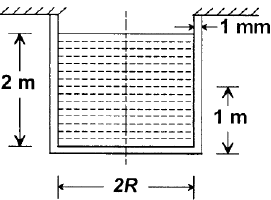
If the Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio of the container material are 100 GPa and 0.3, respectively, the axial strain in the cylinder wall at mid-depth is
A thin cylinder of radius r and thickness t when subjected to an internal hydrostatic pressure P causes a radial displacement u, then the tangential strain caused is
A thin cylindrical shell of diameter d, length „l‟ and thickness t is subjected to an internal pressure p. What is the ratio of longitudinal strain to hoop strain in terms of Poisson's ratio (1/m)?
A thin cylinder contains fluid at a pressure of 500 N/m2, the internal diameter of the shell is 0.6 m and the tensile stress in the material is to be limited to 9000 N/m2. The shell must have a minimum wall thickness of nearly
A water main of 1 m diameter contains water at a pressure head of 100 metres. The permissible tensile stress in the material of the water main is 25 MPa. What is the minimum thickness of the water main? (Take g = 10 m/s2 ).
In strain gauge dynamometers, the use of how many active gauge makes the dynamometer more effective?
For the same internal diameter, wall thickness, material and internal pressure, the ratio of maximum stress, induced in a thin cylindrical and in a thin spherical pressure vessel will be:
The ratio of circumferential stress to longitudinal stress in a thin cylinder subjected to internal hydrostatic pressure is:
A thin cylindrical shell of mean diameter 750 mm and wall thickness 10 mm has its ends rigidly closed by flat steel plates. The shell is subjected to internal fluid pressure of 10 N/mm2 and an axial external pressure P1. If the longitudinal stress in the shell is to be zero, what should be the approximate value of P1?
Match List-I (Terms used in thin cylinder stress analysis) with List-II (Mathematical expressions) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
The maximum shear stress is induced in a thin-walled cylindrical shell having an internal diameter 'D' and thickness‟t‟ when subject to an internal pressure 'p' is equal to
The percentage change in volume of a thin cylinder under internal pressure having hoop stress = 200 MPa, E = 200 GPa and Poisson's ratio = 0·25 is:
If a block of material of length 25 cm. breadth 10 cm and height 5 cm undergoes a volumetric strain of 1/5000, then change in volume will be:
If a thick cylindrical shell is subjected to internal pressure, then hoop stress, radial stress and longitudinal stress at a point in the thickness will be:
In a thick cylinder pressurized from inside, the hoop stress is maximum at
A thick-walled hollow cylinder having outside and inside radii of 90 mm and 40 mm respectively is subjected to an external pressure of 800 MN/m2. The maximum circumferential stress in the cylinder will occur at a radius of
A hollow pressure vessel is subject to internal pressure.
Consider the following statements:
1. Radial stress at inner radius is always zero.
2. Radial stress at outer radius is always zero.
3. The tangential stress is always higher than other stresses.
4. The tangential stress is always lower than other stresses.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A thick cylinder of internal radius and external radius a and b is subjected to internal pressure p as well as external pressure p. Which one of the following statements is correct?
The magnitude of circumferential stress developed is:
Consider the following statements at given point in the case of thick cylinder subjected to fluid pressure:
1. Radial stress is compressive
2. Hoop stress is tensile
3. Hoop stress is compressive
4. Longitudinal stress is tensile and it varies along the length
5. Longitudinal stress is tensile and remains constant along the length of the cylinder
Which of the statements given above are correct?
If the total radial interference between two cylinders forming a compound cylinder is δ and Young's modulus of the materials of the cylinders is E, then the interface pressure developed at the interface between two cylinders of the same material and same length is:
The hemispherical end of a pressure vessel is fastened to the cylindrical portion of the pressure vessel with the help of gasket, bolts and lock nuts. The bolts are subjected to
Consider the following statements:
In a thick walled cylindrical pressure vessel subjected to internal pressure, the Tangential and radial stresses are:
1. Minimum at outer side
2. Minimum at inner side
3. Maximum at inner side and both reduce to zero at outer wall
4. Maximum at inner wall but the radial stress reduces to zero at outer wall
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A thick open ended cylinder as shown in the figure is made of a material with permissible normal and shear stresses 200 MPa and 100 MPa respectively. The ratio of permissible pressure based on the normal and shear stress is:
In a thick cylinder, subjected to internal and external pressures, let r1 and r2 be the internal and external radii respectively. Let u be the radial displacement of a material element at radius Identifying the cylinder axis as z axis, the radial strain component εrr is:
A thin cylinder with closed lids is subjected to internal pressure and supported at the ends as shown in figure.
The state of stress at point X is as represented in
A compound cylinder with inner radius 5 cm and outer radius 7 cm is made by shrinking one cylinder on to the other cylinder. The junction radius is 6 cm and the junction pressure is 11 kgf/cm2. The maximum hoop stress developed in the inner cylinder is
A solid thick cylinder is subjected to an external hydrostatic pressure p. The state of stress in the material of the cylinder is represented as:


















