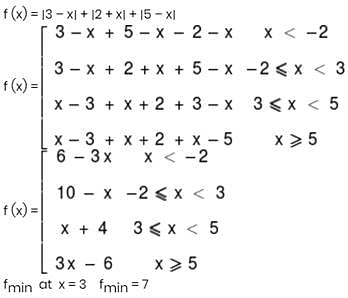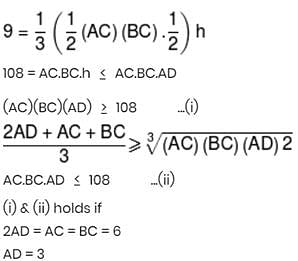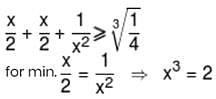JEE Main Maths Test- 9 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Maths Test- 9
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If f(a) = 2, f`(a) = 1, g(a) = –1, g`(a) = 2, then value of
The vertices of a triangle ABC are (2,1),(5,2) and (3,4)respectively. The circumcentre is the point
If A and B are the points (–3,4) & (2,1). Then the co-ordinates of point C on AB produced such that AC = 2 BC are
The equation of the line passing through the intersection of x - √3 y + √3 - 1 = 0 and x y–2 = 0 and
making an angle of 150 with the first line is
If 2x2 + λxy + 2y2 +(λ - 4)x + 6y - 5 = 0is the equation of a circle, then its radius is
Equation of circles which pass through the points (1,–2) and (3,–4) and touch the x-axis is
The circle whose centre is on the x-axis and the line 4x–3y–12 = 0 and whose radius is the distance
between the line 4x–3y–32 = 0 and 4x–3y–12 = 0 has equation
Equation of the circle whose radius is 5 and which touches externally the circle x2 + y2 -2x - 4y - 20 = 0 at
the point (5,5) is
The number of integral values of for λ which x2 + y2 +λx + (1 - λ) y + 5 = 0is the equation of a
circle whose radius cannot exceed 5 is
The angle at which the circle x2 + y2 = 16 can be seen from the point (8,0) is
The slope of the tangent at the point (h,h) of the circle x2 + y2 = a2is
If f (x) = [x sin p x] { where [x] denotes greatest integer function}, then f (x) is
The equation of the locus of the mid-points of the chords of the circle 4x2 + 4y2 - 12x + 4y +1 = 0that subtend an anlge of 2π / 3 at its centre is
The distance of the point (1,2) from the radical axis of the circles x2 + y2 +6x - 16 = 0 and x2 + y2 -2x + 6y = 0 is
Let f(x) be a twice-differentiable function and f''(0) = 2. Then evaluate.

The minimum value of f(x) = ∣3 - x∣ + ∣2 + x∣ + ∣5 - x∣ is:
If m is the slope of common tangent of y = x2 – x + 1 & y = x2 – 3x + 1, then |m| is
The volume of a tetrahedron DABC is 9 cubic units. If ∠ACB = π/6 and 2AD + AC + BC = 18, then the length AD is
If expression x + 1/x2 (x > 0) attains its minimum value at x = α, then α3 is