JEE Main Maths Test- 12 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Maths Test- 12
If z is any complex number satisfying |z–1|=1, then which of the following is correct ?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
If (a ib)(c id)(e if)(g ih) = A iB, then (a2+b2) x (c2+d2) (e2+f2)(g2+h2) is equal to
In how many ways 7 men and 7 women can be seated around a round table such that no two women can sit together ?
A lady gives a dinner party to six guests. The number of ways in which they may be selected from among ten friends, if two of the friends will not attend the party together is
How many numbers less than 40,000 can be formed from the digits 1,2,3,4,5 where repetition is not allowed ?
The sum of the digits at the unit place of all the numbers formed with the help of 3,4,5,6 taken all at a time is
The letters of the word RANDOM are written in all possible orders and these words are written out as in dictionary. Then the rank of the word RANDOM is
Number of divisors of the form 4n+2 of the integer 240 is
If x = a b,y = aω + bω, z = aω2 + bω then xyz is equal to
The smallest positive number n for with (1 + i)2n = (1– i)2n is
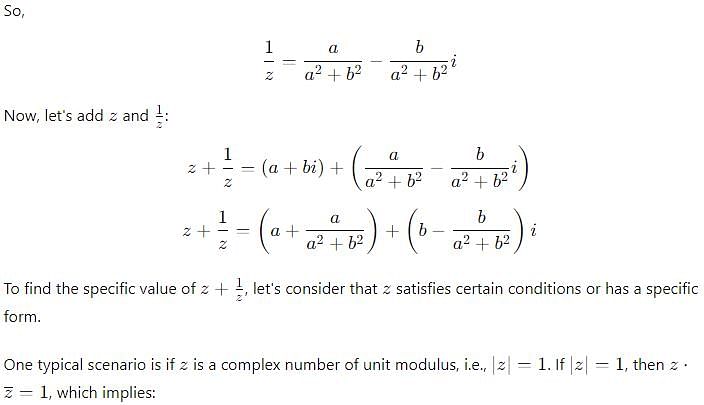
If z is a complex number such that z ≠ 0 and Re(z) =0, then



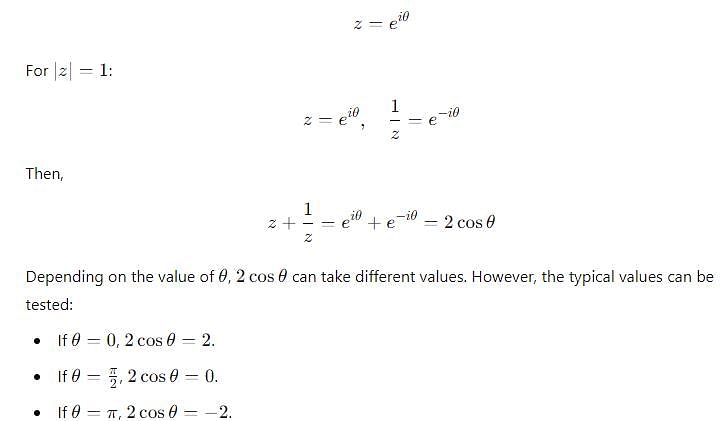



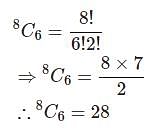
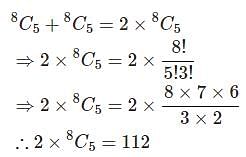
 Hence there are four such numbers.
Hence there are four such numbers.














