Atomic Structure, Quantum Chemistry & Physical Spectroscopy - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Atomic Structure, Quantum Chemistry & Physical Spectroscopy
Which of the following is true for the radial part of the H atom wave function Rn, l (r) (n-principal quantum number and l-azimuthal quantum number) and the nodes associated with them:
The bond that gives the most intense band in the infrared spectrum for its stretching vibration is:
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The nuclear g-factors of 1H and 14N are 5.6 and 0.40 respectively. If the magnetic field in an NMR spectrometer is set such that the proton resonates at 700 MHz, the 14N nucleus would resonate at:
The ionization energy of H atom in its ground state is approximately 13.6 eV. The potential energy of He+, in its ground state is approximately:
In NMR spectroscopy, the product of the nuclear ‘g’ factor (gN), the nuclear magneton βN and the magnetic field strength (B0) gives the:
In the Bohr’s model of hydrogen-like atom the force between the nucleus and the electron is modified as 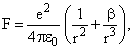 where β is a constant. For this atom, the radius of the nth orbit in terms of the Bohr radius
where β is a constant. For this atom, the radius of the nth orbit in terms of the Bohr radius 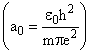 is:
is:
In H-atom, if ‘x’ the radius of this Bohr-orbit, de Broglie wavelength of an e– in 3rd orbit is:
The most populated rotational state for HCl (B = 8.5 cm–1) at 300 K is:
The rotational Raman spectrum of 19F2 shows a series of stokes lines at 19230.769 cm–1, 19227.238 cm–1 and 19223.707 cm–1. The rotational constant for 19F, in GHz is:
The molecule with the smallest rotational constant (in the microwave spectrum) among the following is:
Which of the following radial distribution graphs correspond to l = 2 for H atom for the least value of ‘n’ which l = 2 is allowed?
A plot of the kinetic energy (1/2)(mu2) of ejected electrons as a function of the frequency  of incident radiation for four alkali metals (M1, M2, M3, M4) is given below:
of incident radiation for four alkali metals (M1, M2, M3, M4) is given below:
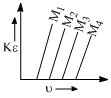
The alkali metals M1, M2, M3, M4 are respectively:
The frequency  of certain line of the Lyman series of the atomic spectrum of hydrogen satisfies the following conditions:
of certain line of the Lyman series of the atomic spectrum of hydrogen satisfies the following conditions:
(I) It is the sum of frequencies of another Lyman line and a Balmer line
(II) It is the sum of frequencies of a certain Lyman line, a Balmer line and a Paschen line.
(III) It is the sum of the frequencies of a Lyman line, and a Paschen line but no Brackett line.
To what transition does ν correspond?
Which of the following graphs of radial part of wave function (ψ) versus distance from nucleus is not correctly labeled?
The variation of de-Broglie wavelength (l) with the potential (λ) which an electron is accelerated from rest is represented by which one of the following?
In the vibrational spectrum of CO2, the number of fundamental vibrational modes common in both infrared and Raman are:
The difference between nth and (n + 1)th Bohr’s radius of H atom is equal to its (n –1)th Bohr’s radius the value of n is:
The electronic configuration of 46Pd is:
IE1 for 1H2 and IE1 for 1H1 are related as:
The electron in the H-atom undergoes transition from higher orbitals to orbital of radius 211.6 pm. This transition is associated with:
If the shortest wavelength in Lyman series of H-atom is A, then the longest wavelength in Paschen series of He+ is:
A hydrogen atom makes a transition from n = 2 to n = 1 and emits a photon this strikes a doubly ionized lithium atom in excited state and completely removes the orbiting electron. The least quantum number for the excited state of the ion for the process is:
Which of the following pairs can form correct set of isosters ?
The maximum velocity of the photoelectrons emitted from the surface is v when light of frequency is falls on a meal surface. If the incident frequency is increased to 3n, the maximum velocity of the ejected photoelectrons will be:
De-Broglie wavelength of an electron accelerated by a voltage of 50 V is close to
(1 eV = 1.6 × 10–19 J, me = 9.1 × 10–31 kg, h = 6.6 × 10–34 Js):
If the principal quantum number n = 6, the correct sequence of filling of electrons will be:
Ionization energy of gaseous Na atoms is 495.5 kJ mol–1. The lowest possible frequency of light that ionizes a sodium atom is (h = 6.626 × 10–34 Js, NA = 6.022 × 1023 mol–1)
Which of the following spectroscopic techniques will be useful to distinguish between M-SCN and
M-NCS binding modes?
In which of the following molecular properties the energy is not quantized:
The radii of maximum probability for 3s, 3p and 3d electrons are in the order:

















