(05-01-2018) Electrochemistry, Conductance & Solid State - IIT JAM MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - (05-01-2018) Electrochemistry, Conductance & Solid State
An electric current of 0.965 ampere is passed for 2000 seconds through a solution containing [Cu(CH3CN)4]+ and metallic copper is deposited at the cathode. The amount of Cu deposited is:
The equivalent conductance of M/32 solution of a weak monobasic acid is 8.0 mhos cm2 and at infinite dilution is 400 mhos cm2. The dissociation constant of this acid is
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
A crystal is made up of atoms X, Y and Z. Atoms X are in FCC packing. Y occupies all octahedral voids and Z occupies all tetrahedral voids. If all the atoms along two body diagonals are removed, the ratio of sum of effective number of atoms of Y and Z to the effective number of atoms of X is a:1, what is the value of “a”?
Scandium oxide, Sc2O3, crystallizes with the oxide ions in a closest packed array with the scandium ions in octahedral holes. What fraction of the octahedral holes are filled?
In diamond, the lattice is FCC with C atoms occupying lattice points as well as some of the voids. Which of the following statement(s) is correct about the diamond structure?
(I) In the diamond lattice, half of the tetrahedral voids are occupied
(II) Percentage space occupied (packing efficiency) is 74%
(III) In the diamond lattice all octahedral voids are occupied
Sodium crystallizes in a FCC lattice at certain temperature. The edge length (a) is 5.2 Å. The fifth nearest neighbor distance in FCC lattice is:
An atomic solid has hexagonal arrangement of unit cell with height of hexagonal (in close packed arrangement) as “h”. The radius of atom in terms of height is:
Gold crystallizes in a FCC lattice if the edge length is “a”. The closest distance between the gold atom and an impurity atom if it occupies an octahedral void without any change in volume of the unit cell is:
Calcium has a face centered cubic lattice and radius of calcium atom is 195.6 pm. The number of Ca atoms present on surfaces of a mm3 block of calcium metal assuming that atoms are in the closest packing is:
A uniform cylindrical, polymer molecule crystallizes in BCC array. The packing fraction of this polymer in solid state assuming that molecules are in their closest contact is:
In a face centered unit cell with all positions occupied by A atoms, the body centered octahedral hole in it is occupied by an atom B of an appropriate size. The void space per unit volume of unit cell for such crystal is:
A compound made of particles A, B and C forms ccp lattice. In the lattice, ions A occupy the lattice points and ions B and C occupy the alternate tetrahedral voids. If all the ions along one of the body diagonals are removed, then formula of the compound is:
Volume occupied by single CsCl ion pair in a crystal is 7.014 × 10–23 cm3. The smallest
Cs—Cs internuclear distance is equal to length of the side of the cube corresponding to volume of one CsCl ion pair. The smallest Cs to Cs internuclear distance is nearly:
Match axial parameters given in List-I with crystal systems given in List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
List-I (Axial parameters) List-II (Crystal system)
(P) a = b = c, α = β = γ ≠ 90° 1. Orthorhombic
(Q) a ≠ b ≠ c, α = γ = 90° = β 2. Triclinic
(R) a ≠ b ≠ c, α ≠ β ≠ γ ≠ 90° 3. Monoclinic
(S) a ≠ b ≠ c, α = β = γ = 90° 4. Rhombohedral
For the following cell at 298 K,
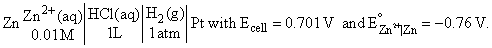
Which of the following amounts of NaOH (equivalent weight = 40) will just make the pH of cathodic compartment to be equal to 7.0
The conductivity of 0.01 M HA is 3.8 × 10–5 Ω–1cm–1 and the conductivity of solution formed by mixing 100 cm3 of 0.01 M HA and 1 cm3 of 1M NaOH is 80.0 × 10–5 Ω–1cm–1. Calculate
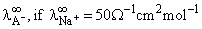
Consider the four different cells

The correct option for solubility product for all the four cases is (by considering all cells are in equilibrium stage)
The distance between two successive (110) planes in a simple cubic lattice with lattice parameter ‘a’ is:
Which of following cell can produce more electrical work?
Electrolysis is carried out in three cells:
(A) –1.0 M CuSO4, Pt electrodes;
(B) –1.0 M CuSO4, Copper electrodes;
(C) –1.0 M KCl, Pt electrodes.
If volume of electrolytic solution is maintained constant in each of the cells, which is correct set of pH changes in (A), (B) and (C) cells respectively?
A silver wire dipped in 0.1 M HCl solution saturated with AgCl develops a potential of –0.25 V. If 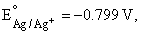 the Ksp of AgCl in pure water will be
the Ksp of AgCl in pure water will be
The X at 1 atm is bubbled through a solution containing a mixture of 1 MY– and 1 MZ– at 25°C. If the order of reduction potential is Z < Y > X, then:
Electrochemical equivalent of an element is
The standard reduction potential at 298 K for the following half cells are given:
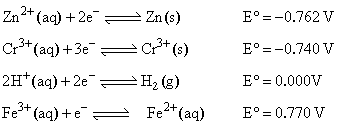
Which is the strongest reducing agent:
The correct order of equivalent conductance at infinite dilution of LiCl, and KCl is:
During electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate, 2.4 L of oxygen at STP was liberated at anode. The volume of hydrogen at STP, liberated at cathode would be:
For the electrochemical cell, M | M+ || X– | X, 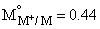 and
and 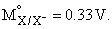 From this data we can deduce that:
From this data we can deduce that:
At 25° the specific conductivity of pure water is 5.5 × 10–8 mho cm–1. The ionic conductance of H+ and OH– ions at this temperature are 349.8 and 198.5 mho cm2 respectively. The ionic product of water is:
Specific conductance of 0.01 M KCl solution is x ohm–1 cm–1. When conductivity cell is filled with 0.01 M KCl the conductance observed is y ohm–1. When the same cell is filled with 0.01 M H2SO4, the observed conductance was z ohm–1 cm–1. The specific conductance of 0.01 M H2SO4 is:
An aqueous solution containing 0.01 M FeCl3 and 0.06 M HClO4 has the same ionic strength as a solution of:

















