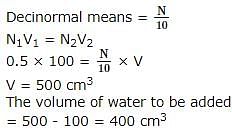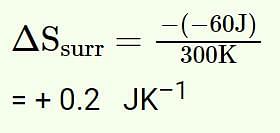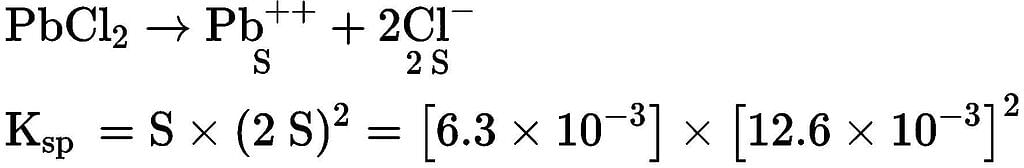BITSAT Chemistry Test - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - BITSAT Chemistry Test - 2
A compound X with molecular formula C₃H₈O can be oxidized to a compound Y with the molecular formula C₃H₆O₂. X is most likely to be a
Which of the following reagents cannot be used to distinguish between hexanal and 2-hexanone?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Elimination of bromine from 2- bromobutane results in the formation of
The volume of water to be added to 100 cm3 of 0.5N H2SO4 to get decinormal concentration is
The order of decreasing stability of the carbanions (CH₃)₃C-(I) ; (CH₃)₂CH-(II) ; CH₃CH₂-(III) ; C₆H₅CH₂-(IV) is
'The atomic orbitals are progressively filled in the order of increasing energy'. This statement is known as
60 J of heat flows out from 600 g of water at 30oC into surroundings at 25oC.The net entropy change in universe is approximately
N2O is isoelectronic with CO2 and N 3 − , which is the structure of N2O?
Just before attaining equilibrium by a reversible reaction, it is found that
For the square planar complex [M(a) (b) (c) (d)] (where M = central metal and a,b,c and d are monodentate ligands), the number of possible geometrical isomers are
Which of the following gas is evolved on heating ammonium dichromate?
For standard reduction potentials of three metals A, B and C are + 0.5 V, -3.0 V and -1.2 v respectively. The reducing powers of these metals are
When n-propyl iodide is heated with alcoholic KOH,one of the products is
If the solubility of PbCl₂ at 25oC is 6.3 x 10⁻3 mole/litre, its solubility product at that temperature is
Treatment of ammonia with excess of ethyl chloride with yield
The dihedral angle HCH in staggered conformation of C₂H₆ is
What are the products formed when ammonia reacts with excess chlorine?
Which of the following types of forces bind together the carbon atoms in diamond?