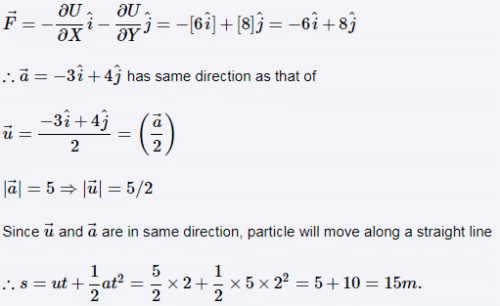JEE Main Mock Test 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Mock Test 1
In the figure shown the acceleration of A is,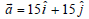 then the acceleration of B is: (A remains in contact with B)
then the acceleration of B is: (A remains in contact with B)
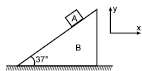
A transparent cylinder has its right half polished so as to act as a mirror. A paraxial light ray is incident from left, that is parallel to principal axis, exits parallel to the incident ray as shown.The refractive index n of the material of the cylinder is :
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
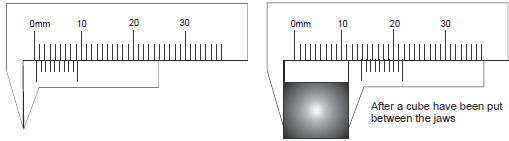
Find the thickness of the cubical object using the defective vernier calliper main scale has mm marks and 10 divisions of vernier scale coincide with 9 divisions of main scale.
A collar ‘B’ of mass 2 kg is constrained to move along a horizontal smooth and fixed circular track of radius 5 m. The spring lying in the plane of the circular track and having spring constant 200 N/m is undeformed when the collar is at ‘A’. If the collar B starts from rest, the normal reaction exerted by the track on the collar when it passes through ‘A’ is :
Two elastic rods are joined between fixed supports as shown in the figure. Condition for no change in the lengths of individual rods with the increase of temperature.( α1, α2 = linear expansion co-efficient A1, A2 = Area of rods y1, y2 = Young modulus )
A light ray gets reflected from a pair of mutually mirrors, not necessarily along axes. The intersection point of mirrors is at origin. The incident light is along y = x + 2. If the light ray strikes both mirrors in succession, then it may get reflected finally along the line :
The graph shown gives the temperature along an x axis that extends directly through a wall consisting of three layers A, B and C. The air temperature on one side of the wall is 150°C and on the other side is 80°C. Thermal conduction through the wall is steady. Out of the three layers A, B and C, thermal conductivity is greatest of the layer
When a metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic light of wavelength λ, the stopping potential is 5 V0. When the same surface is illuminated with light of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is V0. Then the work function of the metallic surface is :
A Young’s double slit experiment is conducted in water (μ1) as shown in the figure, and a glass plate of thickness t and refractive index μ2 is placed in the path of S2. The magnitude of the phase difference at O is : (Assume that ‘λ’ is the wavelength of light in air). O is symmetrical w.r.t. S1 and S2
The ratio of r.m.s. speed to the r.ms. angular speed of a diatomic gas at certain temperature is: (assume m = mass of one molecule, M = molecular mass, I = moment of inertia of the molecules)
Block ‘ A ‘ is hanging from a vertical spring and is at rest. Block ‘ B ‘ strikes the block ‘A’ with velocity ‘ v ‘ and sticks to it. Then the value of ‘ v ‘ for which the spring just attains natural length is:
Radii of curvature of a concavo-convex lens (refractive index = 1.5) are 40 cm (concave side) and 20 cm (convex side) as shown. The convex side is silvered. The distance x on the principal axis where an object is placed so that its image is created on the object itself, is equal to :
The readings of a constant potential difference is noted four times by a student. The student averages these readings but does not take into account the zero error of the voltmeter. The average measurement of the potential difference is
In the figure shown the potential energy U of a particle is plotted against its position ' x ' from origin. Then which of the following statement is correct. A particle at :
In the figure (i) an extensible string is fixed at one end and the other end is pulled by a tension T. In figure (ii) another identical string is pulled by tension 'T' at both the ends. The ratio of elongation in equilibrium of string in (i) to the elongation of string in (ii) is
A linear object AB is placed along the axis of a concave mirror. The object is moving towards the mirror with speed V. The speed of the image of the point A is 4 V and the speed of the image of B is also 4V. If centre of the line AB is at a distance L from the mirror then length of the object AB will be
The wall of a house is made of two different materials of same thickness. The temperature of the outer wall is T2 and that of inner wall is T1 < T2. The temperature variation inside the wall as shown in the figure. Then :
In a photoelectric experiment, with light of wavelength λ, the fastest electron has speed v. If the exciting wavelength is changed to 3λ/4 the speed of the fastest emitted electron will become
Two coherent light sources P and Q each of wavelength λ are separated by a distance 3λ as shown . The maximum number of minima formed on line AB which runs from – ∞ to + ∞ is :
The average rotational kinetic energy of hydrogen molecule at a temperature T is E. The average translational kinetic energy of helium at same temperature will be :
A system consists of two point masses, A and B of masses 1 kg and 2 kg respectively. At an instant the kinetic energy of A with respect to the centre of mass is 2 Joules and the velocity of centre of mass is 2 m/s. The kinetic energy of the system at this instant is :
A convex lens is cut into two parts inaaz different ways that are arranged in four manners, as shown. Which arrangement will give maximum optical power ?
A vernier calipers which is used to measure length of a cylinder has 1mm marks on the main scale. It has 10 equal division on the vernier scale which match with 8 marks of main scale. If main scale reading is 4 and vernier reading is 5 then the length of cylinder is 1.25 N × 10-3 m then the value of N is :
The potential energy (in SI units) of a particle of mass 2 kg in a conservative field is U = 6x – 8y. If the initial velocity of the particle is then the total distance travelled by the particle in first two seconds is
The elongation in a metallic rod hinged at one end and rotating in a horizontal plane becomes four times of the initial value. The angular velocity of rotation becomes :
A triangular medium has varying refracting index n = n0 + ax, where x is the distance (in cm) along x–axis from origin and n0 = 4/3 . A ray is incident normally on face OA at the mid–point of OA. The range of a so that light does not escape through face AB when it falls first time on the face AB (O = 4 cm, OB = 3 cm and AB = 5 cm) : (Surrounding medium is air)
A tugsten bulb radiates 2 W of energy. The filament of the bulb has surface area 2 mm2 and an emissivity of 0.9.The temperature of the bulb is: (Stefan’s Constant σ = 5.6 × 10-8 S.I. units)
In an x - ray tube, if the accelerating potential difference is changed, then:
In a calm pond, water (μ = 4/3) is filled uniformly upto 1 m depth.The maximum wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation incident normally from air onto the water surface, that will be strongly reflected is:[ assume: nground > nwater ]
In an adiabatic expansion the product of pressure and volume :