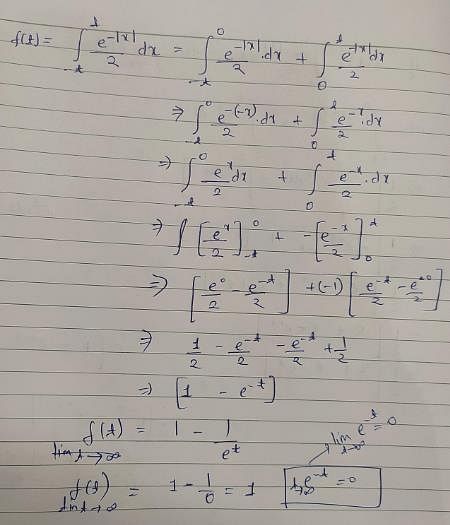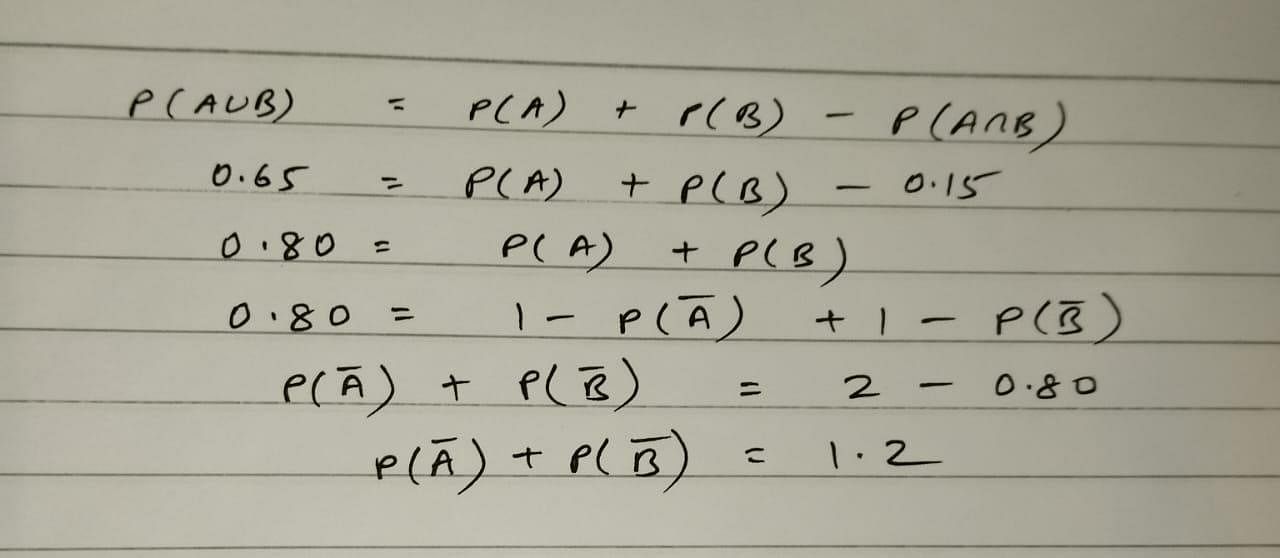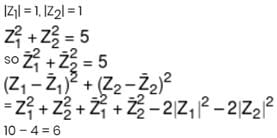JEE Main Maths Mock Test- 2 - JEE MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Main Maths Mock Test- 2
The orthocentre of the traingle whose vertices are (5, -2), (-1, 2) and (1,4) is
If the equation [(k(x+1)2/3)]+[(y+2)2/4]=1 represents a circle, then k=
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The eccentric angles of the extremities of the latus-rectum intersecting positive x-axis of the ellipse ((x2/a2) + (y2/b2) = 1) are given by
If N N+ denotes the set of all positive integers and if f : NN+ → N is defined by f(n) = the sum of positive divisors of (n) then f (2k . 3), where k is a positive integer is
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion (A): Angle between is acute angle
Reason (R): If is acute then
is obtuse then
The point on the curve y = x2 which is nearest to (3, 0) is
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion (A): are non zero vectors then
is a vector perpendicular to all the vectors a → , b → , c →
Reason (R): are perpendicular to both
If i2 = -1, then the sum i + i2 + i3 + ..... upto 1000 terms is equal to
A parallelogram is cut by two sets of m lines parallel to the sides, the number of parallelogram thus formed is
The probability that a leap year will have exactly 52 Tuesdays is
Product of the real roots of the equation t2x2 + ∣x∣ + 9 = 0
If A.M. between two numbers is 5 and their G.M. is 4, then their H.M. is
If the coefficient of correlation between x and y is 0.28, covariance between x and y is 7.6, and the variance of x is 9, then the standard deviation of the y series is
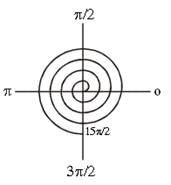
The equation line passing through the point P(1,2) whose portion cut by axes is bisected at P, is
If 2 tan2x – 5 sec x is equal to 1 for exactly 7 distinct values of X ∈ [0, nπ/2], n ∈ N, then the greatest value of n is
If the mean deviation of the number 1, 1 + d, ... , 1 + 8d from their mean is 205, then d is equal to
The number of 5-digit numbers of the form xyzyx in which x < y is :-
If z1 and z2 are two unimodular complex numbers that satisfy z12 + z22 = 5, then 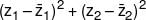 is equal to -
is equal to -
The AM of 9 term is 15. If one more term is added to this series, then the A.M. becomes 16. The value of added term is :