Test: Electronic Devices & Circuits - 3 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Electronic Devices & Circuits - 3
As per Einstein's equation, the velocity of emitted electron in photoelectric emission is given by the equation
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
For an P-channel enhancement type MOSFET determine the drain current if K = 0.278 x 10-3A/V2, VGS = -4V, VT = -2V, Voltage equivalent at 27�C = 26 mV.
The skin depth of copper is found to be 66 mm at 1 MHz at a certain temperature. At the same temperature and at 2 MHz, the skin depth would be approximately
When p-n junction is reverse biased the holes in p material move towards the junction and electrons in n material move away from the junction.
A semiconductor diode is biased in forward direction and carrying current I. The current due to holes in p material is
Between which regions does BJT act like switch?
Assertion (A): When a photoconductive device is exposed to light, its bulk resistance increases.
Reason (R): When exposed to light, electron hole pairs are generated in the photoconductive device.
Which of the following elements act as donor impurities?
- Gold
- Phosphorus
- Boron
- Antimony
- Arsenic
- Indium
Assertion (A): When VDS is more than rated value the drain current in a JFET is very high.
Reason (R): When VDS is more than rated value, avalanche breakdown occurs.
If ib is plate current, eb is plate voltage and ec is grid voltage the v-i curve of a vacuum triode is
ib = 0.003 (eb + kec)n. Typical values of k and n are
In which material do conduction and valence bands overlap
For a photoconductor with equal electron and hole mobilities and perfect ohmic contacts at the ends, an increase in illumination results in
Discrete transistors T1 and T2 having maximum collector current rating of 0.75 amp are connected in parallel as shown in the figure, this combination is treated as a single transistor to carry a total current of 1 ampere, when biased with self bias circuit. When the circuit is switched on, T1 draws 0.55 amps and T2 draws 0.45 amps. If the supply is kept on continuously, ultimately it is very likely that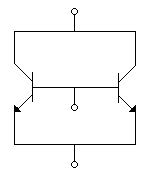
The number of p-n junctions in a semiconductor diode are
Assertion (A): A high junction temperature may destroy a diode.
Reason (R): As temperature increases the reverse saturation current increases.
When a diode is not conducting, its bias is
The SCR would be turned OFF by voltage reversal of applied anode-cathode ac supply of frequency of
The number of valence electrons in a donor atom is
An electron rises through a voltage of 100 V. The energy acquired by it will be
Measurement of hall coefficient enables the determination of


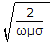
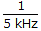 = 200 μsec.
= 200 μsec.














