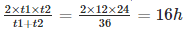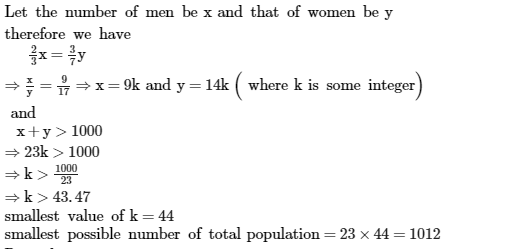Linear Equation In Two Variables - Olympiad Level MCQ, Class 10 Mathematics - Class 10 MCQ
23 Questions MCQ Test - Linear Equation In Two Variables - Olympiad Level MCQ, Class 10 Mathematics
The number of solutions of the equation 2x + y = 40, where both x and y are positive integers and x ≤ y is :
A confused bank teller transposed the rupees and paise when he cashed a cheque for Mansi, giving her rupees instead of paise and paise instead of rupees. After buying a toffee for 50 paise, Mansi noticed that she was left with exactly three times as much as the amount on the cheque. Which of the following is a valid statement about the cheque amount?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
John inherited $25000 and invested part of it in a money market account, part in municipal bonds, and part in a mutual fund. After one year, he received a total of $ 1620 in simple interest from the three investments. The money market paid 6% annually, the bonds paid 7% annually, and the mutual funds paid 8% annually. There was $ 6000 more invested in the bonds than the mutual funds. The amount John invested in each category are in the ratio:
Which one of the following conditions must p,q and r satisfy so that the following system of linear simultaneous
equations has atleast one solution, such that p + q + r = 0?
x + 2y – 3z = p ; 2x + 6y – 11z = q ; x – 2y + 7z = r
If x and y are integers, then the equation 5x + 19y = 64 has :
Rozly can row downstream 20km in 2 hours, and the upstream 4km in 2 hours. What will be the speed of rowing in still water?
Study the question and statements given below : Decide whether any information provided in the statement(s)
is rebundant and/or can be dispensed with, to answer it.If 7 is added to numerator and denominator each of fraction a/b, will the new fraction be less than the original one? (Assume both a and b to be positive)
Statement-I : a = 73, b = 103
Statement-II : The average of a and b is less than b.
Statement-III : a – 5 is greater than b – 5.
A cyclist drove 1 km, with the wind in his back, in 3 min and drove the same way back, against the wind in 4 min. If we assume that the cyclist always puts constant force on the pedals, how much time would it take to drive 1 km without wind?
A person buys 18 local tickets for Rs. 110. Each first class ticket costs Rs. 10 and each second class ticket costs Rs. 3. What will another lot of 18 tickets in which the number of first class and second class tickets are interchanged cost?
Rajesh walks to and fro to a shopping mall. He spends 30 min. shopping. If he walks at a speed of 10 km/h, he returns to home at 19:00h. If he walks at 15 km/h, he returns at 18:30 h. How fast must he walk in order to return home at 18:15 h?
A single reservoir supplies the petrol to the whole city, while the reservoir is fed by a single pipeline filling the reservoir with the stream of uniform volume. When the reservoir is full and if 40000 litres of petrol is used daily, the supply fails in 90 days. If 32000 litres of petrol is used daily, the supply fails in 60 days. How much petrol can be used daily without the supply ever failing?
Two horses start trotting towards each other, one from A to B and another from B to A. They cross each other
after one hour and the first horse reaches B, 5/6 hours before the second horse reaches A. If the distance
between A and B is 50 km. What is the speed of the slower horse?
A man row downstream at 12 km/h and upstream at 8 km/h. What is the speed of man in still water?
A motor boat takes 12 hours to go downstream and it takes 24 hours to return the same distance. What is the time taken by boat in still water?
Equation yx2 + xy2 = 2xy : x, y = 0 is
Sum of two integers is 88. If the greater is divided by the smaller, the quotient is 5 and the remainder is 10. The greater integer is :
The length of the sides of a triangle are 3x + 2y, 4x + y and 3(x + 1) +
(y – 1). If the triangle is equilateral, then its side is
The largest angle of a triangle is twice the sum of the other two. The smaller angle is one fourth of the largest.
The largest angle is :
In town, 2/3 of men are married to 3/7 of the women. In the town total population is more than 1000. If all
marriages happen within the town. The smallest possible number of total population is (assume there are only
adults in the town) :
The solution of the equations : , 7x + 8y + 5z = 62 is :
Customers are asked to stand in the lines. If one customer is extra in a line, then there would be two less lines. If one customer is less in line, there would be three more lines. Find the number of students in the class.
The solution of the equations : = 110,
= 132,
=
is :
Four men earn as much in a day as 7 women. 1 woman earns as much as 2 boys. If 6 men, 10 women and 14 boys work together for 8 days to earn Rs. 2200, then what will be the earning of 8 men and 6 women working together for 10 days?