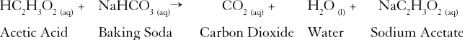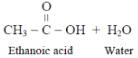NTSE Test: Carbon & Its Compounds - SSS 1 MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - NTSE Test: Carbon & Its Compounds
Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
Which family of organic compounds does not contain any multiple bonds?
Which of the following is not a saturated hydrocarbon?
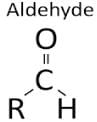
The functional group in methanol and methanal respectively are :
In graphite carbon atoms are arranged in layers of
Graphite is a soft lubricant extremely difficult to melt. The reason for this anomalous behaviour is that graphite.
Which of the following represent the correct order of unsaturation?
The reaction 2C2H5OH + 2Na → 2C2H5ONa + H2 suggests that ethanol is
Which of the following substance is added to denature ethanol?
Which of the following substances cannot be used to distinguish ethanol from ethanoic acid?
Detergents are sodium and potassium salts of long chain
Which of the following salts when dissolved in water produce hard water?
Which class of organic compounds give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution ?
Carboxylic acids are obtained from alcohols by -