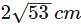All Exams >
CTET & State TET >
Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Mensuration for CTET & State TET Exam
Find the perimeter of the a square with side 4cm.- a)16 cm
- b)12 cm
- c)10 cm
- d)8 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the perimeter of the a square with side 4cm.
a)
16 cm
b)
12 cm
c)
10 cm
d)
8 cm

|
Sreesha Phalod answered |
Sol. perimeter of square=4* sides
=4*4 (sides is 4)
=16.
=4*4 (sides is 4)
=16.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In a right circular cylinder, the line segments joining the centre of circular faces is ________ to the base- a)parallel
- b)rectangular
- c)circular
- d)perpendicular
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a right circular cylinder, the line segments joining the centre of circular faces is ________ to the base
a)
parallel
b)
rectangular
c)
circular
d)
perpendicular
|
|
Anand Iyer answered |
Explanation:
A right circular cylinder is a three-dimensional solid object that has two circular bases parallel to each other, and the lateral surface is perpendicular to the circular bases. The axis joining the centers of the circular faces is called the height of the cylinder.
In a right circular cylinder, the line segments joining the center of the circular faces are called the axis of the cylinder. The axis of the cylinder is perpendicular to the base. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - perpendicular.
To understand this concept more clearly, let's look at the following points:
- A right circular cylinder has two circular bases that are parallel to each other. The bases are circles, and they lie in parallel planes.
- The lateral surface of the cylinder is a curved surface that connects the two circular bases. It forms a right angle with the bases.
- The axis of the cylinder is the line segment that joins the center of the circular bases. It passes through the center of the cylinder.
- Since the bases are parallel to each other, the axis of the cylinder is perpendicular to the bases. It is easy to see this if we draw a diagram of a cylinder.
Therefore, we can conclude that in a right circular cylinder, the line segments joining the center of circular faces is perpendicular to the base.
A right circular cylinder is a three-dimensional solid object that has two circular bases parallel to each other, and the lateral surface is perpendicular to the circular bases. The axis joining the centers of the circular faces is called the height of the cylinder.
In a right circular cylinder, the line segments joining the center of the circular faces are called the axis of the cylinder. The axis of the cylinder is perpendicular to the base. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - perpendicular.
To understand this concept more clearly, let's look at the following points:
- A right circular cylinder has two circular bases that are parallel to each other. The bases are circles, and they lie in parallel planes.
- The lateral surface of the cylinder is a curved surface that connects the two circular bases. It forms a right angle with the bases.
- The axis of the cylinder is the line segment that joins the center of the circular bases. It passes through the center of the cylinder.
- Since the bases are parallel to each other, the axis of the cylinder is perpendicular to the bases. It is easy to see this if we draw a diagram of a cylinder.
Therefore, we can conclude that in a right circular cylinder, the line segments joining the center of circular faces is perpendicular to the base.
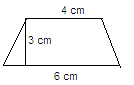
If the parallel sides of a parallelogram are 2 cm apart and their sum is 10 cm then its area is:- a)20 cm2
- b)5 cm2
- c)10 cm2
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the parallel sides of a parallelogram are 2 cm apart and their sum is 10 cm then its area is:
a)
20 cm2
b)
5 cm2
c)
10 cm2
d)
none of these
|
|
Shruti Das answered |
Solution:
Given, the distance between the parallel sides of a parallelogram is 2 cm and their sum is 10 cm.
Let the length of the longer parallel side be x cm. Then, the length of the shorter parallel side is (10 - x) cm.
Area of the parallelogram = base x height
Here, base = length of the shorter parallel side = (10 - x) cm
Height = distance between the parallel sides = 2 cm
So, Area of the parallelogram = (10 - x) x 2 cm²
= 20 - 2x cm²
Therefore, the area of the parallelogram is 20 - 2x cm².
Option (d) none of these is the correct answer as the value of x is not given, so we cannot find the exact area of the parallelogram.
Given, the distance between the parallel sides of a parallelogram is 2 cm and their sum is 10 cm.
Let the length of the longer parallel side be x cm. Then, the length of the shorter parallel side is (10 - x) cm.
Area of the parallelogram = base x height
Here, base = length of the shorter parallel side = (10 - x) cm
Height = distance between the parallel sides = 2 cm
So, Area of the parallelogram = (10 - x) x 2 cm²
= 20 - 2x cm²
Therefore, the area of the parallelogram is 20 - 2x cm².
Option (d) none of these is the correct answer as the value of x is not given, so we cannot find the exact area of the parallelogram.
Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, width is 3 cm and height is 5 cm. - a)135 cm3
- b)125 cm3
- c)120 cm3
- d)130 cm3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, width is 3 cm and height is 5 cm.
a)
135 cm3
b)
125 cm3
c)
120 cm3
d)
130 cm3

|
R.k. Verma answered |
Volume of cubiod =l×b×h
=8×3×5
=120cm3 .
=8×3×5
=120cm3 .
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for chapter Mensuration, Class 8, Mathematics . You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic. Q.Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, breadth 6 cm and height 3.5 cm. - a)215 cm3
- b)172 cm3
- c)150 cm3
- d)168 cm3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with solutions are available for Practice, which would help you prepare for chapter Mensuration, Class 8, Mathematics . You can practice these practice quizzes as per your speed and improvise the topic.
Q.
Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, breadth 6 cm and height 3.5 cm.
a)
215 cm3
b)
172 cm3
c)
150 cm3
d)
168 cm3
|
|
Ankita Shah answered |
Given,
Length (l) = 8 cm
Breadth (b) = 6 cm
Height (h) = 3.5 cm
We know that the volume of a cuboid is given by the formula:
Volume = length × breadth × height
Substituting the given values, we get:
Volume = 8 cm × 6 cm × 3.5 cm
Volume = 168 cm³
Therefore, the volume of the given cuboid is 168 cm³.
Hence, the correct option is (d) 168 cm³.
Length (l) = 8 cm
Breadth (b) = 6 cm
Height (h) = 3.5 cm
We know that the volume of a cuboid is given by the formula:
Volume = length × breadth × height
Substituting the given values, we get:
Volume = 8 cm × 6 cm × 3.5 cm
Volume = 168 cm³
Therefore, the volume of the given cuboid is 168 cm³.
Hence, the correct option is (d) 168 cm³.
The quantity that a container holds is called its - a)surface area
- b)lateral surface area
- c)capacity
- d)volume
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The quantity that a container holds is called its
a)
surface area
b)
lateral surface area
c)
capacity
d)
volume
|
|
Prerna Mehta answered |
Explanation:
Capacity is defined as the maximum amount that a container can hold. It is the volume of the container, which is the space occupied by the container's contents. Capacity is usually measured in liters, gallons, or other units of volume.
For example, a water bottle with a capacity of 750 ml means that the bottle can hold up to 750 ml of water. Similarly, a fuel tank with a capacity of 50 liters means that the tank can hold up to 50 liters of fuel.
It is important to note that capacity is different from the weight of the container's contents. For example, a container with a capacity of 1 liter can hold 1 liter of water, which weighs about 1 kilogram. However, the same container can also hold 1 liter of feathers, which weighs significantly less than 1 kilogram.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - capacity, as it refers to the maximum amount that a container can hold.
Capacity is defined as the maximum amount that a container can hold. It is the volume of the container, which is the space occupied by the container's contents. Capacity is usually measured in liters, gallons, or other units of volume.
For example, a water bottle with a capacity of 750 ml means that the bottle can hold up to 750 ml of water. Similarly, a fuel tank with a capacity of 50 liters means that the tank can hold up to 50 liters of fuel.
It is important to note that capacity is different from the weight of the container's contents. For example, a container with a capacity of 1 liter can hold 1 liter of water, which weighs about 1 kilogram. However, the same container can also hold 1 liter of feathers, which weighs significantly less than 1 kilogram.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - capacity, as it refers to the maximum amount that a container can hold.
If the side of the cube is 2 m, then the surface area of the cube is - a)12 m2
- b)12 m
- c)24 m2
- d)24 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the side of the cube is 2 m, then the surface area of the cube is
a)
12 m2
b)
12 m
c)
24 m2
d)
24 m
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
Surface Area of a cube = 6 a²Then, a = 2 ( given), So, = 6(2)²= 6 × 4= 24m²So the correct option is {C} 24m².
Find the area of adjoining figure is

- a)1.54 cm2
- b)15.4 cm2
- c)7.7 cm2
- d)260 cm2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the area of adjoining figure is


a)
1.54 cm2
b)
15.4 cm2
c)
7.7 cm2
d)
260 cm2

|
Shraddha Yeole answered |
D)
reason=
diameter=2×radius
diameter =4cm
radius=2cm
area of circle= pie×radius²=
22/7×4=
12.57
as it is a semi-circle
area=area of full circle/2
=12.57/2=
6.28
reason=
diameter=2×radius
diameter =4cm
radius=2cm
area of circle= pie×radius²=
22/7×4=
12.57
as it is a semi-circle
area=area of full circle/2
=12.57/2=
6.28
Find the area of a triangle whose base is 4 cm and altitude is 6 cm.- a)10 cm2
- b)14 cm2
- c)16 cm2
- d)12 cm2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the area of a triangle whose base is 4 cm and altitude is 6 cm.
a)
10 cm2
b)
14 cm2
c)
16 cm2
d)
12 cm2
|
|
Kavya Saxena answered |
We know that area of triangle is equals to 1/2 base × altitude.
Here, base = 4 cm and altitude = 6 cm.
So, area = 1/2 × 4 × 6= 24 /2= 12 cm2.
Here, base = 4 cm and altitude = 6 cm.
So, area = 1/2 × 4 × 6= 24 /2= 12 cm2.
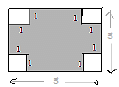
In fig., a square of side 5 cm, the area of shaded portion is
- a)25 cm2
- b)30 cm2
- c)21 cm2
- d)90 cm2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In fig., a square of side 5 cm, the area of shaded portion is

a)
25 cm2
b)
30 cm2
c)
21 cm2
d)
90 cm2
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
Area of square having sides 5 cm = 52 = 25 cm2
Area of smaller square having sides 1 cm = 12 = 1 cm2
Then area of 4 squares will be 4 cm2
Area of shaded portion will be = Area of square having sides 5 cm - area of 4 smaller squares (Unshaded portion)
Area of shaded portion = 25 cm2 - 4 cm2
Area of shaded portion = 21 cm2
Find the area of the given quadrilateral.
- a)45 cm3
- b)45 cm2
- c)45 cm
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the area of the given quadrilateral.
a)
45 cm3
b)
45 cm2
c)
45 cm
d)
None of these
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
Quad ABCD is made of two triangles ADC and ABC
so, area(ABCD) = area(ABC) + area(ADC)
= 4 x 12/2 + 3.5 x12/2
= 24 + 21
= 45 cm2
The formula for finding total surface area of cuboid is - a)2 (lb x bh x hl)
- b)2 (lb + bh + hl)
- c)2h (l + b)
- d)2 lb (bh + hl)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula for finding total surface area of cuboid is
a)
2 (lb x bh x hl)
b)
2 (lb + bh + hl)
c)
2h (l + b)
d)
2 lb (bh + hl)
|
|
Gopal Iyer answered |
Explanation:
A cuboid is a three-dimensional solid shape that has six rectangular faces. To find the total surface area of a cuboid, we need to find the area of each face and add them together.
Formula:
The formula for finding the total surface area of a cuboid is:
2(lb + bh + hl)
where l, b, and h are the length, width, and height of the cuboid.
Derivation:
The cuboid has six faces, and each face is a rectangle. The total surface area of the cuboid is the sum of the areas of all six faces. We can find the area of each face by multiplying its length and width.
- Area of the top and bottom faces = lb
- Area of the front and back faces = bh
- Area of the left and right faces = hl
Therefore, the total surface area of the cuboid is:
2(lb + bh + hl)
Example:
Let's take an example to understand this formula.
Suppose we have a cuboid with length l = 4 cm, width b = 3 cm, and height h = 5 cm.
Using the formula, we can find the total surface area of the cuboid as:
2(4x3 + 3x5 + 5x4) = 2(12 + 15 + 20) = 2(47) = 94 cm²
Therefore, the total surface area of the given cuboid is 94 cm².
Conclusion:
The formula for finding the total surface area of a cuboid is 2(lb + bh + hl). It is derived by finding the sum of the areas of all six faces of the cuboid. The formula can be used to find the total surface area of any cuboid, given its length, width, and height.
A cuboid is a three-dimensional solid shape that has six rectangular faces. To find the total surface area of a cuboid, we need to find the area of each face and add them together.
Formula:
The formula for finding the total surface area of a cuboid is:
2(lb + bh + hl)
where l, b, and h are the length, width, and height of the cuboid.
Derivation:
The cuboid has six faces, and each face is a rectangle. The total surface area of the cuboid is the sum of the areas of all six faces. We can find the area of each face by multiplying its length and width.
- Area of the top and bottom faces = lb
- Area of the front and back faces = bh
- Area of the left and right faces = hl
Therefore, the total surface area of the cuboid is:
2(lb + bh + hl)
Example:
Let's take an example to understand this formula.
Suppose we have a cuboid with length l = 4 cm, width b = 3 cm, and height h = 5 cm.
Using the formula, we can find the total surface area of the cuboid as:
2(4x3 + 3x5 + 5x4) = 2(12 + 15 + 20) = 2(47) = 94 cm²
Therefore, the total surface area of the given cuboid is 94 cm².
Conclusion:
The formula for finding the total surface area of a cuboid is 2(lb + bh + hl). It is derived by finding the sum of the areas of all six faces of the cuboid. The formula can be used to find the total surface area of any cuboid, given its length, width, and height.
The formula for volume of cube is - a)l3
- b)6 l2
- c)4 l3
- d)6 l3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula for volume of cube is
a)
l3
b)
6 l2
c)
4 l3
d)
6 l3

|
Tej Narayan answered |
Because it is
side × side × side = (side )^3
side × side × side = (side )^3
In the given figure find the area of the path.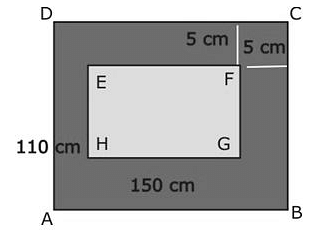
- a)2500 cm
- b)2500 cm2
- c)2500 cm3
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given figure find the area of the path.
a)
2500 cm
b)
2500 cm2
c)
2500 cm3
d)
none of these
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Area of Rectangle ABCD = 110*150 = 16500cm2
Area of rectangle EFGH = (150-10)(110-10) = 14000cm2
Area of path = 16500-14000 = 2500cm2
Area of rectangle EFGH = (150-10)(110-10) = 14000cm2
Area of path = 16500-14000 = 2500cm2
Find the side of a cube whose surface area is 2400 cm2.- a)15 cm
- b)20 cm
- c)10 cm
- d)25 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the side of a cube whose surface area is 2400 cm2.
a)
15 cm
b)
20 cm
c)
10 cm
d)
25 cm

|
Pronami Rajbongshi answered |
Surface area of Cube = 2400cm²
6l²=2400
l²=2400/6
l=√400
=√20²
=20
Proved.....
6l²=2400
l²=2400/6
l=√400
=√20²
=20
Proved.....
The formula for finding the surface area of cube is- a)3 (side)2
- b)4 (side)2
- c)5 (side)2
- d)6 (side)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula for finding the surface area of cube is
a)
3 (side)2
b)
4 (side)2
c)
5 (side)2
d)
6 (side)2
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
Total surface area of cube = 6a2
Curved surface area of cube = 4a2
Volume of cube = a2
The volume of cuboid of dimensions 4 cm, 2 cm and 3 cm is- a)24 cm3
- b)12 cm3
- c)24 cm2
- d)26 cm3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The volume of cuboid of dimensions 4 cm, 2 cm and 3 cm is
a)
24 cm3
b)
12 cm3
c)
24 cm2
d)
26 cm3

|
Maya Nambiar answered |
The volume of a cuboid is calculated by multiplying the length, width, and height of the cuboid. In this case, the length is 4 cm, the width is 2 cm, and the height is 3 cm. Therefore, the volume of the cuboid is 4 cm x 2 cm x 3 cm = 24 cm^3.
In the adjoining figure, area of quadrilateral ABCD will be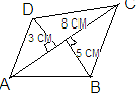
- a)12 cm2
- b)32 cm2
- c)20 cm2
- d)8 cm2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the adjoining figure, area of quadrilateral ABCD will be

a)
12 cm2
b)
32 cm2
c)
20 cm2
d)
8 cm2

|
Deepti Rawat answered |
Area of triangle ADC
Area of triangle= 1/2 ×b × h
Area. = 1/2 ×8×3
Area of ∆ADC = 12 square cm
Area of triangle ABC
Area of triangle=1/2×b×h
Area. = 1/2×8×5
Area of ∆ABC = 20square cm
Now,
Sum of Area of ∆(ADC+ABC). = Area of quadrilateral
Sum of Area of ∆( ADC+ABC ) = (12+20) sq. cm
= 32 sq. cm
If the length of edge of cube is 4 cm, its volume is- a)16 cm2
- b)64 cm3
- c)64 cm2
- d)16 cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the length of edge of cube is 4 cm, its volume is
a)
16 cm2
b)
64 cm3
c)
64 cm2
d)
16 cm3
|
|
Ayush Pillai answered |
Explanation:
A cube has all its sides equal and its volume can be found by multiplying the length of one side by itself three times. Therefore,
Volume of cube = (Length of one side)^3
Given, Length of one side = 4 cm
Volume of cube = (4 cm)^3 = 64 cm^3
Therefore, the correct answer is option B, which is 64 cm^3.
1 m3 is ______________ .- a)10 L
- b)100 L
- c)1000 L
- d)10000 L
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
1 m3 is ______________ .
a)
10 L
b)
100 L
c)
1000 L
d)
10000 L
|
|
Maya Basak answered |
Explanation:
Conversion Factors:
- 1 m^3 = 1000 L
- 1 L = 0.001 m^3
Explanation:
The given question is asking us to determine the number of liters in 1 m^3. We know that 1 m^3 is a unit of volume used in the metric system which is equivalent to 1000 liters. Therefore, the correct option is C, which states that 1 m^3 is equal to 1000 L.
Conversion:
1 m^3 = 1000 L (using the conversion factor)
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, which states that 1 m^3 is equal to 1000 L.
Conversion Factors:
- 1 m^3 = 1000 L
- 1 L = 0.001 m^3
Explanation:
The given question is asking us to determine the number of liters in 1 m^3. We know that 1 m^3 is a unit of volume used in the metric system which is equivalent to 1000 liters. Therefore, the correct option is C, which states that 1 m^3 is equal to 1000 L.
Conversion:
1 m^3 = 1000 L (using the conversion factor)
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, which states that 1 m^3 is equal to 1000 L.
The diagonal of a quadrilateral shaped field is 24 cm and perpendicular dropped on it from the remaining opposite vertices are 6 m and 12 m. Find the area of the field.- a)343 m2
- b)125 m2
- c)216 m2
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The diagonal of a quadrilateral shaped field is 24 cm and perpendicular dropped on it from the remaining opposite vertices are 6 m and 12 m. Find the area of the field.
a)
343 m2
b)
125 m2
c)
216 m2
d)
none of these
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
area=1/2×d×(h1+h2)
=1/2×24×(12+6)
=12(18)
=216 m2
=1/2×24×(12+6)
=12(18)
=216 m2
Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, breadth 6 cm and height 3.5 cm. - a)168 cm2
- b)168 cm3
- c)215 cm3
- d)150 cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Find the volume of a cuboid whose length is 8 cm, breadth 6 cm and height 3.5 cm.
a)
168 cm2
b)
168 cm3
c)
215 cm3
d)
150 cm3

|
Arnav Dasgupta answered |
Length of the cuboid = 8 cm
Breadth of the cuboid = 6 cm
Height of the cuboid = 3.5 cm
Volume of the cuboid = length × breadth × height
= 8 x 6 x 3.5 = 168cm3
Therefore,volume of the cuboid = 168cm3
Surface area of a cube = _________- a)6 l2
- b)4 l2
- c)6 l3
- d)5 l2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Surface area of a cube = _________
a)
6 l2
b)
4 l2
c)
6 l3
d)
5 l2

|
Manshi 8a2020 8a2020 answered |
As cube has 6 faces, that's why TSA of cube will be 6l2
In a quadrilateral, half of the product of the sum of the lengths of parallel sides and the parallel distance between them gives the area of- a)rectangle
- b)parallelogram
- c)triangle
- d)trapezium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a quadrilateral, half of the product of the sum of the lengths of parallel sides and the parallel distance between them gives the area of
a)
rectangle
b)
parallelogram
c)
triangle
d)
trapezium
|
|
Anmol Unni answered |
Given that half of the product of the sum of the lengths of parallel sides and the parallel distance between them gives the area of a quadrilateral.
Let's consider the different types of quadrilaterals and see which one satisfies the given condition:
a) Rectangle:
A rectangle has two pairs of parallel sides, and the distance between them is the same for both pairs. Therefore, the sum of the lengths of parallel sides times the distance between them would be equal to the perimeter of the rectangle times its height, which is twice the area of the rectangle. Thus, the given condition is not satisfied for a rectangle.
b) Parallelogram:
A parallelogram also has two pairs of parallel sides, but the distance between them may not be the same for both pairs. However, we can draw a perpendicular from one side to the opposite side, which divides the parallelogram into two congruent triangles. The length of this perpendicular is the distance between the parallel sides. Thus, the sum of the lengths of parallel sides times the distance between them would be equal to the sum of the bases of the two triangles times their height, which is twice the area of the parallelogram. Therefore, the given condition is satisfied for a parallelogram.
c) Triangle:
A triangle has only one pair of parallel sides, and the distance between them is the height of the triangle. Therefore, the given condition is not satisfied for a triangle.
d) Trapezium:
A trapezium has two pairs of parallel sides, and the distance between them is different for both pairs. Therefore, the sum of the lengths of parallel sides times the distance between them would be equal to the sum of the areas of two triangles and a rectangle, which is twice the area of the trapezium. Thus, the given condition is satisfied for a trapezium.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', which is trapezium.
Let's consider the different types of quadrilaterals and see which one satisfies the given condition:
a) Rectangle:
A rectangle has two pairs of parallel sides, and the distance between them is the same for both pairs. Therefore, the sum of the lengths of parallel sides times the distance between them would be equal to the perimeter of the rectangle times its height, which is twice the area of the rectangle. Thus, the given condition is not satisfied for a rectangle.
b) Parallelogram:
A parallelogram also has two pairs of parallel sides, but the distance between them may not be the same for both pairs. However, we can draw a perpendicular from one side to the opposite side, which divides the parallelogram into two congruent triangles. The length of this perpendicular is the distance between the parallel sides. Thus, the sum of the lengths of parallel sides times the distance between them would be equal to the sum of the bases of the two triangles times their height, which is twice the area of the parallelogram. Therefore, the given condition is satisfied for a parallelogram.
c) Triangle:
A triangle has only one pair of parallel sides, and the distance between them is the height of the triangle. Therefore, the given condition is not satisfied for a triangle.
d) Trapezium:
A trapezium has two pairs of parallel sides, and the distance between them is different for both pairs. Therefore, the sum of the lengths of parallel sides times the distance between them would be equal to the sum of the areas of two triangles and a rectangle, which is twice the area of the trapezium. Thus, the given condition is satisfied for a trapezium.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D', which is trapezium.
Diagonals of rhombus are- a) equal
- b) half of one diagonal
- c) of different length
- d) none of above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Diagonals of rhombus are
a)
equal
b)
half of one diagonal
c)
of different length
d)
none of above
|
|
Akshat Gupta answered |
Explanation:
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all sides equal in length, and opposite sides are parallel. The diagonals of a rhombus are line segments that connect opposite vertices of the rhombus.
Properties of the diagonals of a rhombus:
1. The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at 90 degrees.
2. The length of each diagonal is different.
3. The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
4. The diagonals of a rhombus divide the rhombus into four congruent triangles.
Proof that the diagonals of a rhombus have different lengths:
Let ABCD be a rhombus with diagonals AC and BD. We need to prove that AC and BD have different lengths.
In rhombus ABCD, AB = BC = CD = DA (by definition of a rhombus).
Let E be the midpoint of AC, and F be the midpoint of BD.
Then, AE = EC and BF = FD (by definition of midpoint).
Also, AF = FB (by definition of a rhombus).
Now, consider triangle AEF and triangle BEF.
AE = EC, BF = FD, and AF = FB (as proved above).
Therefore, by the Side-Side-Side (SSS) congruence criterion, triangle AEF is congruent to triangle BEF.
So, EF = EF (by CPCTC - Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent).
Since EF is a line segment that connects two opposite sides of the rhombus, it is a diagonal of the rhombus.
Therefore, we have proved that the diagonals of a rhombus have different lengths.
Hence, the correct answer is option C - of different length.
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all sides equal in length, and opposite sides are parallel. The diagonals of a rhombus are line segments that connect opposite vertices of the rhombus.
Properties of the diagonals of a rhombus:
1. The diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at 90 degrees.
2. The length of each diagonal is different.
3. The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of each other.
4. The diagonals of a rhombus divide the rhombus into four congruent triangles.
Proof that the diagonals of a rhombus have different lengths:
Let ABCD be a rhombus with diagonals AC and BD. We need to prove that AC and BD have different lengths.
In rhombus ABCD, AB = BC = CD = DA (by definition of a rhombus).
Let E be the midpoint of AC, and F be the midpoint of BD.
Then, AE = EC and BF = FD (by definition of midpoint).
Also, AF = FB (by definition of a rhombus).
Now, consider triangle AEF and triangle BEF.
AE = EC, BF = FD, and AF = FB (as proved above).
Therefore, by the Side-Side-Side (SSS) congruence criterion, triangle AEF is congruent to triangle BEF.
So, EF = EF (by CPCTC - Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent).
Since EF is a line segment that connects two opposite sides of the rhombus, it is a diagonal of the rhombus.
Therefore, we have proved that the diagonals of a rhombus have different lengths.
Hence, the correct answer is option C - of different length.
The formula for lateral surface area of cuboid is - a)2h (l + b)
- b)2l (h + b)
- c)2b (l + h)
- d)2 (lb + bh + hl)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula for lateral surface area of cuboid is
a)
2h (l + b)
b)
2l (h + b)
c)
2b (l + h)
d)
2 (lb + bh + hl)
|
|
Aditya Datta answered |
Explanation:
A cuboid is a 3-dimensional figure that has six rectangular faces. The lateral surface area of a cuboid is the area of the four vertical rectangular faces, excluding the top and bottom faces.
Let's consider a cuboid with length (l), breadth (b) and height (h).
Formula for Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid:
The formula for the lateral surface area of a cuboid is:
Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid = 2h(l+b)
Proof:
To find the lateral surface area of a cuboid, we need to add the areas of all the four vertical rectangular faces.
- The area of the first vertical face = l x h
- The area of the second vertical face = b x h
- The area of the third vertical face = l x h
- The area of the fourth vertical face = b x h
Adding all these areas, we get:
Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid = lh + bh + lh + bh
= 2lh + 2bh
= 2h(l+b)
Therefore, the formula for the lateral surface area of a cuboid is 2h(l+b).
A cuboid is a 3-dimensional figure that has six rectangular faces. The lateral surface area of a cuboid is the area of the four vertical rectangular faces, excluding the top and bottom faces.
Let's consider a cuboid with length (l), breadth (b) and height (h).
Formula for Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid:
The formula for the lateral surface area of a cuboid is:
Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid = 2h(l+b)
Proof:
To find the lateral surface area of a cuboid, we need to add the areas of all the four vertical rectangular faces.
- The area of the first vertical face = l x h
- The area of the second vertical face = b x h
- The area of the third vertical face = l x h
- The area of the fourth vertical face = b x h
Adding all these areas, we get:
Lateral Surface Area of Cuboid = lh + bh + lh + bh
= 2lh + 2bh
= 2h(l+b)
Therefore, the formula for the lateral surface area of a cuboid is 2h(l+b).
Which of the following shape has two dimensions- a)ring
- b)soap
- c)chalk box
- d)cylinder
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following shape has two dimensions
a)
ring
b)
soap
c)
chalk box
d)
cylinder
|
|
Swara Das answered |
Chalk box and soap have breadth,length and height . Cylinder has 2 radii and height. A ring (here) is made up of two concentric circles which is a 2d figure. Hence ring is 2 dimensional
If each edge of a cube is doubled, its surface are will increase- a)two times
- b)three times
- c)four times
- d)five times
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If each edge of a cube is doubled, its surface are will increase
a)
two times
b)
three times
c)
four times
d)
five times
|
|
Aman Chawla answered |
Explanation:
When we double the edge of a cube, we are essentially multiplying the length of each edge by 2. Let the original edge length be l. After doubling the edge, new edge length will be 2l.
Calculating the surface area of the original cube:
The surface area of a cube is given by the formula 6l^2, where l is the length of an edge. Here, l is the original edge length. So, the surface area of the original cube is 6l^2.
Calculating the surface area of the doubled cube:
The surface area of the doubled cube is given by the formula 6(2l)^2, since each edge length is now 2l. Simplifying this expression, we get:
6(2l)^2 = 6(4l^2) = 24l^2
So, the surface area of the doubled cube is 24l^2.
Calculating the ratio of the surface areas:
To find the ratio of the surface areas, we need to divide the surface area of the doubled cube by the surface area of the original cube:
(24l^2) / (6l^2) = 4
So, the surface area of the doubled cube is 4 times the surface area of the original cube.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct option is C, that is, the surface area of the cube will increase four times if each edge of a cube is doubled.
When we double the edge of a cube, we are essentially multiplying the length of each edge by 2. Let the original edge length be l. After doubling the edge, new edge length will be 2l.
Calculating the surface area of the original cube:
The surface area of a cube is given by the formula 6l^2, where l is the length of an edge. Here, l is the original edge length. So, the surface area of the original cube is 6l^2.
Calculating the surface area of the doubled cube:
The surface area of the doubled cube is given by the formula 6(2l)^2, since each edge length is now 2l. Simplifying this expression, we get:
6(2l)^2 = 6(4l^2) = 24l^2
So, the surface area of the doubled cube is 24l^2.
Calculating the ratio of the surface areas:
To find the ratio of the surface areas, we need to divide the surface area of the doubled cube by the surface area of the original cube:
(24l^2) / (6l^2) = 4
So, the surface area of the doubled cube is 4 times the surface area of the original cube.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the correct option is C, that is, the surface area of the cube will increase four times if each edge of a cube is doubled.
If the diagonals of rhombus are 6 cm & 8 cm, its area will be- a)48 cm2
- b)24 cm
- c)48 cm
- d)24 cm2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the diagonals of rhombus are 6 cm & 8 cm, its area will be
a)
48 cm2
b)
24 cm
c)
48 cm
d)
24 cm2
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Area of rhombus is ½* d1*d2 =6*8/2=24cm2.
Which of the following is an example of two dimensions - a)cuboid
- b)cone
- c)sphere
- d)circle
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of two dimensions
a)
cuboid
b)
cone
c)
sphere
d)
circle
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
2d shapes are on the plane . The circle is not in space ,it is in plane. So it is a 2d shape.
The parallel sides of a trapezium are 25 cm and13 ... morecm. Its non-parallel sides are equal, eachbeing 10 cm. Find the area of the trapezium.a)142 cmb)152 cm2c)152 cmd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Aditi Saxena answered |
Area of trapezium= 1/2*d*(a+b) sq. Units.
Where d= perpendicular distance between parellel sides which are a & b respectively, 25 &13 cm.
25–13=12, 12/2= 6 cm is base of RT. Angled ∆.
Non parallel sides=10cm, this is hypotenuese of this ∆.
Find ‘d ‘ to solve.
d=√{10^2–6^2}=8 cm.
Area of trapezium= 1/2*8*(25+13)=152 cm^2
A godown is in the form of a cuboid of measures 60 m × 40 m × 30 m. How many cuboidal boxes can be stored in it if the volume of one box is 0.8 m3?- a)40000
- b)50000
- c)30000
- d)90000
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A godown is in the form of a cuboid of measures 60 m × 40 m × 30 m. How many cuboidal boxes can be stored in it if the volume of one box is 0.8 m3?
a)
40000
b)
50000
c)
30000
d)
90000
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
The volume of the godown is:
V = l � b � h = 60 � 40 � 30 = 72000 m�
The volume of one box is 0.8 m�.
To find out how many boxes can be stored in the godown, we need to divide the volume of the godown by the volume of one box:
Number of boxes = V � volume of one box
Number of boxes = 72000 � 0.8
Number of boxes = 90000
Therefore, the godown can store 90,000 cuboidal boxes. The answer is (d) 90,000.
V = l � b � h = 60 � 40 � 30 = 72000 m�
The volume of one box is 0.8 m�.
To find out how many boxes can be stored in the godown, we need to divide the volume of the godown by the volume of one box:
Number of boxes = V � volume of one box
Number of boxes = 72000 � 0.8
Number of boxes = 90000
Therefore, the godown can store 90,000 cuboidal boxes. The answer is (d) 90,000.
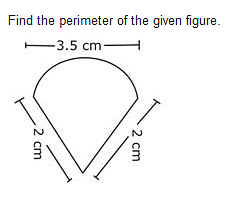
- a)11 cm
- b)9.5 cm
- c)13 cm
- d)12 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
11 cm
b)
9.5 cm
c)
13 cm
d)
12 cm
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Circumference of semi circle = 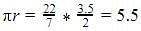
perimeter = sum of two sides + circumference = 4 + 5.5 = 9.5cm
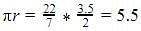
perimeter = sum of two sides + circumference = 4 + 5.5 = 9.5cm
The area of rhombus is- a) side × side
- b)d1 × d2
- c)d1 + d2
- d)1/2 d1 × d2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The area of rhombus is
a)
side × side
b)
d1 × d2
c)
d1 + d2
d)
1/2 d1 × d2
|
|
Gowri Khanna answered |
B) (1/2) x diagonal1 x diagonal2
Plane figures are- a)3 D
- b)2 D
- c)1 D
- d)4 D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plane figures are
a)
3 D
b)
2 D
c)
1 D
d)
4 D
|
|
Mihir Goyal answered |
Plane figures are 2D
Introduction:
Plane figures are basic shapes that exist on a flat surface or plane. They are the fundamental building blocks of geometry and are used to construct more complex shapes. In this article, we will discuss what plane figures are and their properties.
What are plane figures?
Plane figures are two-dimensional shapes that exist on a flat surface or plane. They have length and width but no depth. Some examples of plane figures include triangles, rectangles, circles, and squares.
Properties of plane figures:
1. They are two-dimensional: As mentioned earlier, plane figures exist on a flat surface or plane. They have only length and width, and no depth.
2. They have area: Plane figures have area, which is the amount of space they occupy on a flat surface. The area of a plane figure is measured in square units.
3. They have perimeter: Plane figures have a perimeter, which is the total length of the boundary of the figure. The perimeter is measured in linear units.
4. They have angles: Plane figures have angles, which are formed by two intersecting lines.
Examples of plane figures:
1. Triangle: A triangle is a plane figure with three sides and three angles. It can be classified as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene depending on the length of its sides.
2. Rectangle: A rectangle is a plane figure with four sides and four angles. Its opposite sides are equal and parallel, and all its angles are right angles.
3. Circle: A circle is a plane figure with a curved boundary that is equidistant from its center. It has no sides or angles.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, plane figures are two-dimensional shapes that exist on a flat surface. They have length and width but no depth. Some examples of plane figures include triangles, rectangles, circles, and squares. They have properties such as area, perimeter, and angles.
Introduction:
Plane figures are basic shapes that exist on a flat surface or plane. They are the fundamental building blocks of geometry and are used to construct more complex shapes. In this article, we will discuss what plane figures are and their properties.
What are plane figures?
Plane figures are two-dimensional shapes that exist on a flat surface or plane. They have length and width but no depth. Some examples of plane figures include triangles, rectangles, circles, and squares.
Properties of plane figures:
1. They are two-dimensional: As mentioned earlier, plane figures exist on a flat surface or plane. They have only length and width, and no depth.
2. They have area: Plane figures have area, which is the amount of space they occupy on a flat surface. The area of a plane figure is measured in square units.
3. They have perimeter: Plane figures have a perimeter, which is the total length of the boundary of the figure. The perimeter is measured in linear units.
4. They have angles: Plane figures have angles, which are formed by two intersecting lines.
Examples of plane figures:
1. Triangle: A triangle is a plane figure with three sides and three angles. It can be classified as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene depending on the length of its sides.
2. Rectangle: A rectangle is a plane figure with four sides and four angles. Its opposite sides are equal and parallel, and all its angles are right angles.
3. Circle: A circle is a plane figure with a curved boundary that is equidistant from its center. It has no sides or angles.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, plane figures are two-dimensional shapes that exist on a flat surface. They have length and width but no depth. Some examples of plane figures include triangles, rectangles, circles, and squares. They have properties such as area, perimeter, and angles.
The area of four walls of the room is - a)2 (lb + bh + hl)
- b)2l (h + b)
- c)2 (lb x bh x hl)
- d)2h (l + b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The area of four walls of the room is
a)
2 (lb + bh + hl)
b)
2l (h + b)
c)
2 (lb x bh x hl)
d)
2h (l + b)
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Since we have area of wall as b*h and h*l .So area of 4 walls is 2h*b+2h*l=2h(b+l)
The height of cuboid whose volume is 200 cm3 and base area is 20 cm2 is
- a)220 cm
- b)100 cm
- c)10 cm
- d)20 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The height of cuboid whose volume is 200 cm3 and base area is 20 cm2 is
a)
220 cm
b)
100 cm
c)
10 cm
d)
20 cm
|
|
Athira Rane answered |
Finding the Height of a Cuboid
Given information: Volume = 200 cm³, Base Area = 20 cm²
To find: Height of the cuboid
Formula to find the volume of a cuboid: V = l × b × h, where l is the length, b is the breadth, and h is the height of the cuboid.
Formula to find the base area of a cuboid: A = l × b
We are given that the volume of the cuboid is 200 cm³. Therefore, we can write:
l × b × h = 200
We are also given that the base area of the cuboid is 20 cm². Therefore, we can write:
l × b = 20
Solving the above two equations, we get:
h = 200 / (l × b)
l × b = 20
h = 200 / 20
h = 10 cm
Therefore, the height of the cuboid is 10 cm.
Answer: Option (c) 10 cm.
Given information: Volume = 200 cm³, Base Area = 20 cm²
To find: Height of the cuboid
Formula to find the volume of a cuboid: V = l × b × h, where l is the length, b is the breadth, and h is the height of the cuboid.
Formula to find the base area of a cuboid: A = l × b
We are given that the volume of the cuboid is 200 cm³. Therefore, we can write:
l × b × h = 200
We are also given that the base area of the cuboid is 20 cm². Therefore, we can write:
l × b = 20
Solving the above two equations, we get:
h = 200 / (l × b)
l × b = 20
h = 200 / 20
h = 10 cm
Therefore, the height of the cuboid is 10 cm.
Answer: Option (c) 10 cm.
1 m l = ___________ .- a)1 cm3
- b)10 cm3
- c)100 cm3
- d)1000 cm3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
1 m l = ___________ .
a)
1 cm3
b)
10 cm3
c)
100 cm3
d)
1000 cm3
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
1m3 = 1000 L and 1m3=1000000cm3 and 1000L= 1000000ml
So 1000000cm3 = 1000000ml which is 1ml = 1cm3
So 1000000cm3 = 1000000ml which is 1ml = 1cm3
The area of a trapezium is - a)1/2 (sum of parallel sides) × h
- b)2 (sum of parallel sides) × h
- c)(sum of parallel sides) × h
- d)1/2 (sum of parallel sides) + h
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The area of a trapezium is
a)
1/2 (sum of parallel sides) × h
b)
2 (sum of parallel sides) × h
c)
(sum of parallel sides) × h
d)
1/2 (sum of parallel sides) + h
|
|
Manasa Joshi answered |
B)1/2(product of height and sum of parallel sides)
c)sum of parallel sides multiplied by the height
d)difference of parallel sides multiplied by the height
Answer: b) 1/2(product of height and sum of parallel sides)
c)sum of parallel sides multiplied by the height
d)difference of parallel sides multiplied by the height
Answer: b) 1/2(product of height and sum of parallel sides)
The formula for finding total surface area of cylinder is - a)2πrh
- b)2πr(r+h)
- c)πr2h
- d)2πr 2h2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The formula for finding total surface area of cylinder is
a)
2πrh
b)
2πr(r+h)
c)
πr2h
d)
2πr 2h2
|
|
Shubham Sharma answered |
Total surface area of a cylinder = πr2+2πrh+πr2=2πr(r+h)
A rectangular paper of width 7 cm is rolled along its width and a cylinder of radius 20 cm is formed. Find the volume of the cylinder. - a)8800 cm3
- b)8800 cm
- c)8800 cm2
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A rectangular paper of width 7 cm is rolled along its width and a cylinder of radius 20 cm is formed. Find the volume of the cylinder.
a)
8800 cm3
b)
8800 cm
c)
8800 cm2
d)
none of these

|
Malavika Basu answered |
Given : A rectangular paper of width 14 cm is rolled along its width to form a cylinder.
Height of cylinder = h = 7 cm = width of the rectangular paper
And
Radius of cylinder ( Given ) = r = 20 cm
And
we know Volume of cylinder = π r^2 h , So
Volume of our given cylinder = 22/7 x 20 x 20 x 7 = 8800 cm^3
The length of parallel sides of trapezium is 14 cm and 6 cm and its height is 5 cm. Its area will be
- a)50 cm2
- b)100 cm2
- c) 210 cm2
- d)10 cm2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The length of parallel sides of trapezium is 14 cm and 6 cm and its height is 5 cm. Its area will be
a)
50 cm2
b)
100 cm2
c)
210 cm2
d)
10 cm2
|
|
Anand Basu answered |
Finding the area of a trapezium
To find the area of a trapezium, we can use the formula:
Area = (a + b) × h ÷ 2
Where:
- a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides
- h is the height (perpendicular distance between the parallel sides)
Given:
- Length of parallel sides: 14 cm and 6 cm
- Height: 5 cm
Substituting the values in the formula, we get:
Area = (14 + 6) × 5 ÷ 2
Area = 20 × 5 ÷ 2
Area = 100 ÷ 2
Area = 50 cm²
Therefore, the area of the trapezium is 50 cm², which is option A.
To find the area of a trapezium, we can use the formula:
Area = (a + b) × h ÷ 2
Where:
- a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides
- h is the height (perpendicular distance between the parallel sides)
Given:
- Length of parallel sides: 14 cm and 6 cm
- Height: 5 cm
Substituting the values in the formula, we get:
Area = (14 + 6) × 5 ÷ 2
Area = 20 × 5 ÷ 2
Area = 100 ÷ 2
Area = 50 cm²
Therefore, the area of the trapezium is 50 cm², which is option A.
Chapter doubts & questions for Mensuration - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams 2024 is part of CTET & State TET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CTET & State TET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CTET & State TET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Mensuration - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of CTET & State TET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CTET & State TET Exam by signing up for free.
Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams
76 videos|228 docs|70 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup