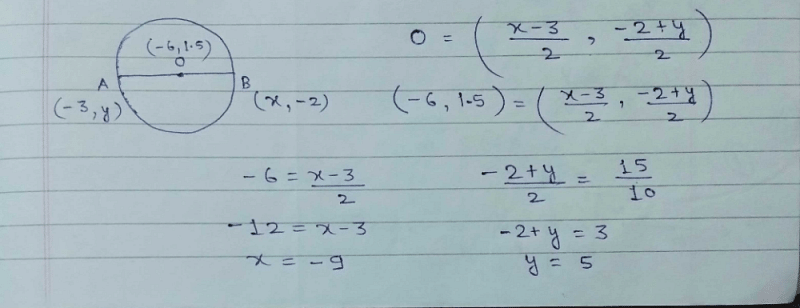All Exams >
MAT >
Geometry for MAT >
All Questions
All questions of Coordinate Geometry for MAT Exam
The line segment joining (2, – 3) and (5, 6) is divided by x-axis in the ratio:- a)2 : 1
- b)3 : 1
- c)1 : 2
- d)1 : 3.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The line segment joining (2, – 3) and (5, 6) is divided by x-axis in the ratio:
a)
2 : 1
b)
3 : 1
c)
1 : 2
d)
1 : 3.
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
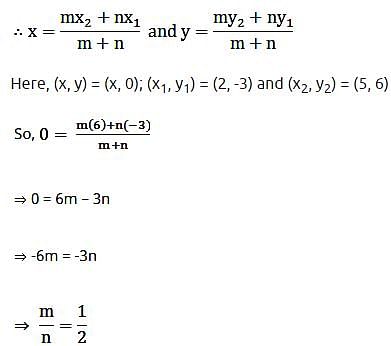
Hence, the ratio is 1:2 and the division is internal.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Coordinate Geometry" are available for CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths) and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths) Q. The distance between the points (a, b) and (– a, – b) is :- a)a2+b2
- b)
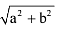
- c)0
- d)
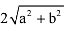
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Practice Test/Quiz or MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Solutions of Chapter "Coordinate Geometry" are available for CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths) and have been compiled as per the syllabus of CBSE Class 10 Mathematics (Maths)
Q. The distance between the points (a, b) and (– a, – b) is :
a)
a2+b2
b)
c)
0
d)
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
We have distance formula as d = 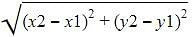
Where x1=a,y1=b,x2=-a,y2=-b
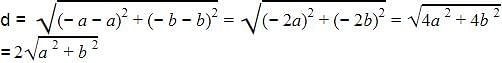
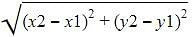
Where x1=a,y1=b,x2=-a,y2=-b
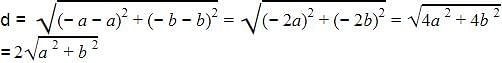
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines y = 15, 3x – 4y = 0, 5x + 12y = 0, the incentre is :- a)(1, 8)
- b)(8, 1)
- c)(-1, 8)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines y = 15, 3x – 4y = 0, 5x + 12y = 0, the incentre is :
a)
(1, 8)
b)
(8, 1)
c)
(-1, 8)
d)
None of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Given equations:
3x – 4y = 0 …(1)
5x+12y = 0 …(2)
Y-15 = 0 …(3)
From the given equations, (1), (2) and (3) represent the sides AB, BC and CA respectively.
Solving (1) and (2), we get
x= 0, and y= 0
Therefore, the side AB and BC intersect at the point B (0, 0)
Solving (1) and (3), we get
x= 20, y= 15
Hence, the side AB and CA intersect at the point A (20, 15)
Solving (2) and (3), we get
x= -36, y = 15
Thus, the side BC and CA intersect at the point C (-36, 15)
Now,
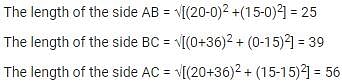
BC = a = 39
CA = b = 56
AB = c = 25
Similarly, (x1, y1) = A(20, 15)
CA = b = 56
AB = c = 25
Similarly, (x1, y1) = A(20, 15)
(x2, y2) = B(0, 0)
(x3, y3) = C(-36, 15)
(x3, y3) = C(-36, 15)
Therefore, incentre is
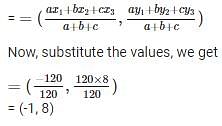
The points (– 2, 2), (8, – 2) and (– 4, – 3) are the vertices of a :- a)equilateral Δ
- b)isosceles Δ
- c)right Δ
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The points (– 2, 2), (8, – 2) and (– 4, – 3) are the vertices of a :
a)
equilateral Δ
b)
isosceles Δ
c)
right Δ
d)
None of these
|
|
Izumi answered |
Let A(-2, 2)
B(8, -2)
C(-4, -3)
distance
AB=√(x2-x1) ²+(y2-y1) ²
=√(8+2) ²+(-2-2) ²=√100+16=√116
BC=√(-4-8) ²+(-3+2) ²=√144+1=√145
AC=√(-4+2) ²+(-3-2) ²=√4+25=√29
from the above
AB²=(√116) ²=116
BC²=(√145) ²=145
AC²=(√29) ²=29
AB²+AC²=BC²=145units
hence, by Converse of Pythagoras theorem
ABC is a right triangle
and hence,
A, B, C are the vertices of a right ∆
hence, option (C) is correct
B(8, -2)
C(-4, -3)
distance
AB=√(x2-x1) ²+(y2-y1) ²
=√(8+2) ²+(-2-2) ²=√100+16=√116
BC=√(-4-8) ²+(-3+2) ²=√144+1=√145
AC=√(-4+2) ²+(-3-2) ²=√4+25=√29
from the above
AB²=(√116) ²=116
BC²=(√145) ²=145
AC²=(√29) ²=29
AB²+AC²=BC²=145units
hence, by Converse of Pythagoras theorem
ABC is a right triangle
and hence,
A, B, C are the vertices of a right ∆
hence, option (C) is correct
The distance between points (a + b, b + c) and (a – b, c – b) is :- a)
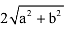
- b)
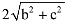
- c)
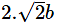
- d)
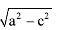
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance between points (a + b, b + c) and (a – b, c – b) is :
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Distance between two point is
root[{(a+b)-(a-b)}^2] + [{(b+c)-(c-b)}^2]
=root [{(a+b-a+b)^2}] + [((b+c-c+b)}^2]
=root[(2b)^2 + (2b)^2]
=root[4b^2 +4b^2]
=root[8b^2]
=2.root(2)b
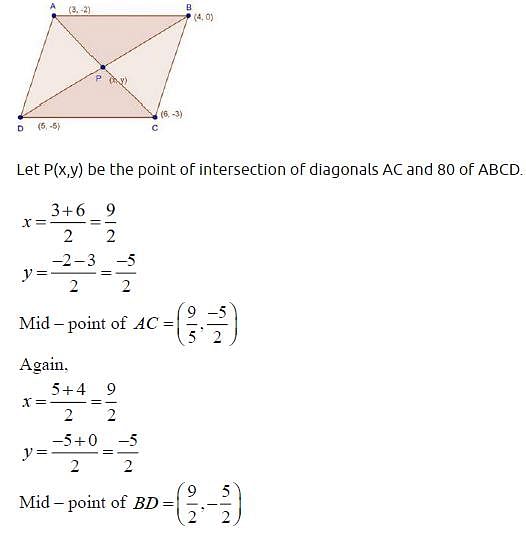
The points (1, 7), (4, 2), (– 1, 1) and (– 4, 4) are the vertices of a :- a)parallelogram
- b)rhombus
- c)rectangle
- d)square.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The points (1, 7), (4, 2), (– 1, 1) and (– 4, 4) are the vertices of a :
a)
parallelogram
b)
rhombus
c)
rectangle
d)
square.
|
|
Akshay chauhan answered |
Vertices of a Square
The given points (1, 7), (4, 2), (-1, 1), and (-4, 4) can form the vertices of a square.
Properties of a Square
- A square is a special type of rectangle and rhombus.
- All sides of a square are equal in length.
- Opposite sides of a square are parallel.
- All angles in a square are right angles (90 degrees).
- The diagonals of a square are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
Verifying the Given Points
To verify if the given points form a square, we need to check the properties mentioned above.
- Calculate the distances between the points to ensure that all sides are equal.
- Check if the slopes of opposite sides are equal to show that they are parallel.
- Calculate the angles between the sides to confirm that they are all right angles.
- Calculate the lengths of the diagonals and check if they are equal.
Conclusion
After verifying the properties of the given points, if all conditions hold true, then the points (1, 7), (4, 2), (-1, 1), and (-4, 4) form the vertices of a square. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D' - square.
The given points (1, 7), (4, 2), (-1, 1), and (-4, 4) can form the vertices of a square.
Properties of a Square
- A square is a special type of rectangle and rhombus.
- All sides of a square are equal in length.
- Opposite sides of a square are parallel.
- All angles in a square are right angles (90 degrees).
- The diagonals of a square are equal in length and bisect each other at right angles.
Verifying the Given Points
To verify if the given points form a square, we need to check the properties mentioned above.
- Calculate the distances between the points to ensure that all sides are equal.
- Check if the slopes of opposite sides are equal to show that they are parallel.
- Calculate the angles between the sides to confirm that they are all right angles.
- Calculate the lengths of the diagonals and check if they are equal.
Conclusion
After verifying the properties of the given points, if all conditions hold true, then the points (1, 7), (4, 2), (-1, 1), and (-4, 4) form the vertices of a square. Hence, the correct answer is option 'D' - square.
If the points (p, 0), (0, q) and (1, 1) are collinear then 1/p+1/q is equal to :- a)– 1
- b)2
- c)1
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the points (p, 0), (0, q) and (1, 1) are collinear then 1/p+1/q is equal to :
a)
– 1
b)
2
c)
1
d)
0
|
|
Deepak khanna answered |
1b) 2c) 3d) 4
Solution:
Since the points (p, 0), (0, q) and (1, 1) are collinear, the slope of the line passing through these points is the same. Therefore,
(q-1)/(0-1) = (0-1)/(p-1)
Simplifying this, we get:
q-1 = 1-p
or
p+q=2
Multiplying both sides by 1/pq, we get:
1/q + 1/p = 2/pq
Therefore, the answer is (b) 2.
Solution:
Since the points (p, 0), (0, q) and (1, 1) are collinear, the slope of the line passing through these points is the same. Therefore,
(q-1)/(0-1) = (0-1)/(p-1)
Simplifying this, we get:
q-1 = 1-p
or
p+q=2
Multiplying both sides by 1/pq, we get:
1/q + 1/p = 2/pq
Therefore, the answer is (b) 2.
If (3, 2), (4, k) and (5, 3) are collinear then k is equal to :- a)3/2
- b)2/5
- c)5/2
- d)3/5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If (3, 2), (4, k) and (5, 3) are collinear then k is equal to :
a)
3/2
b)
2/5
c)
5/2
d)
3/5
|
|
Swara sharma answered |
To determine the value of k, we need to check if the three given points (3, 2), (4, k), and (5, 3) are collinear. Two points are collinear if the slope between them is the same as the slope between any other two points on the line.
Calculating the slope between (3, 2) and (4, k):
The slope formula is given by:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Using the coordinates (3, 2) and (4, k), we have:
m = (k - 2) / (4 - 3)
m = (k - 2) / 1
m = k - 2
Calculating the slope between (4, k) and (5, 3):
Using the coordinates (4, k) and (5, 3), we have:
m = (3 - k) / (5 - 4)
m = (3 - k) / 1
m = 3 - k
Since the two slopes are equal, we can equate them:
k - 2 = 3 - k
Solving this equation for k:
2k = 5
k = 5/2
Therefore, the value of k is 5/2, which corresponds to option C.
Calculating the slope between (3, 2) and (4, k):
The slope formula is given by:
m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
Using the coordinates (3, 2) and (4, k), we have:
m = (k - 2) / (4 - 3)
m = (k - 2) / 1
m = k - 2
Calculating the slope between (4, k) and (5, 3):
Using the coordinates (4, k) and (5, 3), we have:
m = (3 - k) / (5 - 4)
m = (3 - k) / 1
m = 3 - k
Since the two slopes are equal, we can equate them:
k - 2 = 3 - k
Solving this equation for k:
2k = 5
k = 5/2
Therefore, the value of k is 5/2, which corresponds to option C.
The co-ordinates of the point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points (5, 4) and (– 2, 3) are :- a)(2, 0)
- b)(3, 0)
- c)(0, 2)
- d)(0, 3).
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The co-ordinates of the point on x-axis which is equidistant from the points (5, 4) and (– 2, 3) are :
a)
(2, 0)
b)
(3, 0)
c)
(0, 2)
d)
(0, 3).

|
Surbhi Gupta answered |
Let the point on x-axis be (a,0)
Since PA = PB PA2 = PB2
(a + 2)2 + (0 - 5)2 = (a - 2)2 + (0 + 3)2
(a + 2)2 - (a - 2)2 = 9 - 25 = -16
8a = -16 a = -2.
The required point is (-2,0).
If two vertices of a parallelogram are (3, 2) and (–1, 0) and the diagonals intersect at (2, –5), then the other two vertices are :- a)(1, –10), (5, –12)
- b)(1, –12), (5, –10)
- c)(2, –10), (5, –12)
- d)(1, – 10), (2, – 12)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If two vertices of a parallelogram are (3, 2) and (–1, 0) and the diagonals intersect at (2, –5), then the other two vertices are :
a)
(1, –10), (5, –12)
b)
(1, –12), (5, –10)
c)
(2, –10), (5, –12)
d)
(1, – 10), (2, – 12)
|
|
Parth Chawla answered |
Let's call the two given vertices A and B, with coordinates (3, 2) and (x, y) respectively.
Since a parallelogram has opposite sides that are parallel, we can find the coordinates of the other two vertices by applying the same translation to points A and B.
To find the translation, we can subtract the x-coordinate of point A from the x-coordinate of point B, and subtract the y-coordinate of point A from the y-coordinate of point B:
x - 3 = 3 - 3 = 0
y - 2 = 2 - 2 = 0
So the translation is (0, 0).
To find the coordinates of the other two vertices, we can add the translation to points A and B:
Point A + translation = (3, 2) + (0, 0) = (3, 2)
Point B + translation = (x, y) + (0, 0) = (x, y)
Therefore, the other two vertices of the parallelogram are (3, 2) and (x, y).
Since a parallelogram has opposite sides that are parallel, we can find the coordinates of the other two vertices by applying the same translation to points A and B.
To find the translation, we can subtract the x-coordinate of point A from the x-coordinate of point B, and subtract the y-coordinate of point A from the y-coordinate of point B:
x - 3 = 3 - 3 = 0
y - 2 = 2 - 2 = 0
So the translation is (0, 0).
To find the coordinates of the other two vertices, we can add the translation to points A and B:
Point A + translation = (3, 2) + (0, 0) = (3, 2)
Point B + translation = (x, y) + (0, 0) = (x, y)
Therefore, the other two vertices of the parallelogram are (3, 2) and (x, y).
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6+y/8 = 1, the incentre is :- a)(3, 4)
- b)(2, 2)
- c)(2, 3)
- d)(3, 2)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6+y/8 = 1, the incentre is :
a)
(3, 4)
b)
(2, 2)
c)
(2, 3)
d)
(3, 2)
|
|
Kalyan singh answered |
Finding the Incentre of a Triangle
To find the incentre of a triangle, we need to find the point where the angle bisectors of the triangle meet. The angle bisectors are the lines that divide the angles of the triangle into two equal parts. The incentre is the intersection of these angle bisectors and is equidistant from all three sides of the triangle.
Given Triangle
The triangle in the question has sides along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1. Let's first plot these lines on a graph to get a visual representation of the triangle.
We can see that the triangle is a right-angled triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (6, 0) and (0, 8). Now, let's find the equation of the angle bisectors of this triangle.
Finding the Equation of Angle Bisectors
To find the equation of the angle bisectors, we need to first find the equations of the two lines that form each angle. We can then find the midpoint of these lines and the slope of the angle bisector. Finally, we can use the point-slope form of a line to find the equation of the angle bisector.
Let's start with the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (6, 0) and (0, 8). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = -3/4x + 8. Now, let's find the equation of the line perpendicular to this line that passes through the midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0).
The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is (3, 0). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is 0. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is undefined (since it is a vertical line). The equation of the line passing through (3, 0) with undefined slope is x = 3.
Using the same method, we can find the equation of the angle bisector of the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (0, 8) and (6, 0). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = 8/6x = 4/3x. The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is (0, 4). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is undefined. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is 0. The equation of the line passing through (0, 4) with slope 0 is y = 4.
Intersection of Angle Bisectors
Now that we have the equations of the two angle bisectors, we can find their intersection point, which is the incentre of the triangle. The intersection point is the solution to the system of equations:
x = 3
y = 4
y = 4
The solution to this system of equations is (3, 4), which is option (c). Therefore, the incentre of the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1 is
To find the incentre of a triangle, we need to find the point where the angle bisectors of the triangle meet. The angle bisectors are the lines that divide the angles of the triangle into two equal parts. The incentre is the intersection of these angle bisectors and is equidistant from all three sides of the triangle.
Given Triangle
The triangle in the question has sides along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1. Let's first plot these lines on a graph to get a visual representation of the triangle.
We can see that the triangle is a right-angled triangle with vertices at (0, 0), (6, 0) and (0, 8). Now, let's find the equation of the angle bisectors of this triangle.
Finding the Equation of Angle Bisectors
To find the equation of the angle bisectors, we need to first find the equations of the two lines that form each angle. We can then find the midpoint of these lines and the slope of the angle bisector. Finally, we can use the point-slope form of a line to find the equation of the angle bisector.
Let's start with the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (6, 0) and (0, 8). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = -3/4x + 8. Now, let's find the equation of the line perpendicular to this line that passes through the midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0).
The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is (3, 0). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (6, 0) is 0. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is undefined (since it is a vertical line). The equation of the line passing through (3, 0) with undefined slope is x = 3.
Using the same method, we can find the equation of the angle bisector of the angle formed by sides (0, 0) to (0, 8) and (6, 0). The equation of the line joining these two points is y = 8/6x = 4/3x. The midpoint of the line segment joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is (0, 4). The slope of the line joining (0, 0) and (0, 8) is undefined. Therefore, the slope of the line perpendicular to this line is 0. The equation of the line passing through (0, 4) with slope 0 is y = 4.
Intersection of Angle Bisectors
Now that we have the equations of the two angle bisectors, we can find their intersection point, which is the incentre of the triangle. The intersection point is the solution to the system of equations:
x = 3
y = 4
y = 4
The solution to this system of equations is (3, 4), which is option (c). Therefore, the incentre of the triangle whose sides are along the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x/6 y/8 = 1 is
Chapter doubts & questions for Coordinate Geometry - Geometry for MAT 2024 is part of MAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MAT 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Coordinate Geometry - Geometry for MAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MAT Exam by signing up for free.
Geometry for MAT
1 videos|15 docs|4 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup