31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Biodiversity & Conservation - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Biodiversity & Conservation
Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)
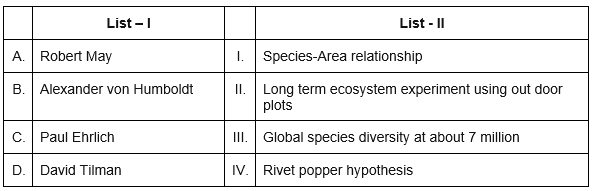
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:

These are regarded as major causes of biodiversity loss: (NEET 2024)
A. Over exploitation
B. Co-extinction
C. Mutation
D. Habitat loss and fragmentation
E. Migration
Choose the correct option:
A. Over exploitation
B. Co-extinction
C. Mutation
D. Habitat loss and fragmentation
E. Migration
Choose the correct option:
The type of conservation in which the threatened species are taken out from their natural habitat and placed in special setting where they can be protected and given special care is called (NEET 2024)
List of endangered species was released by (NEET 2024)
Tropical regions show greatest level of species richness because (NEET 2024)
A. Tropical latitudes have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years, hence more time was available for species diversification.
B. Tropical environments are more seasonal.
C. More solar energy is available in tropics.
D. Constant environments promote niche specialization.
E. Tropical environments are constant and predictable.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
The historic Convention on Biological Diversity, ‘The Earth Summit’ was held in Rio de Janeiro in the year (NEET 2023)
Among ‘The Evil Quartet’, which one is considered the most important cause driving extinction of species? (NEET 2023)
In-situ conservation refers to : (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Habitat loss and fragmentation, over exploitation, alien species invasion and co-extinction are causes for : (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Which of the following is not a method of ex situ conservation? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Match the List-I with List-II: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
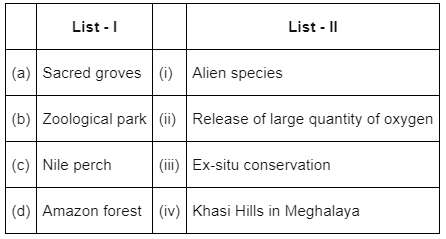
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The World Summit on sustainable development held in 2002 in Johannesburg, South Africa pledged for (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Frugivorous birds are found in large numbers in tropical forests mainly because of : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
According to Robert May, the global species diversity is about [2020]
Which one of the following is not a method of in situ conservation of biodiversity? [2019]
All of the following are included in lex-situ conservation’ except [2018]
Alexander von Humboldt described for the first time [2017]
How many hotspots of biodiversity’ in the world have been identified till date by Norman Myers? [2016]
The highest number of species in the world is represented by
[2012]
Which one of the following areas in India, is a hotspot of biodiversity
[2012]
Biodiversity of a geographical region represents
[2011M]
Which one of the following shows maximum genetic diversity in India ?
[2011]
Which one of the following is an example of Exsitu conservation?
[2010]
Which one of the following has maximum genetic diversity in India?
[2009]
Which of the following is considered a hot-spot of biodiversity in India ?
[2006]














