31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Neural Control & Coordination - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Neural Control & Coordination
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: The cerebral hemispheres are connected by nerve tract known as corpus callosum.
Statement II: The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and cerebrum.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Statement I: The cerebral hemispheres are connected by nerve tract known as corpus callosum.
Statement II: The brain stem consists of the medulla oblongata, pons and cerebrum.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)
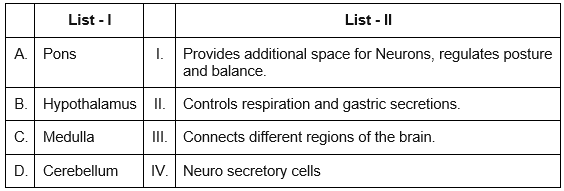
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :

The parts of human brain that helps in regulation of sexual behaviour, expression of excitement, pleasure, rage, fear etc. are: (2023)
Select the incorrect statement regarding synapses: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Match List-I with List - II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
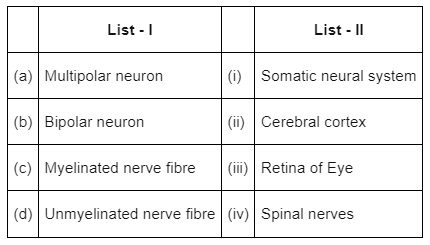
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Which part of the brain is responsible for thermoregulation? [2019]
Which of the following structures or regions is incorrectly paired with its functions? (NEET 2018)
Receptor sites for neurotransmitters are present on (NEET 2017)
Which of the following regions of the brain is incorrectly paired with its function? (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper )
Injury localized to the hypothalamus would most likely disrupt: (2014)
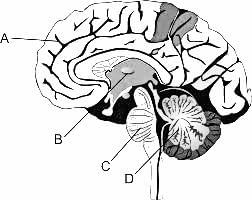
A sagittal section of human-brain is shown here. Identify at least two labels from A-D. [NEET Kar. 2013]
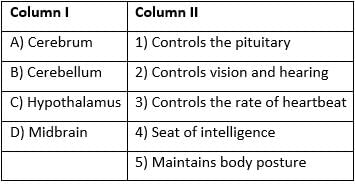
Column 'I' list the parts of human brain and column 'II' lists the functions. [KARNATAKA CET-2005]
Match the two columns and identify the correct choice from those given:
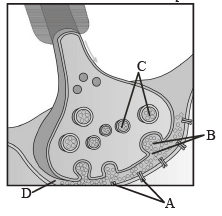
A diagram showing axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D. [NEET 2013]
The most abundant intracellular cation is : [NEET 2013]
When a neuron is in resting state I not conducting any impulse, the axonal membrane is: [2011]
The nerve centres which control the body temperature and the urge for eating are contained in: [2010]
Which part of human brain is concerned with the regulation of body temperature? [2009]
During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of : [2008]
During the transmission of nerve impulse through a nerve fibre, the potential on the inner side of the plasma membrane has which type of electric change? [2007]
In the resting state of the neural membrane, diffusion due to concentration gradients, if allowed, would drive [2004]
In which animal nerve cell is present but brain is absent? [2002]
Which of the following statements is correct for ‘nodes of Ranvier’ of nerve? [2002]



















