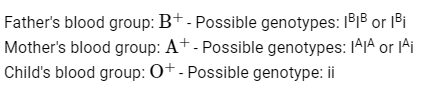31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Years NEET Previous Year Questions: Principles of Inheritance & Variation - 1
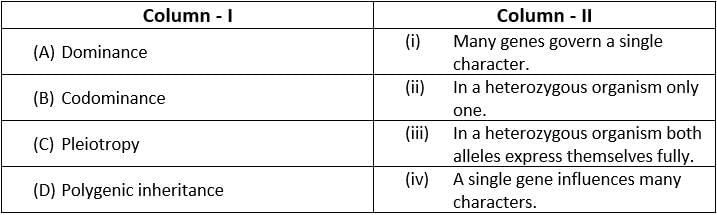
Match List I with List II : (NEET 2024)
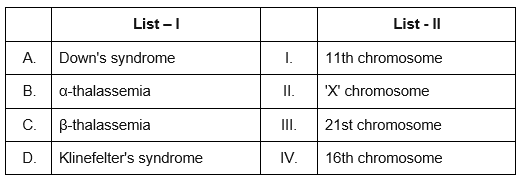
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :

As per ABO blood grouping system, the blood group of father is B+ , mother is A+ and child is O+ . Their respective genotype can be
A. IBi / IAi / ii
B. IBIB/ IAIA/ ii
C. IAIB/ iIA/ IBi
D. IAi/IBi/IAi
E. iIB / iIA / IAIB
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below : (NEET 2024)
A. IBi / IAi / ii
B. IBIB/ IAIA/ ii
C. IAIB/ iIA/ IBi
D. IAi/IBi/IAi
E. iIB / iIA / IAIB
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below : (NEET 2024)
Which one of the following can be explained on the basis of Mendel's Law of Dominance? (NEET 2024)
A. Out of one pair of factors one is dominant and the other is recessive.
B. Alleles do not show any expression and both the characters appear as such in F2 generation.
C. Factors occur in pairs in normal diploid plants.
D. The discrete unit controlling a particular character is called factor.
E. The expression of only one of the parental characters is found in a monohybrid cross.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
B. Alleles do not show any expression and both the characters appear as such in F2 generation.
C. Factors occur in pairs in normal diploid plants.
D. The discrete unit controlling a particular character is called factor.
E. The expression of only one of the parental characters is found in a monohybrid cross.
Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)
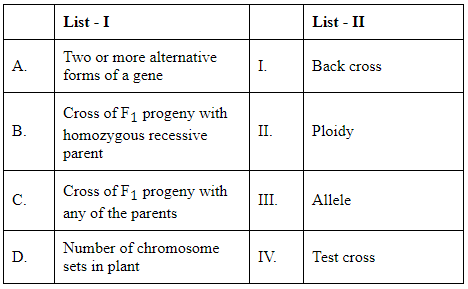
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
In a plant, black seed color (BB/Bb) is dominant over white seed color (bb). In order to find out the genotype of the black seed plant, with which of the following genotype will you cross it? (NEET 2024)
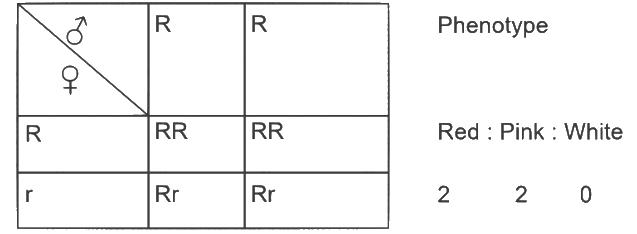
A pink flowered Snapdragon plant was crossed with a red flowered Snapdragon plant. What type of phenotype/s is/are expected in the progeny? (2024)
The phenomenon of pleiotropism refers to (NEET 2023)
Which of the following statements are correct about Klinefelter’s Syndrome? (NEET 2023)
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866).
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine developement is also expressed.
C. The affected individual is short statured.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
E. Such individuals are sterile.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Broad palm with single palm crease is visible in a person suffering from- (NEET 2023)
Frequency of recombination between gene pairs on same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes to map their position on chromosome, was used for the first time by (NEET 2023)
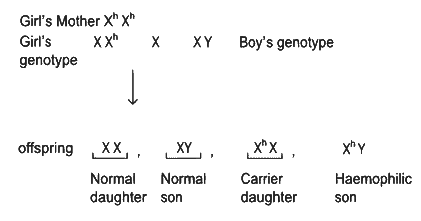
A normal girl, whose mother is haemophilic marries a male with no ancestral history of haemophilia. What will be the possible phenotypes of the offspring? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Haemophilic son and haemophilic daughter.
(b) Haemophilic son and carrier daughter.
(c) Normal daughter and normal son.
(d) Normal son and haemophilic daughter.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
If a female individual is with small round head, furrowed tongue, partially open mouth and broad palm with characteristic palm crease. Also the physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded. The karyotype analysis of such an individual will show : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
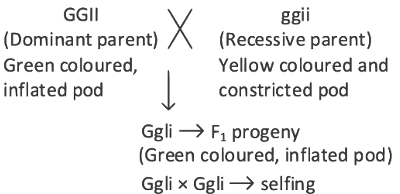
What is the expected percentage of F2 progeny with yellow and inflated pod in dihybrid cross experiment involving pea plants with green coloured, inflated pod and yellow coloured constricted pod? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
The chromosomal theory of inheritance was proposed by (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
In meiosis, crossing over and exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes are catalyzed by the enzyme (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
XO type of sex determination can be found in: (NEET 2022)
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Statement I : Sickle cell anaemia and haemophilia are autosomal dominant traits.
Statement II : Sickle cell anaemia and haemophilia are disorders of the blood.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
If a geneticist uses the blind approach for sequencing the whole genome of an organism, followed by assignment of function to different segments, the methodology adopted by him is called as: (NEET 2022)
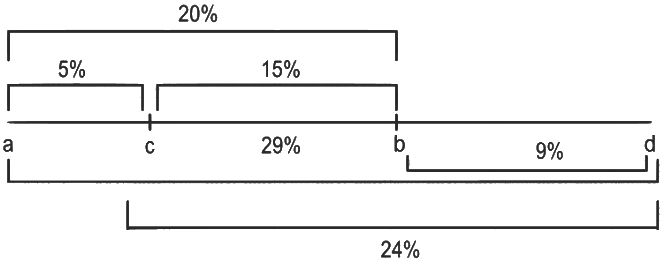
The recombination frequency between the genes a & c 5&, b & c is 15%, b & d is 9%, a & b is 20%, c & d is 24% and a & d is 29%. What will be the sequence of these genes on a linear chromosome? (NEET 2022)
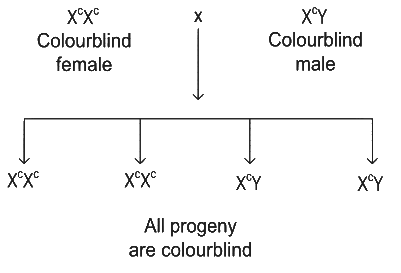
If a colour blind female marries a man whose mother was also colour blind, what are the chances of her progeny having colour blindness? (NEET 2022)
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason(R). (NEET 2022)
Assertion (A): Mendel's law of Independent assortment does not hold good for the genes that are located closely on the same chromosome.
Reason (R): Closely located genes assort independently. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following occurs due to the presence of autosome linked dominant trait? (NEET 2022)
Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022)
Statement I : Mendel studied seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea plants and proposed the Laws of Inheritance
Statement II : Seven characters examined by Mendel in his experiment on pea plants were seed shape and colour, flower colour, pod shape and colour, flower position and stem height
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The production of gametes by the parents, formation of zygotes, the F1 and F2 plants, can be understood from a diagram called: [2021]
Experimental verification of the chromosomal theory of inheritance was done by: [2020]
The frequency of recombination between gene present on the same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes was explained by [2019]
A cell at telophase stage is observed by a student in a plant brought from the field. He tells his teacher that this cell is not like other cells at telophase stage. There is no formation of cell plate and thus the cell is containing more number of chromosomes as compared to other dividing cells. This would result in: [2016]
In a testcross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant-type offspring. This indicates ______. [2016]
Pick out the correct statements : [2016]
(a) Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disease.
(b) Down's syndrome is due to aneuploidy.
(c) Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive gene disorder.
(d) Sickle cell anaemia is a X-linked recessive gene disorder.
Match the terms in Column-I with their description in Column-II and choose the correct option : [2016]