Agriculture Exams Exam > Agriculture Exams Tests > ASRB NET Mock Test Series 2025 > ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Agriculture Exams MCQ
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Agriculture Exams MCQ
Test Description
30 Questions MCQ Test ASRB NET Mock Test Series 2025 - ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 for Agriculture Exams 2025 is part of ASRB NET Mock Test Series 2025 preparation. The ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 questions and answers have been
prepared according to the Agriculture Exams exam syllabus.The ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 MCQs are made for Agriculture Exams 2025 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 below.
Solutions of ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 questions in English are available as part of our ASRB NET Mock Test Series 2025 for Agriculture Exams & ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 solutions in
Hindi for ASRB NET Mock Test Series 2025 course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for Agriculture Exams Exam by signing up for free. Attempt ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 | 150 questions in 120 minutes | Mock test for Agriculture Exams preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study ASRB NET Mock Test Series 2025 for Agriculture Exams Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 1
The maximum number of ergot seeds permitted in the certified seed of bajra will be?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 1
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 2
Which of the following solution is used for testing pollen viability?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 2
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 3
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 4
GA synthesis and signalling dominate the transition of?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 4
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 5
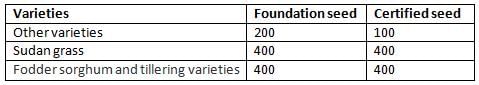
Isolation distance for certified seed in sorghum field for sudan grass is?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 5
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 6
The Indian Seeds Act was passed by Govt. of India to regulate quality of seeds in the year-
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 6
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 7
If the flower is having only male and female organs, the flower is called as?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 7
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 8
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 9
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 10
Temperature dependent pistillate lines are used for hybrid seed production in?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 10
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 11
What is the top screen size for wheat seed processing-
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 11
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 12
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 13
The treatment of seeds with an osmotic solution i.e., polyethylene glycol to initiate germination and then dried to get more uniform and rapid germination of certain vegetable seeds is called as?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 13
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 14
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 15
Germination test results are to be reported in?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 15
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 16
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 17
The genetic contaminant present in hybrid maize field is-
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 17
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 18
The most widespread group of flavonoid pigment is?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 18
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 19
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 20
Suspension of germination by unfavourable environmental conditions is called?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 20
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 21
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 22
At what stage, the urea foliar spray should be undertaken for synchronization of flowering in sorghum hybrid seed production?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 22
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 23
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 24
When the difference in length exists between the seeds and impurities, the following separation is used?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 24
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 25
What is the primary function of the secondary nucleus in the embryo sac?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 25
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 26
Which type of trial is conducted to assess whether a variety that performed well in one zone will show the same performance in another zone?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 26
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 27
What is the maximum percentage of seeds infected by Paddy Bunt (Neovossia horrida) allowed in certified seed?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 27
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 28
The outermost part of the flower, typically green and leaf-like, is known as:
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 28
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 29
Which of the following describes flowers where the stamens remain free?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 29
ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 30
During megasporogenesis, how many megaspores typically degenerate?
Detailed Solution for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 - Question 30
View more questions
Information about ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5 solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for ASRB NET Seed Science Mock Test - 5, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice