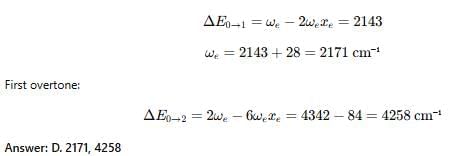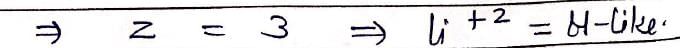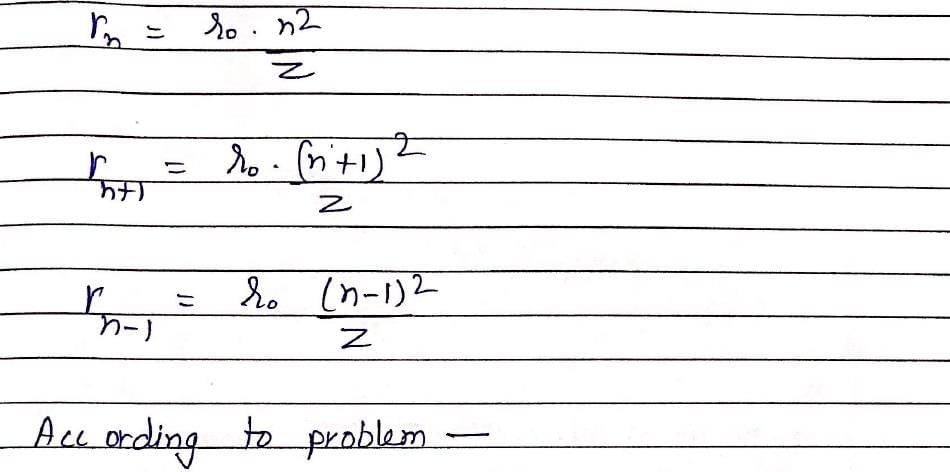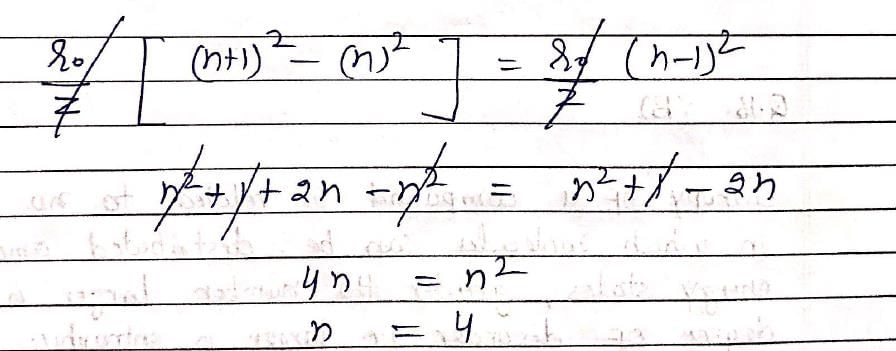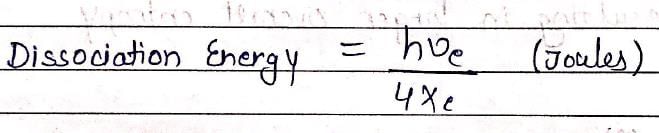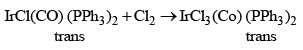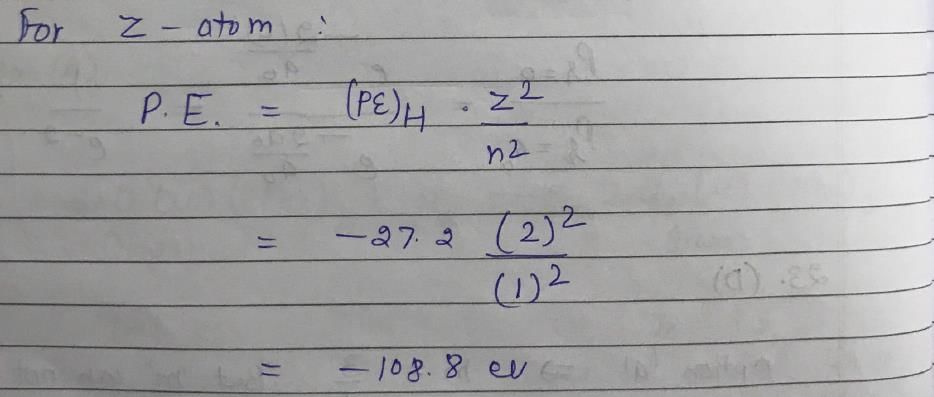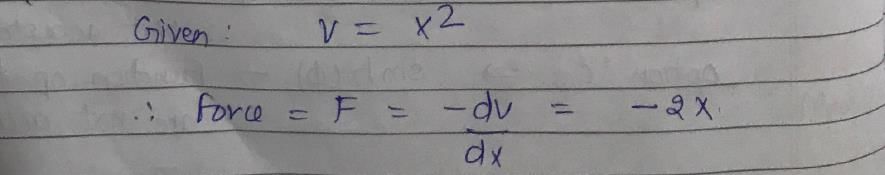Atomic Structure & Quantum - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Atomic Structure & Quantum
The vibrational energy levels, v11 = 0 and v1 = 1 of a diatomic molecule are separated by 2143 cm-1. Its Anharmonicity (ωe Xe ) is 14 cm-1. The values of ωe (in cm-1) and first overtone (cm-1) of this molecules are respectively.
The bond that gives the most intense band in the infrared spectrum for its stretching vibration is:
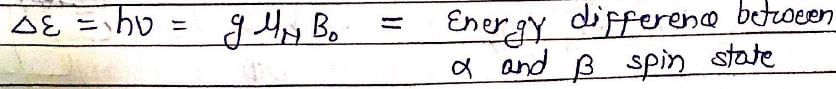
In NMR spectroscopy, the product of the nuclear ‘g’ factor (gN), the Nuclear Magneton βN and the magnetic field strength (B0) gives the:
The molecule with the smallest rotational constant (in the microwave spectrum) among the following is:
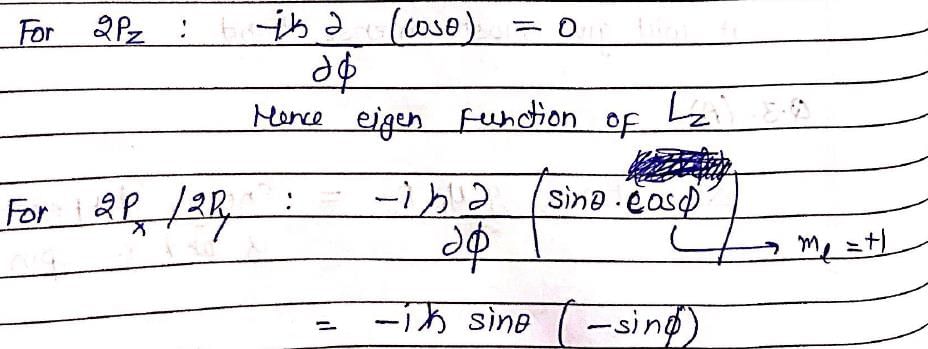
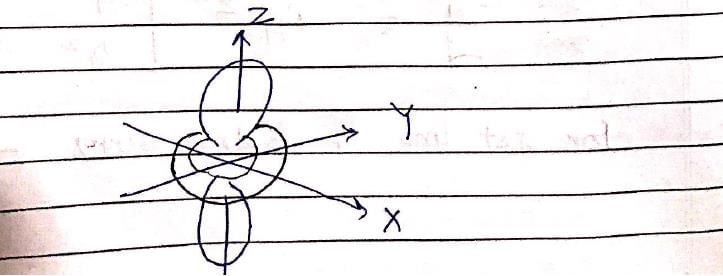
The following is true of 2px, 2py and 2pz orbitals of a H-atom:
The wave function for a quantum mechanical particle in a 1-dimetional box of length ‘a’ is given as 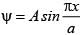 . The value of ‘A’ for a box of length 200 nm is:
. The value of ‘A’ for a box of length 200 nm is:
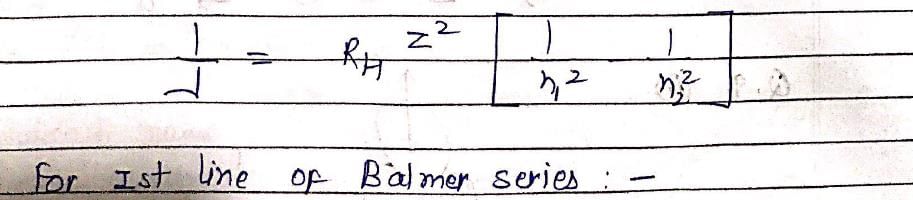
Which hydrogenic atom ion has the wavelength difference between first line of Balmer and Lymen Series equal to 59.3 nm? (RH = 109678 cm–1).
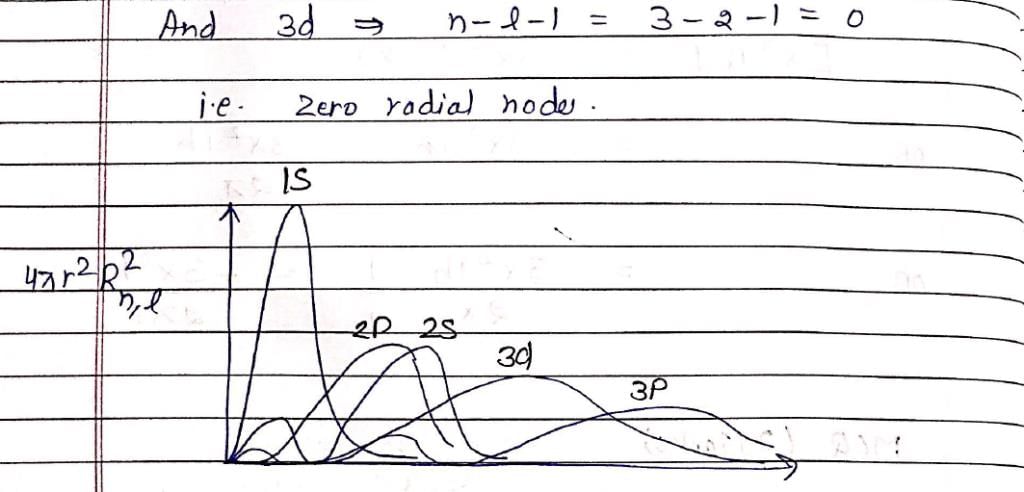
Which of the following is true for the radial part of the H atom wave function Rn, l(r) (n-principal quantum number and l-azimuthal quantum number) and the nodes associated with them:
Which of the following radial distribution graphs correspond to l = 2 for H atom for the least value of ‘n’ for which l = 2 is allowed?
The difference between nth and (n + 1)th Bohr’s radius of H atom is equal to its (n –1)th Bohr’s radius the value of n is:
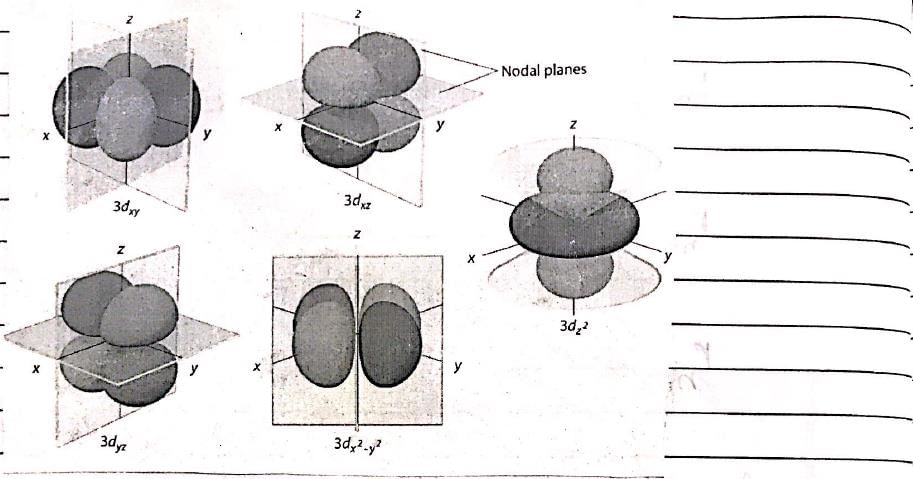
Consider the following statements: (I) Electron density in the XY plane in 3d x2 -y2 orbital is zero (II) Electron density in the XY plane in 3dz2 orbital is zero (III) 2s orbital has one nodal surface (IV) For 2pz orbital, YZ is the nodal plane, Which are the correct statements
At room temperature, which molecule has maximum rotational entropy?
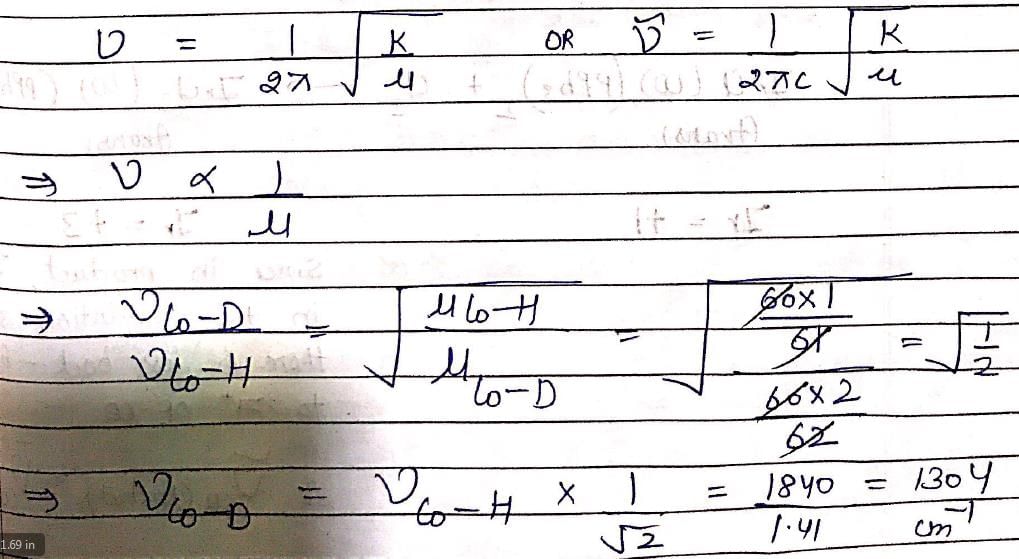
In IR spectrum of [Co(CN)5H]3–, the Co—H stretching is observed at 1840 cm–1. The Co—D stretch in [Co(CN)5D]3– will appear at nearly:
In 400 MHz 1H MNR spectrum of an organic compound exhibited a doublet. The two lines of the doublet are at δ = 2.35 and 2.38 ppm. The coupling constant (J) value is:
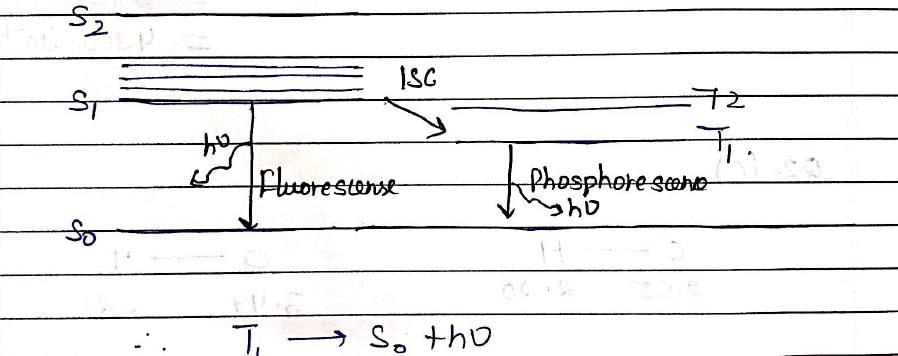
The spectroscopic technique, by which ground state dissociation energies of diatomic molecules can be estimated is:
For an electron in a hydrogen atom, the wave function, ψ is proportional to exp(-r/a0), where a0 is the Bohr’s radius. What is the ratio of the probability of finding the electron at the nucleus to the probability of finding it at a0:
Which one of the following is an acceptable wave function for an electron in the hydrogen atom? (r, θ, φ) denote the spherical polar co-ordinates and N is a suitable constant which you are allowed to choose suitably:
If the principal quantum number n = 6, the correct sequence of filling of electrons will be:
The ionization energy of H atom in its ground state is approximately 13.6 eV. The potential energy of He+, in its ground state is approximately:
Vibrations of a diatomic molecule are usually modelled by a harmonic potential. If the potential is given by X2, the correct statement is:
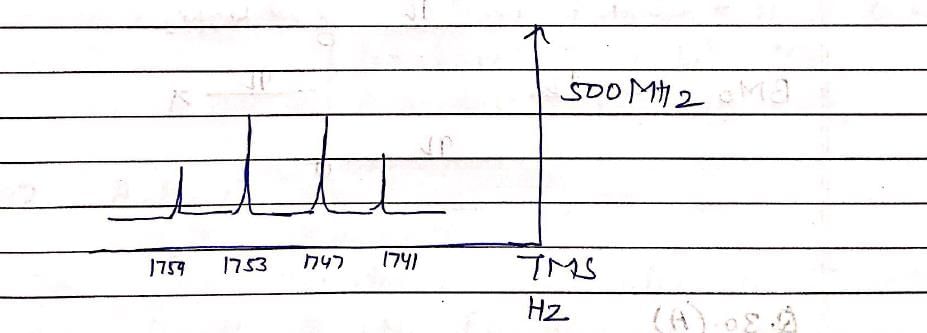
1H NMR spectrum of an organic compound recorded on a 500 MHz spectrometer showed a quartet with line positions at 1759, 1753, 1747, 1741 Hz. Chemical shift (s) and coupling constant (Hz) of the quartet are:
Which of the following spectroscopic techniques will be useful to distinguish between M-SCN and M-NCS binding modes?
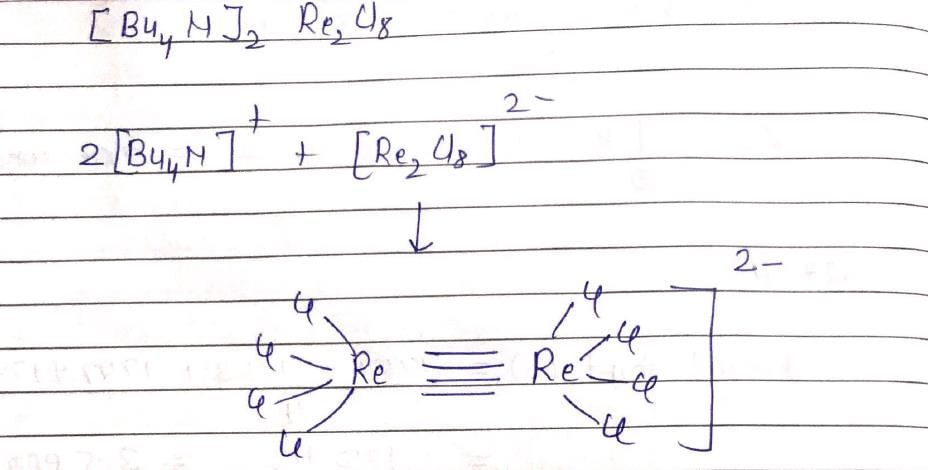
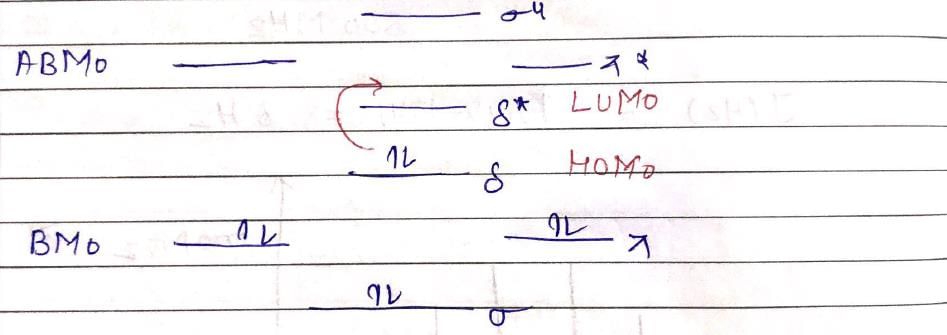
The inters bond at 15000 cm–1 in UV visible spectrum of [Bu4N]2 Re2Cl8 is due to transition:
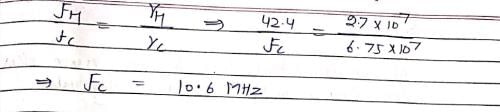
The 1H NMR frequency at 1.07 T is 42.4 MHz. If gyromagnetic ratio of 1H and 13C are 2.7 × 107 and 6.75 × 107 T–1 S–1, respectively, what will be the 13C frequency at 1.07 T:?